What is the function of the syncytium in the heart?
The smooth muscle in the heart works as a functional syncytium. This means that the individual cells work with adjacent cells for coordinated action. Rapid transmission of electrical impulses transfers between cells to trigger simultaneous contraction of the heart muscle. What is a syncytium?
What is an example of a functional syncytium?
A group of cells that functions or works as a single unit while maintaining the individuality of its cells is called functional syncytium. One of the best examples of functional syncytium can be seen in cardiac muscles of the heart. These muscles, also known as heart muscles or myocardium, are found in the walls of the heart.
What is a syncytium made of?
A syncytium is a mass of cells that have merged together. The muscle cells in the cardiac syncytium are derived from the mesoderm. Most syncytia are composed of a single mass of protoplasm with multiple cell nuclei. The mass is the result of surrounding cells fusing together into one larger cell.
What are the phases of syncytium formation?
Syncytium formation can be divided roughly into three phases with blending transitions. During phase I only one single cell, the ISC, is affected. Secretions are released through the stylet which is inserted into the cell but does not perforate the plasmalemma.

Why does the cardiac muscle acts as a functional syncytium?
This joining is called electric coupling, and in cardiac muscle it allows the quick transmission of action potentials and the coordinated contraction of the entire heart. This network of electrically connected cardiac muscle cells creates a functional unit of contraction called a syncytium.
How many functional syncytium are in the heart?
two separate functional syncytiumsThe heart is composed of two separate functional syncytiums, the atrial syncytium and the ventricular syncytium.
Which muscle is a functional syncytium?
Cardiac muscle behaves as a functional syncytium, although it is composed of individual cells. At the lateral regions of the intercalated disks, gap junctions are protected from forces during contraction.
Why is the heart a syncytium?
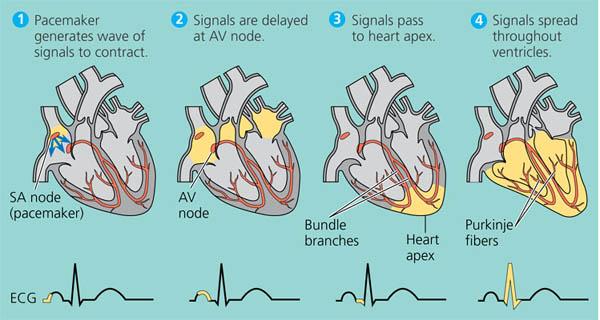
The heart is a functional syncytium that pumps blood most effectively with a synchronous contraction, coordinated by the electrical system of the heart (Fig. 8.1). Organized contraction begins with depolarization of the sinoatrial (SA) node that transmits an electrical signal impulse to the right atrium.
What syncytium means?
Listen to pronunciation. (sin-SIH-shee-um) A large cell-like structure formed by the joining together of two or more cells. The plural is syncytia.
What is a syncytium give an example?
Syncytium may be formed by the fusion of two or more cells, forming a giant cell. An example of syncytium can be found in skeletal muscles, which is essential since it allows rapid coordinated contraction of muscles along the entire length. Word origin: New Latin syn- (together with) + cyto (cell) + -ium.
What is the difference between true syncytium and functional syncytium?
The key difference between true syncytium and functional syncytium is that true syncytium is a multinucleated mass of cytoplasmic cells that results from the fusion of cells while functional syncytium is a unit of contraction that comprise a network of electrically connected cardiac muscle cells.
What is an atrial syncytium ventricular syncytium?
Muscles of the atria and those of the ventricles are arranged to form an atrial and ventricular syncytium. syncytium is an arrangement of muscle fibers in which the fibers fuse to form an interconnected mass of fibers.
What is the syncytium function?
A syncytium is a single cell with multiple nuclei. The function of a syncytium includes the rapid transfer of information between cells to trigger...
Is smooth muscle functional syncytium?
The smooth muscle in the heart works as a functional syncytium. This means that the individual cells work with adjacent cells for coordinated actio...
What is a syncytium? Give an example.
A syncytium is a single cell containing multiple nuclei as seen in the skeletal muscle of humans. This differs from a functional syncytium in which...
What is the function of the syncytium?
