What is decision tree in management?
A decision tree is a type of supervised machine learning used to categorize or make predictions based on how a previous set of questions were answered. The model is a form of supervised learning, meaning that the model is trained and tested on a set of data that contains the desired categorization.
What is meant by decision tree?
A decision tree is a graph that uses a branching method to illustrate every possible output for a specific input. Decision trees can be drawn by hand or created with a graphics program or specialized software. Informally, decision trees are useful for focusing discussion when a group must make a decision.
What is decision tree and example?
What is a Decision Tree? A decision tree is a very specific type of probability tree that enables you to make a decision about some kind of process. For example, you might want to choose between manufacturing item A or item B, or investing in choice 1, choice 2, or choice 3.
What is the purpose of a decision tree?
Decision trees help you to evaluate your options. Decision Trees are excellent tools for helping you to choose between several courses of action. They provide a highly effective structure within which you can lay out options and investigate the possible outcomes of choosing those options.
What is a decision tree diagram?
A decision tree diagram is a type of flowchart that simplifies the decision-making process by breaking down the different paths of action available. Decision trees also showcase the potential outcomes involved with each path of action.
What is another word for decision tree?
What is another word for decision tree?flow chartflow diagramflow sheetschemaschema chartschemestep-by-step diagramstructural outline
What are the advantages and disadvantages of decision trees?
They are very fast and efficient compared to KNN and other classification algorithms. Easy to understand, interpret, visualize. The data type of decision tree can handle any type of data whether it is numerical or categorical, or boolean. Normalization is not required in the Decision Tree.
How do you write a decision tree give one example?
How do you create a decision tree?Start with your overarching objective/ “big decision” at the top (root) ... Draw your arrows. ... Attach leaf nodes at the end of your branches. ... Determine the odds of success of each decision point. ... Evaluate risk vs reward.
What is decision trees and its rules?
Tree Rules Decision trees work by recursively partitioning the data based on input field values. The data partitions are called branches . The initial branch (sometimes called the root ) encompasses all data records. The root is split into subsets, or child branches , based on the value of a particular input field.
What is the advantage of decision tree?
A significant advantage of a decision tree is that it forces the consideration of all possible outcomes of a decision and traces each path to a conclusion. It creates a comprehensive analysis of the consequences along each branch and identifies decision nodes that need further analysis.
What are the components of decision tree?
Decision trees are composed of three main parts—decision nodes (denoting choice), chance nodes (denoting probability), and end nodes (denoting outcomes).
Which of the following are advantages of decision tree?
A decision tree is a flowchart-like structure in which each internal node represents an attribute "test," each branch reflects the test's conclusion, and each leaf node represents a class label (decision taken after computing all attributes). We can add possible scenarios to decision trees.
What is meant by decision tree in Machine Learning?
Introduction Decision Trees are a type of Supervised Machine Learning (that is you explain what the input is and what the corresponding output is in the training data) where the data is continuously split according to a certain parameter. The tree can be explained by two entities, namely decision nodes and leaves.
What is meant by decision tree in data mining?
A decision tree is a class discriminator that recursively partitions the training set until each partition consists entirely or dominantly of examples from one class. Each non-leaf node of the tree contains a split point that is a test on one or more attributes and determines how the data is partitioned.
What is a decision tree Mcq?
Structure in which internal node represents test on an attribute, each branch represents outcome of test and each leaf node represents class label.
Where is decision tree used in AI?
In the world of artificial intelligence, decision trees are used to develop learning machines by teaching them how to determine success and failure. These learning machines then analyze incoming data and store it. Then, they make innumerable decisions based on past learning experiences.
What is decision tree?
1. What is a decision tree? In its simplest form, a decision tree is a type of flowchart that shows a clear pathway to a decision. In terms of data analytics, it is a type of algorithm that includes conditional ‘control’ statements to classify data. A decision tree starts at a single point (or ‘node’) which then branches (or ‘splits’) ...
How does a decision tree work?
A decision tree starts at a single point (or ‘node’) which then branches (or ‘splits’) in two or more directions. Each branch offers different possible outcomes, incorporating a variety of decisions and chance events until a final outcome is achieved. When shown visually, their appearance is tree-like…hence the name!
What is the blue decision node?
It is the node from which all other decision, chance, and end nodes eventually branch.
What is overfitting in decision tree?
Overfitting (where a model interprets meaning from irrelevant data) can become a problem if a decision tree’s design is too complex.
What is branching in biology?
