Is deferred tax an asset or liability?
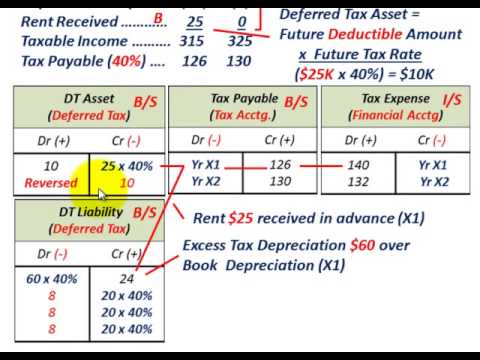
Deferred tax could be deferred tax asset or deferred tax liability, in which it will be deductible or taxable in the future. Deferred tax is the tax effect that occurs due to the temporary differences, either taxable temporary difference or deductible temporary difference.
How is a deferred tax liability or asset created?
When to Create a Deferred Tax Asset or Liability in Books of Accounts?
- If the book profit is more than taxable profit then create a deferred tax liability.
- In case the book profit is less than taxable profit then create a deferred tax asset.
- If there is any loss in the books of accounts, but shows as profit as per income tax create deferred tax asset.
Is deferred gain an asset or liability?
Since you still have a potential capital gains tax liability, your deferred gain goes on your balance sheet as a liability, not a true accounts receivable asset. Section 453 of the Internal Revenue Code specifically authorizes the installment method when selling appreciated assets such as real estate, businesses, etc.
Is deferred income tax current asset?
Updated on December 29, 2021. Deferred taxes are a non-current asset for accounting purposes. A current asset is any asset that will provide an economic benefit for or within one year. Deferred taxes are items on the balance sheet that arise from overpayment or advance payment of taxes, resulting in a refund later.

What do you mean by deferred asset?
A deferred asset is an expenditure that is made in advance and has not yet been consumed.
Is a deferred account an asset?
Since a business does not immediately reap the benefits of its purchase, both prepaid expenses and deferred expenses are recorded as assets on the balance sheet for the company until the expense is realized.
What are some examples of a deferred tax asset?
Examples of deferred tax assets Net operating loss: The business incurred a financial loss for that period. Tax overpayment: You paid too much in taxes in the previous period. Business expenses: When expenses are recognized in one accounting method but not the other.
What is an example of deferred?
An example of deferred is income or interest which will be not be paid until a certain date. (accounting) Of or pertaining to a value that is not realized until a future date, e.g. annuities, charges, taxes, income, either as an asset or liability.
What is the journal entry for deferred expenses?
Accounting for Deferred Expenses Like deferred revenues, deferred expenses are not reported on the income statement. Instead, they are recorded as an asset on the balance sheet until the expenses are incurred. As the expenses are incurred the asset is decreased and the expense is recorded on the income statement.
Is deferred the same as prepaid?
A deferred charge is the equivalent of a long-term prepaid expense, which is an expenditure paid for an underlying asset that will be consumed in future periods, usually a few months. Prepaid expenses are a current account, whereas deferred charges are a non-current account.
What is deferred tax in simple terms?
IAS 12 defines a deferred tax liability as being the amount of income tax payable in future periods in respect of taxable temporary differences. So, in simple terms, deferred tax is tax that is payable in the future.
What is a deferred tax asset and why might one be created?
A deferred tax asset is an item on a company's balance sheet that reduces its taxable income in the future. Such a line item asset can be found when a business overpays its taxes. This money will eventually be returned to the business in the form of tax relief.
What creates a deferred tax asset?
A deferred tax liability or asset is created when there are temporary differences between book tax and actual income tax. There are numerous types of transactions that can create temporary differences between pre-tax book income and taxable income, thus creating deferred tax assets or liabilities.
What is the difference between deferred and accrued?
Deferred revenue, also known as unearned revenue, refers to advance payments a company receives for products or services that are to be delivered or performed in the future. Accrued expenses refer to expenses that are recognized on the books before they have actually been paid.
What expenses can be deferred?
Common examples of deferred expenditures include:Rent on office space.Startup costs.Advertising fees.Advance payment of insurance coverage.An intangible asset cost that is deferred due to amortisation.Tangible asset depreciation costs.
