
The logic model is a tool often relegated to program evaluation that clinicians and researchers can use in designing and interpreting the results of interventions. In this commentary, we define logic models and discuss their potential value in bridging the theory-research-practice divide frequently encountered in medicine.
What are logic models, and when should you use them?
Logic models are a good tool to help focus an evaluation to determine what to measure and what areas of your program might be most in need of evaluation. You can develop a logic model which depicts how an entire program operates (i.e. global) or focuses more closely on a component or specific activity (i.e. nested). Example of Logic Model
What are the types of logic models?
Various types of logic models
- The Inputs → Activities → Outputs → Outcomes template. Many refinements and variations have been added to the basic template. ...
- Intervention mapping logic models. Logic Model of the Problem for Management information Decision Support Epilepsy Tool (MINDSET program) from Ruiter, DeSmet and Schneider (2007).
- Progressive Outcomes Scale (POS) logic models. ...
What are the components of a logic model?
one another. Logic models include process and outcome components. Process Components of Model (planning elements) Examples Inputs (resources) Funding, staff, materials Activities (program events or strategies) Patient testing and treatment, staff trainings Outputs (products of activities) Number of patients treated, quality of trainings Outcome Components of Model (intended effects) Examples
What are outputs in a logic model?
The outcomes are divided into three levels, represented in levels 4 - 6 of the logic model:
- Level 4 indicates changes at the level of knowledge, skills and attitudes.
- Results at level 5 of the logic model build on the outcomes of level 4 and describe changes in behavior and action.
- Results at level 6 once again build on the outcomes at level 5.
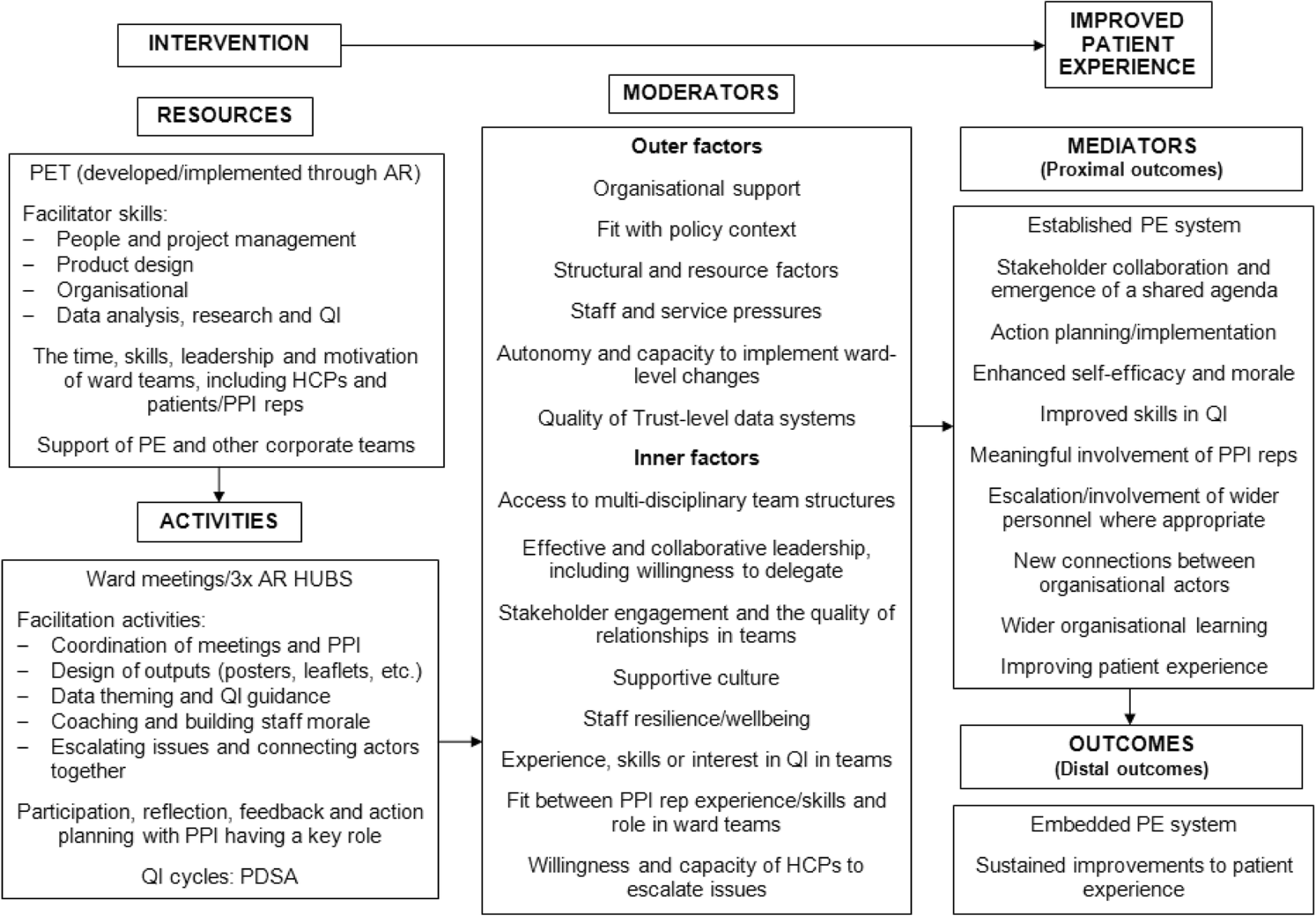
What is meant by logic model?
A logic model is a graphic depiction (road map) that presents the shared relationships among the resources, activities, outputs, outcomes, and impact for your program.
