
The line that separates the accumulation and ablation areas is called the equilibrium line. The elevation of the equilibrium line depends on temperature, precipitation and the surrounding landscape. If the climate conditions remained constant, neither the equilibrium line nor the glacier
Glacier
A glacier is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight; it forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation (melting and sublimation) over many years, often centuries. Glaciers slowly deform and flow due to stresses induced by their weight, cre…
What is equilibrium line in geography?
equilibrium line. [‚ē·kwə′lib·rē·əm ‚līn] (hydrology) The level on a glacier where the net balance equals zero and accumulation equals ablation.
What do the tuples of the equilibrium line mean?
The equilibrium line, the discretization, the safe region and the leaks in the system. The tuples show the numbering of the hypercubes. From the fact that two phases in equilibrium have the same value of G, and if the equilibrium is shifted by changing P and T such that equilibrium is maintained, the changes in G for the two phases are equal:
What is the equilibrium line in the Arctic?
In Arctic: Present-day glaciation …equal is known as the equilibrium line and is roughly equivalent to the snow line.
What is the diamond-graphite equilibrium line?
The diamond-graphite equilibrium line most frequently employed is attributed to the work of Berman and Simon (1955), which was progressively refined as more accurate experimental thermodynamic data on diamond became available ( Berman, 1979 ). A brief overview of the approach used is given below.
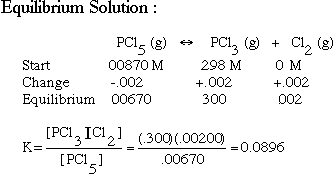
What is the equilibrium line in geology?
Abstract. The equilibrium-line altitude (ELA) marks the area or zone on a glacier where accumulation is balanced by ablation over a 1-year period.
What is the equilibrium line on a glacier quizlet?
More ice melts than accumulates as snow. Equilibrium Line. Marks the boundary between the zones of accumulation and ablation.
How does the equilibrium line move?
Motion and Movement The equilibrium line moves down (1) or up (2) a glacier as the mass balance changes. Ice Flow: Glaciers move by internal deformation (changing due to pressure or stress) and sliding at the base.
Why is equilibrium line important?
Glacier equilibrium lines are very important because they represent the lowest boundary of the climatic glacierization. The climates which prevail at glacier equilibrium lines are considered to be just sufficient to maintain the existence of glaciers.
What is the equilibrium line and why is it important quizlet?
The equilibrium line separates the ablation zone and the accumulation zone; it is the altitude where the amount of new snow gained by accumulation is equal to the amount of ice lost through ablation.
What is a slow moving river of ice called?
Glaciers: Moving Rivers of Ice A glacier is a huge mass of ice that moves slowly over land.
What happens to equilibrium line as glaciers retreat?
How does the equilibrium line move when snowfall increases? c) It moves down the valley. What happens to the glacier? c) The glacier retreats and then advances, reaching a new steady state with an equilibrium line higher up the valley.
What is a small iceberg called?
Smaller icebergs, known as bergy bits and growlers, can be especially dangerous for ships because they are harder to spot. The North Atlantic and the cold waters surrounding Antarctica are home to most of the icebergs on Earth.
What does it mean for a glacier to be in equilibrium?
If the two processes result in no net gain or loss of snow and ice, the mass balance is zero and the glacier is in equilibriumequilibrium: a balanced state with no net gain or loss..
What is always equal in an equilibrium system?
Chemical equilibrium is the state in which the forward reaction rate and the reverse reaction rate are equal.
How do you find the equilibrium altitude of a line?
It can be calculated from the glacier hypsometry using the following equation (Furbish and Andrews (1984)): B R = Z ¯ a c A a c Z ¯ a b A a b Where: =Area-weighted mean altitude of the accumulation area. A a c =Area of accumulation. Z ¯ a b =Area-weighted mean altitude of the ablation area.
Do all glaciers occur on land?
Glaciers form only on land and are distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that forms on the surface of bodies of water.
Who developed the diamond graphite equilibrium line?
The diamond-graphite equilibrium line most frequently employed is attributed to the work of Berman and Simon (1955), which was progressively refined as more accurate experimental thermodynamic data on diamond became available ( Berman, 1979 ). A brief overview of the approach used is given below. To determine the equilibrium conditions, Berman started with the standard definition of Gibbs free energy
What is the phase diagram of hexagonal boron nitride?
The pressure/temperature phase diagram for hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) and cubic boron nitride (cBN) was initially published by Wentorf (1961) and co-workers ( Bundy and Wentorf, 1963 ). The boundary between these phases was experimentally determined by mapping the regions where the alkaline metals and nitrides used as catalytic solvents were successful in promoting the hBN to cBN transformation. The phase diagram reported by these researchers is given in Fig. 15.3. The precise determination of the equilibrium line between these phases has been the subject of some continuing research and debate in the ensuing decades and many modifications to the pressure/temperature phase diagram have been proposed (Vel et al., 1991 ). The controversy has been the result of the experimental nature of the phase diagram determination, in which the thermodynamic equilibrium line is determined from the observed hBN to cBN conversion. As pointed out by Turkevich (2002), it is often required to go far beyond equilibrium conditions in order to overcome kinetic limitations required for diffusion-related phase transformations. Therefore the non-conversion of hBN to cBN does not necessarily provide reliable thermodynamic data, but rather can be an indication of inadequate kinetics. Another important issue pointed out by various researchers is the role of oxygen-related surface impurities in the hBN/cBN equilibrium ( Endo et al., 1979 ). This equilibrium line was shown to be highly dependent on the surface oxygen in the starting materials, which can lead to pressure shifts as high as 1.3 GPa over the temperature range of 1000 to 3000 °C ( Turkevich, 2002 ). Since surface impurities in raw materials are difficult to control and monitor, it is likely that surface oxygen on the starting hBN powders has contributed to the experimental controversies regarding precise determination of the equilibrium line.
Where is the equilibrium line?
The equilibrium line is at the boundary of the accumulation area and the ablation area, however, the elevation varies from year to year.
How high is the equilibrium line in Vatnajökull?
At present, the equilibrium line altitude on southern Vatnajökull is generally in the range of 1000–1200 m above sea level, but it varies from place to place.
What is the line that separates the accumulation and ablation areas called?
Equilibrium line. The line that separates the accumulation and ablation areas is called the equilibrium line . The elevation of the equilibrium line depends on temperature, precipitation and the surrounding landscape.
