
What is the difference between continuous motor skill and discrete skill?
Therefore a second discrete skill must be executed in order to move the stick from the neutral notch of the gear box, towards the notch for 2nd gear. A Continuous Motor skill is a skill which is repeated continuously, therefore they are repetative and the start and end points are hard to distinguish.
What is an example of continuous skills?
Continuous skills have no clear beginning and end – running, cycling and swimming are three examples of continuous skills, as these skills have no clear start or end points within the movement cycle. When analysing continuous skills, coaches are often required to select phases of the movement based on key events.
What is a closed motor skill?
A closed motor skill is a skill that takes place in a controlled environment where the person decides when to start and stop the movement. Closed motor skills are typically easy to execute since they rely on one person's actions.
What are the different types of motor skills?
In this way, motor skills are organized into discrete skills, serial skills, and continuous skills. Another way to classify skills, as stated, is according to the level of environmental predictability. In this way, skills are classified as either open or closed skills.
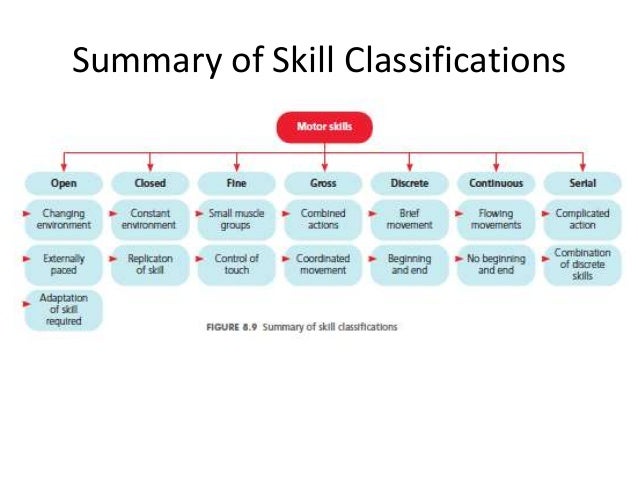
What is an example of a continuous skill?
Continuous skills have no apparent beginning or end. The end of one cycle of movements is the beginning of the next, and the skill is repeated like a cycle. These skills could be stopped at any moment during the performance of the skill. i.e. Swimming, Running, Cycling.
What is a continuous skill in sport?
A continuous skill is one which has no clear beginning or end but is more a cycle of movements repeated over and over again. Examples of this are running, cycling and swimming.
What's an example of a discrete motor skill?
First, discrete movements are the kinds of skills and actions that have an observable start and finish. In other words, you can identify them as skills where you can see when a person begins and ends them. So, for example, shooting a basketball is a discrete movement. You stand, aim, throw the ball, and it's done!
Is dribbling in football a continuous skill?
Dribbling in football - There are several types of dribbling but it usually involves technical complex skills such as using the inside and outside of the foot, while performing a continuous skill - running.
Why is dribbling a continuous skill?
Continuous skills are those that cannot be split up very easily into subroutines, for example, a hockey player dribbling a ball.
What is a continuous skill in gymnastics?
Continuous Skills The skill is repeated continuously unbroken with the beginning and end of the skill being determined by the performer, opposed to the skill itself.
Is juggling a continuous skill?
Finally, juggling is a continuous skill because there is no defined start or end point the performer decides when to start and finish.
Is golf a discrete serial or continuous skill?
Golf putting is an appropriate task for investigating such problems. It is a discrete motor skill in which phases can be classified, that is, from environmental perception to the end of skill execution.
Is tennis discrete or continuous?
discrete skillsA skill containing a single unit of activity with a definite beginning and end. A tennis serve and golf swing are examples of discrete skills.
Is running a continuous skill?
Continuous vs discrete skill continuum Continuous skills have no clear beginning and end – running, cycling and swimming are three examples of continuous skills, as these skills have no clear start or end points within the movement cycle.
Is high jump a closed skill?
Closed skills are not affected by the environment and are predominantly pre-learned i.e. movements follow a set pattern e.g. shot putt, a gymnastics routine. perceptual requirements are high e.g. the Fosbury Flop high jump technique.
Is bowling a closed skill?
If motor skills are classified according to the stability of the environment, bowling would be placed in the category of closed motor skills.