What does deferred in accounting mean?
Deferrals are a type of “adjusting” entry in a company's general ledger that delays the recognition of a transaction in the company's accounting records until a future fiscal period or periods. Deferrals are used to put off revenue — meaning, the amount to be collected, and expenses, or the amount to be paid.
Is deferred revenue a liability?
Deferred revenue is a liability because it reflects revenue that has not been earned and represents products or services that are owed to a customer.
How do you record deferred tax assets?
Suppose a company has overpaid its tax or paid advance tax for a given financial period. In that case, the excess tax paid is known as deferred tax asset....In year 1:EBITDA. read more = $50,000.Depreciation as per books = 30,000/3 = $10,000.Profit Before Tax. ... Tax as per books = 40000*30% = $12,000.
Is deferred tax liability a current liability?
Deferred income tax shows up as a liability on the balance sheet. The difference in depreciation methods used by the IRS and GAAP is the most common cause of deferred income tax. Deferred income tax can be classified as either a current or long-term liability.
What Is a Deferred Tax Asset?
A deferred tax asset is an item on a company's balance sheet that reduces its taxable income in the future.
Why are deferred assets important?
This asset helps in reducing the company’s future tax liability.
What Is a Deferred Tax Asset vs. a Deferred Tax Liability?
A deferred tax asset represents a financial benefit, while a deferred tax liability indicates a future tax obligation or payment due.
When do deferred taxes exist?
For example, deferred taxes exist when expenses are recognized in a company's income statement before they are required to be recognized by the tax authorities or when revenue is subject to taxes before it is taxable in the income statement. 2
When is deferred tax asset recognized?
It is important to note that a deferred tax asset is recognized only when the difference between the loss-value or depreciation of the asset is expected to offset future profit. 1 . A deferred tax asset can conceptually be compared to rent paid in advance or refundable insurance premiums; while the business no longer has cash on hand, ...
When is there an opportunity for the creation of a deferred tax asset?
Essentially, whenever the tax base or tax rules for assets and/or liabilities are different , there is an opportunity for the creation of a deferred tax asset.
Is a loss an asset?
2 In that sense, the loss is an asset. Another scenario where deferred tax assets arise is when there is a difference between accounting rules and tax rules.
What is deferred asset?
Despite being classified as an asset, the concept of deferred asset refers to expenses already paid but not yet used. The main objective of all this is not to alter the financial accounts of the companies in the periods in which those disbursements classified as expenses have not been used. At any time a company can acquire something ...
Why are deferred assets transferred to amortized expenses?
As these assets are used, they are transferred to amortized expense so that the accounting adjusts as closely as possible to reality . The expenses that have not been used by the They must be in the asset chapter, but once the deferred asset begins to help generate income, it will be incorporated as an expense.
When are deferred assets recognized?
Deferred tax assets can also form when expenses are recognized in the income statement before they are recognized in the tax statement and to tax authorities. For example, some legal expenses are not considered as the expense and thus not deducted immediately in tax statement; however, they are shown as the expense in the income statement.
What is Deferred Tax Assets?
A deferred tax asset is an asset to the Company that usually arises when either the Company has overpaid taxes or paid advance tax. Such taxes are recorded as an asset on the balance sheet and are eventually paid back to the Company or deducted from future taxes.
Why are deferred tax assets recorded?
Deferred tax assets in the balance sheet line item on the non-current assets, which are recorded whenever the Company pays more tax. The amount under this asset is then utilized to reduce future tax liability. It can be caused due to many reasons because there are certain items allowed/disallowed in the tax income statement than in the accounting income statement. The difference in the deferred tax calculation of book profits and tax profits may lead to the recording of deferred tax assets.
Why is there a difference in the deferred tax calculation of book profits and tax profits?
It can be caused due to many reasons because there are certain items allowed/disallowed in the tax income statement than in the accounting income statement. The difference in the deferred tax calculation of book profits and tax profits may lead to the recording of deferred tax assets.
Is a future warranty an expense?