Branching or ‘splitting’ is what we call it when any node divides into two or more sub-nodes. These sub-nodes can be another internal node, or they can lead to an outcome (a leaf/ end node.)
What is the purpose of decision trees in emergency room triage?
Emergency room triage might use decision trees to prioritize patient care (based on factors such as age, gender, symptoms, etc.)
Why are decision trees used?
Broadly, decision trees are used in a wide range of industries, to solve many types of problems. Because of their flexibility, they’re used in sectors from technology and health to financial planning. Examples include: A technology business evaluating expansion opportunities based on analysis of past sales data.
What is a decision tree?
A decision tree is a specific type of flow chart used to visualize the decision-making process by mapping out different courses of action, as well as their potential outcomes.
How does a decision tree help you?
Decision trees can dramatically increase your decision making capabilities. The process of identifying your big decision (“root”), possible courses of action (“branches”) and potential outcomes (“leafs”)—as well as evaluating the risks, rewards and likelihood of success—will leave you with a birds eye view of the decision making process.
What is a Venngage decision tree template?
Venngage offers a Brand Kit feature, which makes it easy to incorporate your logo, colors and typography into your decision tree design.
Why is visualizing decision making important?
Visualizing your decision-making process can also alleviate uncertainties and help you clarify your position, like in this decision tree example below.
Why use decision tree diagram?
That’s where a decision tree comes in—it’s a handy diagram to improve your decision-making abilities and help prevent undesirable outcomes.
Why is it important to do research when creating a decision tree?
When creating your decision tree, it’s important to do research, so you can accurately predict the likelihood for success. This research may involve examining industry data or assessing previous projects.
Why do real estate agents use decision trees?
If you’re a real estate agent, decision trees could make a great addition to your real estate marketing efforts, especially since your clients are likely evaluating some major decisions.
What is decision tree?
A decision tree is a branched flowchart showing multiple pathways for potential decisions and outcomes. The tree starts with what is called a decision node, which signifies that a decision must be made. From the decision node, a branch is created for each of the alternative choices under consideration. The initial decision might lead ...
Why are decision trees useful?
Decision trees are useful tools, particularly for situations where financial data and probability of outcomes are relatively reliable. They are used to compare the costs and likely values of decision pathways that a business might take. They often include decision alternatives that lead to multiple possible outcomes, ...
What is the uncertainty node in a decision pathway?
Along the decision pathway, there is usually some point at which a decision leads to an uncertain outcome. That is, a decision could result in multiple possible outcomes, so an uncertainty node is added to the tree at that point. Branches come from that uncertainty node showing the different possible outcomes.
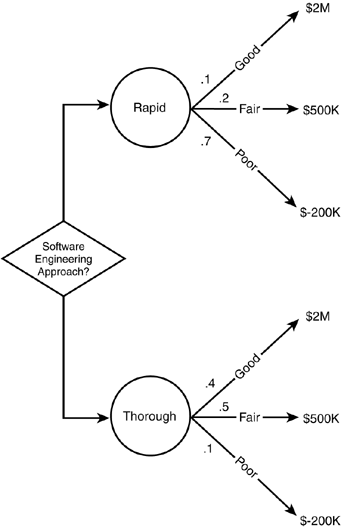
What is the probability of each outcome from the uncertainty nodes?
The other numerical data that needs to be provided is the probability of each outcome from the uncertainty nodes. If an uncertainty node has two branches that are both equally likely, each should be labeled with a 50 percent, or 0.5, probability. Alternatively, an uncertainty node might have three branches with respective probabilities of 60 percent, 30 percent, and 10 percent. In each case, the total of the percentages at each uncertainty node will be 100 percent, representing all possibilities for that node.
What is the goal of the decision tree?
Your parents love the movies, so if they come to town, you'll go to the cinema. Since the goal of the decision tree is to decide your weekend plans, you have an answer.
Why are decision trees important?
Decision trees are helpful, not only because they are graphics that help you 'see' what you are thinking, but also because making a decision tree requires a systematic, documented thought process. Often, the biggest limitation of our decision making is that we can only select from the known alternatives.
What happens if you don't have a decision tree?
If you don't, it's time for the movies. With a decision tree, your weekend plans are made, even though there are a number of factors that could impact your plans. Because you've thought through those situations, you have a plan for every combination of your paycheck, the weather, and the visit by your parents.
Is a decision tree based on the same principles?
But, regardless of the complexity, decision trees are all based on the same principles. Here is a basic example of a decision tree:
What is decision tree analysis?