Is dribbling in basketball a continuous skill?
A skill which has a distinct beginning and end, such as hitting a golf ball, is a discrete skill. If several discrete skills are combined in a series it is said to be a serial skill, eg dribbling a basketball. If there is no beginning or end skills are referred to as a continuous skill.
What are the 4 classifications of skills?
Skill continuumsGross & fine skills continuum. The movement precision of the skill. ... Open & closed skills continuum. The effect of the environment on the skill. ... Simple & complex skills continuum. ... Externally-paced & self-paced skills continuum. ... Discrete, serial & continuous skills continuum.
What are 3 sports skills?
Balancing, running, jumping, catching, hopping, throwing, galloping, skipping, leaping, and kicking are the ten fundamental motor skills.
What is an example of a closed skill?
Closed skills are skills that are not affected by the environment. They are usually self-paced and occur in fixed or predictable situations. The performer uses exactly the same technique every time and is in control of what happens next. An example would be a gymnast performing a floor routine.
What are the 5 motor skills?
Motor skills are important in early childhood development. Mastery of many motor skills are important for normal daily functions. The five basic m...
What is an example of a motor skill?
Motor skills are essential for everyday life. They are the movements our bodies make to perform daily functions such as lifting, moving, writing,...
What do you mean by motor skill?
A motor skill is any movement using the body that a child or person can do unassisted. The motor skills start developing at birth and continue to...
What is closed motor skill?
A closed motor skill is a skill that takes place in a controlled environment where the person decides when to start and stop the movement. Closed motor skills are typically easy to execute since they rely on one person's actions. Examples of closed motor skills are:
What are Motor Skills?
Motor skills are the movements our bodies make to perform daily functions such as lifting, moving, writing, and talking. The motor skills an adult possesses begin to develop at birth and continue through childhood and early adulthood. Motor skills are categorized as gross motor skills or fine motor skills. A person needs to have mastered both to acquire solid movement. Gross motor skills involve the arms, legs, and trunk of the body. Fine motor skills involve small muscle groups such as movements in the hand or wrist.
What is the difference between open motor and closed motor?
Motor skills can also be categorized as open motor, closed motor, or serial motor movements. Open motor is when the environment around the skill is uncontrolled. Closed motor is the opposite of open motor and requires a stable and controlled environment. Serial motor is a combination of continuous movement with discrete motor, or deliberate, motor skills.
What are the different types of motor skills?
Motor skills can also be defined as closed motor, open motor, serial motor, and discrete motor. Closed motor skills are skills that can be performed in a stable and predictable environment. Open motor skills are skills that take place in an uncontrolled and unstable environment. Discrete motor skills are movements that are quick and deliberate, and a series of discrete movements together make serial motor skills. These various types of skills are described in more detail below.
Why is fine motor development so difficult?
A common cause of difficulty with fine motor in children is developmental coordination disorder or DCD which is also referred to as dyspraxia. Difficulty with fine motor skills can improve with occupational therapy (OT).
What is the GMFCS?
The Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) is a system developed to assess a child's gross motor development and is broken into five stages. Stage one is the stage with the most ability and stage five is the stage that needs the most assistance.
When do gross motor skills develop?
Gross motor skills develop as soon as birth and continue to develop into late childhood or early adulthood. Underdeveloped gross motor skills can impact all areas of a person's daily life. Low gross motor skills can make everyday life such as work and school difficult and can cause low self-esteem in the individual. Essential motor skills that develop in early childhood are:
What is continuous motor skill?
A Continuous Motor skill is a skill which is repeated continuously, therefore they are repetative and the start and end points are hard to distinguish. An example of this is walking. pinterest-pin-it.
What is a discrete motor skill?
A Discrete Motor Skill is one which has a clear start and end point. An example of this is flicking a light switch, it is either on or off, from the picture on the right, you can see that in order to turn the switch on, you need to position your hand on/underneath the switch and apply pressure in an upwards motion, once the switch has flicked, the movement is over and the goal of the skill is achieved. The start and end points of the movement are easily definable and don't need to be repeated.
What is the first discrete skill in manual car?
