What are some examples of a genotype?
The genotype that carries the genetic information determines a number of physical characteristics because the entire genetic information about an individual is contained with the genotype. Examples of Genotype: 1. Height For an individual's gene makeup there is tall variety (T) and there is short variety (s). T and s are called the alleles.
What are the characteristics of a genotype?
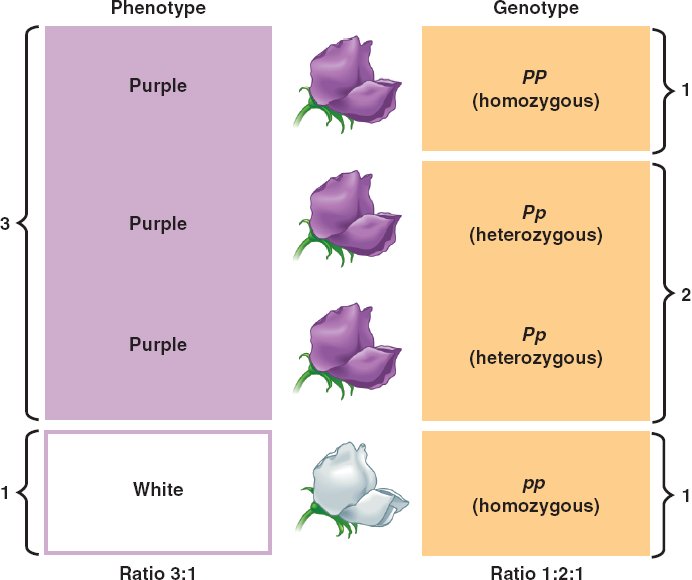
Apr 24, 2020 · Examples of genotype are the genes responsible for: eye color. hair color. One may also ask, what are the 3 types of genotypes? There are three available genotypes, PP (homozygous dominant), Pp (heterozygous), and pp (homozygous recessive). All three have different genotypes but the first two have the same phenotype (purple) as distinct from the …
What is a genotype simple definition?
Sep 07, 2021 · Genotypes determine which characteristics an individual will express, for example: whether they have freckles or not, if they are lactose intolerant, if they have hair on their knuckles or if ...
What are examples of genotypes and phenotypes?
Apr 30, 2022 · A genotype is a scoring of the type of variant present at a given location (i.e., a locus) in the genome. It can be represented by symbols. For example, BB, Bb, bb could be used to represent a given variant in a gene. Genotypes can also be represented by the actual DNA sequence at a specific location, such as CC, CT, TT.

What are 3 examples of genotype?
- Hair color.
- Height.
- Shoe size.
What are 5 examples of genotype?
- Height. For an individual's gene makeup there is tall variety (T) and there is short variety (s). T and s are called the alleles. ...
- Freckles or no freckles. Again the information that is passed from parent to child is carried in the cell of the genotype. ...
- Lactose intolerance.
What is a genotype with examples?
What is phenotype and genotype with examples?
What is AA and AS genotype?
How do I find my genotype?
What is a probable genotype?
What is as genotype?
Is BB a genotype or phenotype?
What is genotype in biology class 10?
How do you write a genotype?
What is genotype in botany?
How can a genotype be determined?
Genotypes can only be determined by biological tests, not observations. Genotype is an inherited trait and hereditary information passed by the parents. The entire genetic information about an organism is contained in a genotype. This genetic information passed from parent to child is responsible for genetic traits such as eye color, height, hair color, the sound of the voice, certain diseases and various behaviors.
What is the meaning of the word "genetype"?
Genotype is what makes the trait ; the information within a gene, and is determined by the makeup of alleles, a word that refers to the form of a gene that produces different effects. When two alleles contain information the genetic makeup of an organism results in some physical characteristics distinguishing that organism from others.
What is the DNA sequence of the genetic makeup of a cell, organism, or individual?
Genotype Examples. The genotype is the DNA sequence of the genetic makeup of a cell, organism or individual, which determines a specific characteristic of that cell, organism, or individual.
Why do not all organisms have the same genotype?
Not all organisms with the same genotype look or act the same way because appearance and behavior are modified by environmental and developmental conditions. Likewise, not all organisms that look alike necessarily have the same genotype.
What are some examples of gene types?
Examples of Genotype: 1. Height. For an individual's gene makeup there is tall variety (T) and there is short variety (s). T and s are called the alleles. The combination of these determines the height.
What is the genetic information passed from parent to child?
This genetic information passed from parent to child is responsible for genetic traits such as eye color, height, hair color, the sound of the voice, certain diseases and various behaviors. Internally coded information that is carried by all organisms is the genotype.
What are some examples of genotypes?
Examples of genotype are the genes responsible for: eye color. hair color.
What does genotype mean?
The term just means "the genes a particular organism has." Any example of a genotype would just be a chart of a particular living thing's chromosomes, or DNA molecules responsible for various genetic traits. However, having certain genes does have observable results.
What is a person's genotype?
As the name suggests, a person's genotype refers to the types of genes he or she has for a particular inheritable trait. Genotypes determine which characteristics an individual will express, for example: whether they have freckles or not, if they are lactose intolerant, if they have hair on their knuckles or if their eyes will be blue, brown or another color.
What is it called when a person has two dominant alleles for a gene?
When a person has two dominant alleles for a gene (e.g. LL), they are referred to as being homozygous dominant for that trait. If they have two recessive alleles (ll), they are homozygous recessive. If they inherited one of each allele (Ll), they are heterozygous for that trait. How Genotypes Are Passed Down.