A decision tree is a type of diagram that clearly defines potential outcomes for a collection of related choices. In project management, a decision tree analysis exercise will allow project leaders to easily compare different courses of action against each other and evaluate the risks, probabilities of success, and potential benefits associated with each.
Why are decision trees useful?
Efficiency: Building off the last point, because decision trees present information in such a straightforward way, they can be quickly analyzed and used to make crucial decisions.
Why is decision tree analysis important?
The decision tree analysis technique allows you to be better prepare for each eventuality and make the most informed choices for each stage of your projects. There are other benefits as well: Clarity: Decision trees are extremely easy to understand and follow. When structured correctly, each choice and resulting potential outcome flow logically ...
Why does Mary need to add potential outcomes for each choice?
Now, Mary needs to add potential outcomes for each choice so that she can accurately predict which materials vendor will best suit her growing company’s needs and budget. On the one hand, the U.S. based vendor will allow her to visit more often in person and check up on operations. But it’s also the more expensive option.
What are the elements of a decision tree?
It’s important to note that a proper decision tree has four main elements: decision nodes, chance nodes, end nodes, and branches. Let’s briefly explore each of these individually.
What is the final step in a project?
The final step is to optimize your actions. Once you know which option provides the greatest chance of success for your project, as well as the one that presents the greatest value, you can confidently make project decisions.
What is a circle in probability?
Chance Nodes: A circle represents a chance node and is used to signify uncertain outcomes. These nodes are used when future results are not guaranteed.

Types of Decisions
- There are two main types of decision trees that are based on the target variable, i.e., categorical variable decision trees and continuous variable decision trees.
Advantages of Decision Trees
- 1. Easy to read and interpret
One of the advantages of decision trees is that their outputs are easy to read and interpret without requiring statistical knowledge. For example, when using decision trees to present demographic information on customers, the marketing department staff can read and interpret the graphical r… - 2. Easy to prepare
Compared to other decision techniques, decision trees take less effort for data preparation. However, users need to have ready information to create new variables with the power to predict the target variable. They can also create classifications of data without having to compute com…
Disadvantages of Decision Trees
- 1. Unstable nature
One of the limitations of decision trees is that they are largely unstable compared to other decision predictors. A small change in the data can result in a major change in the structure of the decision tree, which can convey a different result from what users will get in a normal event. Th… - 2. Less effective in predicting the outcome of a continuous variable
In addition, decision trees are less effective in making predictions when the main goal is to predict the outcome of a continuous variable. This is because decision trees tend to lose information when categorizing variables into multiple categories.
More Resources
- To keep learning and developing your knowledge of business intelligence, we highly recommend the additional CFI resources below: 1. Free Data Science Course 2. Independent Events 3. Flowchart Templates 4. Mutually Exclusive Events 5. Tree Diagram
What Is A Decision Tree?
What Are The Different Parts of A Decision Tree?
- Decision trees can deal with complex data, which is part of what makes them useful. However, this doesn’t mean that they are difficult to understand. At their core, all decision trees ultimately consist of just three key parts, or ‘nodes’: 1. Decision nodes: Representing a decision (typically shown with a square) 2. Chance nodes: Representing probability or uncertainty (typically denote…
An Example of A Simple Decision Tree
- Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s see how a decision tree might look. We’ll keep it really simple. Let’s say that we’re trying to classify what options are available to us if we are hungry. We might show this as follows: In this diagram, our different options are laid out in a clear, visual way. Decision nodes are navy blue, chance nodes are light blue, and end nodes are purple. It is easy f…
Pros and Cons of Decision Trees
- Used effectively, decision trees are very powerful tools. Nevertheless, like any algorithm, they’re not suited to every situation. Here are some key advantages and disadvantages of decision trees.
What Are Decision Trees Used for?
- Despite their drawbacks, decision trees are still a powerful and popular tool. They’re commonly used by data analysts to carry out predictive analysis (e.g. to develop operations strategies in businesses). They’re also a popular tool for machine learning and artificial intelligence, where they’re used as training algorithms for supervised learning (i.e. categorizing data based on differ…
Decision Trees in Summary
- Decision trees are straightforward to understand, yet excellent for complex datasets. This makes them a highly versatile tool. Let’s summarize: 1. Decision trees are composed of three main parts—decision nodes (denoting choice), chance nodes (denoting probability), and end nodes (denoting outcomes). 2. Decision trees can be used to deal with complex datasets, and can be p…