Function of syncytium. The syncytium functions as a transporting epithelium (Sibley et al., 2005 ), a barrier to both maternal cells and pathogens, and an endoc rine cell, producing large quantities of steroids, CG, CS, placental growth hormone, leptin, and soluble VEGF receptor and many other secretory substances ( Evain-Brion and Malassine, 2003 ).
How many phases does Syncytium form?
Syncytium formation can be divided roughly into three phases with blending transitions. During phase I only one single cell, the ISC, is affected. Secretions are released through the stylet which is inserted into the cell but does not perforate the plasmalemma. As first visible changes in the ISC callose-like material is deposited along ...
What is the virus that causes syncytia?
Rabbit syncytium virus was isolated in chicken embryos inoculated with extracts of liver and spleen from a wild Eastern Cottontail rabbit (Sylvilagus floridanus) in Virginia ( Morris et al., 1965). The agent causes a cytopathic effect and syncytia in monkey and hamster kidney cell cultures.
What is the purpose of the syncytial barrier?
The syncytial barrier also protects the mother from chimaerism (though incompletely Gammill and Nelson, 2010 ); some nuclear material is shed into the maternal circulation but the vast majority is not mitotically competent. The presence of a continuous syncytium also reduces the incidence of cells of fetal origin crossing to the maternal circulation and vice versa. The phenomenon of a postmitotic, maternally-exposed layer of trophoblast seems to be shared by hemochorial placentas in many species.
How does syncytium change with light?
The syncytium of horizontal cells formed through electrical coupling of homologous cell types (i.e., axonless type A and axon-bearing type B) shows characteristic changes with different states of light adaptation. Dark adaptation reduces coupling (from space constant determinations, tracer coupling), smaller receptive field sizes (surround-to-center ratio), and decreased sensitivity of horizontal cells. The decreased electrical coupling would also increase input resistance of the cell, resulting in larger voltage changes to a given light stimulus. Several modulators of horizontal cell gap junctional coupling have been identified that appear to mediate the effects of adaptation, including dopamine, nitric oxide and retinoic acid.
What are the functions of connexin43?
Connexin43 serves several functions in the bone, most of which is known in the osteoblast lineage. Connexin43-containing gap junctions allow the exchange of small molecules among cells. These signals have different effects on bone cells depending on contexts, like hormonal stimulation, aging, disuse, or loading. In general, the signals shared through connexin43 gap junctions influence osteoblast proliferation and differentiation, spatially coordinate cellular activity, restrain osteoclast differentiation, maintain osteocyte viability, and organize and orient collagen fibers. However, experimental challenges (e.g., loading, unloading) provide insights into connexin functions, and highlights that much remains to be learned about the information being communicated through bone cellular networks.
What is a syncytia?
Syncytia arising from endothelium, parenchyma, or leukocytes is a hallmark of infection in many tissues including intestine, lung, liver, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, brain, and bone marrow.
Is a neonatal cardiac cell proliferative?
A fetal or neonatal cardiac cell is highly proliferative but in the postnatal condition, post-mitotic cell division is arrested and therefore,cardiac cells lose the capacity to divide.
Is cardiac myocyte dividing?
Further, cardiac myocytes are non dividing cells that render them least favorable for the development of primary tumors.
Which system of the nervous system accelerates or decelerates the heartbeat rate?
The nerves of the autonomic nervous system accelerate or decelerate the heartbeat rate depending on which division is activate. Second, the intrinsic conduction system, or nodal system, of the heart consists of specialized noncontractile myocardial tissue and ensures that the heart muscle depolarizes in an orderly and sequential manner and that the heart beats as a coordinated unit.
What is the term for a condition of rapid uncoordinated heart contractions which makes the heart useless as?
A condition of rapid uncoordinated heart contractions which makes the heart useless as a pump , generally produced by prolonged tachycardia.
How are cardiac muscle cells connected?
Cardiac muscle cells are electrically connected by gap junctions and thus the entire myocardium behaves as as single unit.
Why is the SA node the pacemaker?
The SA node is the pacemaker because it sets the rate of depolarization for the whole heart.
Which arteries supply the myocardium?
The right and left coronary arteries, which supply the myocardium