Why is the lactase enzyme represented by a capital letter?
Notice that the allele for lactase enzyme is represented by a capital letter because it is dominant over faulty lactase production. The 'weaker' allele is referred to as recessive and uses a 'lowercase letter. So, whenever the person has both versions of the gene, in this case Ll, the ability to produce lactase, being the dominant allele, will be the one expressed. For someone to be lactose intolerant, they have to have inherited two recessive 'l' alleles, one from each parent.
How do genes come about?
How do Genotypes Come About? Genes are found on chromosomes, those tightly-packed DNA structures in the cell nucleus. In sexually-reproducing organisms, chromosomes come in pairs, one from the mother and one from the father. For example, each person will have two 'Chromosome 1s' and two 'Chromosome 2s'.
Why are chromosomes called homologous?
Chromosomes in a pair (except sex chromosomes) are called homologous chromosomes because they contain the same genes. For example, both chromosome 8s contain, among many others, the gene that determines whether or not a hairline forms a widow's peak.'. There are always two copies of each gene, one from each parent.
Where is the gene that determines if a person is lactose intolerant?
To better understand how alleles and genotypes work, let's take a look at the gene that determines whether a person is lactose intolerant, which is found on chromosome 2. This gene contains the recipe for the body to make lactase, the enzyme that breaks down lactose sugar in milk.
How many copies of a gene are there?
There are always two copies of each gene, one from each parent. A gene, however, can have different versions, called alleles. Alleles are various versions of a gene. The combination of alleles inherited from the parents is what gives rise to genotypes.
What is a genotype?
Genotype. Genotype. =. A genotype is an individual's collection of genes. The term also can refer to the two alleles inherited for a particular gene. The genotype is expressed when the information encoded in the genes' DNA is used to make protein and RNA molecules.
What is genotype in genetics?
These days, with the ability to test for many different sequence differences between individuals, genotype has taken on a connotation which frequently refers to a difference in sequence in a specific place in a specific gene.
What is the version of a DNA sequence that an individual has?
Genotype, very simply, is the version of a DNA sequence that an individual has. There's a large amount of DNA that we all have in common--of course, that's why we're all humans--but there's also a large amount of variation in sequence among individuals.
What is genotype in biology?
The genotype of an organism defines the hereditary restrictions and potentials from the foetal stage during pregnancy through adulthood. In a simple manner, a genotype definition is given by, the sum of total genes transferred from parents to offspring. Therefore, the genotype of a specific person is their own personal genetic makeup. This genotype is expressed when the information from genes' DNA has utilized to make RNA molecules and proteins.
How to determine a genotype?
Ans. We can determine the Genotype by sending a sample DNA test. Until we have done that, all we can do is only a wild guess. Our genotype is not the ethnicity results. It is exactly how our deoxyribonucleic acids are lined up in each chromosome. Also, there are some phenotypes that cannot be any other genotype. Someone who is albino knows they don't have a gene that codes for active melanin.
What is the blood type allele?
Blood type alleles are an interesting mix, and to better understand them, let's look at background information prior to this. The allele for type A blood is a dominant one. In other words, when someone inherited this allele from a parent, he or she will exhibit the antigen of type A. It is true of the same type B allele: if someone inherited the allele of type B from a parent, he or she would have the type B antigen. The allele of type O is recessive, which means, it will be masked or hidden by the alleles of either A or B.
How is blood type determined?
The type of blood is determined by our genes. These genes are the segments of DNA that code for specific traits. Different versions of genes are referred to as alleles. When determining something like blood type, individuals receive one allele from their biological mother and another from their biological father. The genotype is simply the combination of these alleles that creates the gene for blood type. This allele combination is called a genotype. Now let us relate this genotype (allele combination) to the blood types.
How many alleles can a biological parent donate to their child?
Ans. Every biological parent donates one ABO alleles to their child from their available two alleles. A mother who is with a Type - O blood can only pass an O allele to her daughter or son. A father who is with Type - AB blood could pass either an A or a B allele to his daughter or son. This couple (mother and father) could have children of either blood type A (Type-O from mother and Type-A from father) or blood type B (Type-O from mother and Type-B from father).
Which chromosome is most likely to be aneuploidy?
The most common chromosomal aneuploidy is the trisomy of chromosome 21, which manifests itself as Down syndrome. Typically, the current technological limitations allow only a fraction of an individual's genotype to be efficiently determined.
How many different blood types are there in the human body?
Since there exist four different paternal blood types and four different maternal possible blood types, there are 16 different combinations that are to be considered when predicting the children's blood type. If we know the blood type of our father and mother, possible blood types for their children can be identified.
Types of Genotypes
There are different types of genotypes depending on which versions of a gene are inherited. There are two main types of genotypes, heterozygous and homozygous. If an organism has a heterozygous genotype, this means they inherit two different versions of a gene.
Genes
A gene is a section of DNA that codes for a protein. Genes are made of DNA, the genetic material of the cell. For example, the gene for keratin makes keratin protein for skin and nails. The gene for melanin makes melanin protein that creates skin pigmentation. There are different types of genes, such as structural and regulatory genes.
Chromosomes
Genes are arranged in linear sections of DNA called chromosomes. Humans have two pairs of 23 chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. Each chromosome contains hundreds of genes. Humans get one set of chromosomes from the maternal parent and one set of chromosomes from the paternal parent.
Alleles
The different versions of genes on each homologous chromosome are called alleles. Genes code for a trait and alleles are the different versions of that trait. For example, eye color is a trait coded for by three genes. Each of those genes has two or more different versions called alleles.