The tax authorities do not consider future warranties and returns as an expense. It is because this expense has not been incurred but only accounted for. Therefore, the Company cannot deduct such an expense while calculating taxes; thus, pay tax on $0.5 million as well. Therefore, this amount will be part of the deferred tax assets in the balance sheet.
Is a loss an asset or deferred tax asset?
Hence, such a loss is an asset or deferred tax assets to be precise for the Company.
What is a deferred tax asset?
A deferred tax asset (DTA) is an entry on the balance sheet that represents a difference between the company’s internal accounting and taxes owed. For example, if your company paid its taxes in full and then received a tax deduction for that period, that unused deduction can be used in future tax filings as a deferred tax asset.
When is a deferred tax asset created?
Whenever there is a difference between the income on the tax return and the income in the company’s accounting records (income per book) a deferred tax asset is created.
What is deferred tax liability journal entry?
Certain tax incentives will create a deferred tax liability journal entry, giving the business some temporary tax relief, but will be collected later. Depreciation expenses—like the annual devaluation of a fleet of company vehicles—can generate deferred tax liabilities.
What is the difference between deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities?
A deferred tax asset is a business tax credit for future taxes, and a deferred tax liability means the business has a tax debt that will need to be paid in the future.
What is a temporary difference between the amount of money owed in taxes and the amount of money that is required to?
Any temporary difference between the amount of money owed in taxes and the amount of money that is required to be paid in the current accounting cycle creates a deferred tax liability.
How to illustrate deferred tax liability?
To illustrate the concept of a deferred tax liability, imagine you’re at a bar with an open tab. At the end of the night, you go to the bar to pay off your tab, but the bartender has mistakenly closed out the register and can no longer process your tab. You agree to return to the bar and pay off your tab on your next visit. You make a note to yourself of the outstanding balance, and keep cash on hand to pay it off.
Can you take advantage of deferred tax?
It can be tricky to determine when, and if, you’ll be able to take advantage of a deferred tax asset. The balance isn’t hidden because it’s reported in the financial statements. Analysts can take deferred tax balances into account, so there’s no distortion of the financial picture.
What Does Deferred Tax Asset Mean?
What is the definition of deferred tax asset? A deferred tax asset is an income tax created by a carrying amount of net loss or tax credit, which is eventually returned to the company and reported on the company’s balance sheet as an asset. Companies use tax deferrals to lower the income tax expenses of the coming accounting period, provided that next tax period will generate positive earnings.
Why do companies use tax deferrals?
Companies use tax deferrals to lower the income tax expenses of the coming accounting period, provided that next tax period will generate positive earnings. For example, a company that pays a tax rate of 35% depreciates its equipment that has a value of $25,000 and a life of 5 years.
What is the accounting depreciation in year 8?
In Year 8, the straight-line depreciation is lower than the tax paid, and the company recognizes a deferred tax asset , suggesting that in the coming tax period it expects to claim accounting depreciation in excess of tax depreciation.
Overview: Deferred Tax Asset vs. Liability
Deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities are the opposites of each other. A deferred tax asset is a business tax credit for future taxes, and a deferred tax liability means the business has a tax debt that will need to be paid in the future.
What is a Deferred Tax Asset?
A deferred tax asset (DTA) is an entry on the balance sheet that represents a difference between the company’s internal accounting and taxes owed. For example, if your company paid its taxes in full and then received a tax deduction for that period, that unused deduction can be used in future tax filings as a deferred tax asset.
What is a Deferred Tax Liability?
A deferred tax liability (DTL) is a tax payment that a company has listed on its balance sheet, but does not have to be paid until a future tax filing. A payroll tax holiday is a type of deferred tax liability that allows businesses to put off paying their payroll taxes until a later date.
Evaluating Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities
It can be tricky to determine when, and if, you’ll be able to take advantage of a deferred tax asset. The balance isn’t hidden because it’s reported in the financial statements. Analysts can take deferred tax balances into account, so there’s no distortion of the financial picture.
Additional Considerations
The revenue and expenses you report on your income statement don’t always translate into income and deductions for tax purposes. Tax accounting and financial accounting have slightly different rules, which is why your business’s taxable income isn’t always the same as the net income on your financial statements.