An example of which is changing gears in a manual car. In order to change from 1st to 2nd gear, you are required to make the movement from notch 1 to notch neutral, this is the first discrete skill, however the action is not complete as the gear stick is in neutral not the position of 2nd gear, which is what the goal is.
What is fine motor skill?
Basically, it describes your ability to produce small movements with great accuracy. In a way, fine motor skills are built on gross motor skills and rely on the communication between the brain and your body.
How is motor skill development determined?
Motor skill development is determined by genetics, environment, stimuli, and even access to training facilities.
What is sports specific skills?
Sports-specific skills describes your ability to use a certain skill and adapt it according to the situation that the you face. For example, football players have to be both technically sound with the ball but also move according to other players on the field. The best time for reinforcing old skills and developing new sports-specific motor skills is around 7-12 years of age. So, get out there and practice when it is most efficient!
What is the most efficient way to train?
No matter what kind of motor skill tasks your performance needs, the most efficient way to train is to stay within the needs of your own sport - be sports-specific!
What is the associative phase of motor skills?
Associative phase, or the verbal motor phase of motor skill learning, happens after you’ve found the most efficient way of performing a task. It is the process of refining the same skill by making small adjustments to your performance for more consistency. In a way, it reinforces relevant information regarding the skill while getting rid of unwanted ones.
What is directional skill?
Are directional – skills develop from head-to-toe or from the center of your body towards extremities. Relies on quality – the better the movement is, the better the result is.
How are autonomous motor skills learned?
Autonomous motor skills are also learned through-and-through and stored in long-term memory. Meaning that you’ll also be able to maintain a good level of performance even after some time off. However, for the ultimate performance, you need to constantly practice to maintain your skill level.
What is continuous skill?
Continuous skills have no distinct, identifiable bringing or end. The skill is repeated continuously unbroken with the beginning and end of the skill being determined by the performer, opposed to the skill itself. Continuous skills tend to be learnt the fastest due to their repetitive nature.
What is discrete skill?
Discrete skills have a clear, definite and identifiable beginning and end. Discrete skills are simple, well designed movements such as throwing and kicking a ball, a shot put, discus or javelin throw, or a somersault. Continuous Skills. Continuous skills have no distinct, identifiable bringing or end. The skill is repeated continuously unbroken ...
What are some examples of serial skills?
An example of a serial skill is a javelin throw. While simply throwing a javelin can be classified as a discreet skill, a javelin throw where the run up, release and follow though is performed in a sequence can be classified as a serial skill. Other examples of serial skills include bowling in cricket and a place kick in football.
Why are serial skills so difficult to learn?
Serial skills are the most difficult to learn due to the need to coordinate separate skills into an effective pattern. An example of a serial skill is a javelin throw.
What are some examples of discrete motor skills?
Discrete motor skill examples include a golf swing, a free-throw in Basket Ball and throw-in in Soccer. All of these skills have a clear beginning and end.
What are continuous discrete and serial skills?
Continuous, discrete and serial skills are classified depending on the organisation and sequencing of a skill. For example, are their distinct phases and/or clear start and end points to the movement?
How can you use skill classification as a coach or sport scientist?
However, being able to correctly classify skills allows you to consider the true demands that are needed to perform the skill well. As a result, you can plan more effective training strategies.
What are the different types of skills?
It is important to note that skill classification is not binary, nor is it an exact science. Rather skills can be placed on a continuum relative to other skills. In the following sections we’ll explain the following classifications: 1 Open versus closed skills 2 Continuous, series and discrete skills 3 Gross versus fine skills 4 Self-paced versus externally paced 5 Complex versus simple skills
Why is skill classification important?
Skill classification also allows you to compare and contrast different skills. These may be skill from within the same sport or skills from a different sport. Such analysis allows you to consider how skill may transfer from one skill to another.
What are the two types of soccer skills?
As a thought experiment, read the definitions below, then try to order the following soccer skills in terms of open to closed: 1) a throw in , 2) a penalty kick and 3) successfully tackling a player running with the ball.
What is serial skill?
Serial skills are a third type of classification. Serial skills have a sequence of actions that make up the whole skill. Triple jump is an example of a serial skill. After the run up (approach phase) the performer will perform a hop phase, a step phase and a jump phase. The combined sequence of these phases make up the triple jump skill.