What are examples of logic models?
A logic model has the following components: Inputs: Resources dedicated to or used by your program. Examples include: funding, staff and staff time, volunteer and volunteer time, facilities, supplies, and equipment.
How do you create a logic model for research?
Steps for drafting a logic modelFind the logic in existing written materials to produce your first draft. ... Determine the appropriate scope of the model for its intended users and uses. ... Check whether the model makes sense and is complete. ... Drama (activities, interventions).
What are the five elements of a logic model?
While a basic logic model should include the five basic components of participants, inputs, activities, outputs, and outcomes, similarities end there. You may choose from many different formats, some complex and some simple.
What are the 4 components of the logic model?
Included in most logic models are four components: resources, activities, outputs, and outcomes. Resources are the raw materials needed to create the program, implement its activities, and attain the desired outputs and outcomes.
Why is logical model important?
Benefits of developing and using logic models are: The model helps communicate the program to people outside the program in a concise and compelling way. The model helps program staff gain a common understanding of how the program works and their responsibilities to make it work.
What are the steps of a logic model?
StepsStep 1: Identify the Problem. ... Step 2: Determine the Key Program Inputs. ... Step 3: Determine Key Program Outputs. ... Step 4: Identify Program Outcomes. ... Step 5: Create a Logic Model Outline. ... Step 6: Identify External Influencing Factors. ... Step 7: Identify Program Indicators.
What are two types of logical method of research?
Informal LogicDeductive reasoning: Uses information from various sources and applies that information to the argument at hand to support a larger, generalized conclusion.Inductive reasoning: Uses the specific information given to form a generalized conclusion.
What are the assumptions in a logic model?
Assumptions. Making assumptions explicit is a really important part of the logic model. Assumptions are the beliefs we have about our program, the people involved, and how it will work. Unexamined assumptions are a big risk to program success.
What is the aim of logic model?
What is a logic model? Logic models can assist you in program evaluation by providing a picture of how your program is intended to work. It identifies your programs main components and how they should relate to one another. Logic models include process and outcome components.
What is a logic model plan?
Basically, a Logic Model is a systematic and visual way to present and share your understanding of the relationships among the resources you have to operate your program, the activities you plan to do, and the changes or results you hope to achieve.
What are the three parts of logic?
There are three divisions of the Logic: Being, Essence and the Notion (or Concept).
What is an example of a logic statement?
Anything that lets us infer a new fact about something mathematical from given information is a logical statement. For example, “The diagonals of a rectangle have the same length” is a logical statement. The hypothesis is the part that can help us if we know it's true.
What are the three types of logic?
Three Types and Traditions of Logic: Syllogistic, Calculus and Predicate Logic.
What are the two main types of logic?
Formal and informal logicLogic encompasses both formal and informal logic. ... The most literal approach sees the terms "formal" and "informal" as applying to the language used to express arguments. ... Another approach draws the distinction according to the different types of inferences analyzed.More items...
What are the 3 divisions of logic?
There are three divisions of the Logic: Being, Essence and the Notion (or Concept).
What is a logic model?
A logic model is a graphic representation of a program that shows the relationship between resources (inputs) and results (outcomes). The authors selected each item based on established criteria for high-quality logic models. The LibGuide includes materials in four categories: Logic Models for Program Planning and Implementation, Logic Models for Program Evaluation, Developing Logic Models, and Instructional Materials.
What is a libguide?
The LibGuide includes materials in four categories: Logic Models for Program Planning and Implementation, Logic Models for Program Evaluation, Developing Logic Models, and Instructional Materials.
What is logic model?
Logic Model. A logic model illustrates the association between your program’s resources, activities, and intended outcomes. Logic models can: Focus on a specific aspect of your TB program, such as a single evaluation question or objective, or encompass the entire program.
Why are logic models useful?
Logic models are useful tools for program planning and evaluation because they: Guide staff in thinking about and evaluating their program. Identify assumptions and potential challenges. Assist in identifying intended programmatic outcomes. Organize, connect, and identify gaps in evaluation efforts.
What are the components of a logic model?
Logic Model Component Definitions 1 Inputs are the resources (dollars, staffing, and materials) that go into a program or intervention — what we invest. 2 Activities are events undertaken by the program or partners to produce desired outcomes — what we do. 3 Outputs are the direct, tangible results of activities — what we get. 4 Outcomes are the desired results of the program — what we achieve .#N#Short-term outcomes are the immediate effects of the program or intervention activities.#N#Intermediate outcomes are the intended effects that occur over the midterm of the project period.#N#Long-term outcomes refer to the desired program results.
What is logic model?
A logic model is a graphic which represents the theory of how an intervention produces its outcomes. It represents, in a simplified way, a hypothesis or ‘theory of change’ about how an intervention works. Process evaluations test and refine the hypothesis or ‘theory of change’ of the intervention represented in the logic model.
Why are logic models useful?
Logic models are useful for evaluation because they can help prioritise and structure data collection and analysis to explore the main aspects of an intervention and relationships between them. These data can be used to help to explain how the intervention works to achieve its outcomes, or sometimes why it does not work.
Why is the time order of cause and effect important in logic?
They are not just conceptual maps which represent intervention aspects and the relationships between them; they represent a process of change. Therefore, the time order of ‘cause and effect’ represented in the logic model is important. Cause always comes before effect. The aspects should be arranged so that the arrows between them show how one aspect (such as delivery of training material) causes a subsequent aspect (such as improved skills).
Why are implementation, outcome, and context separated in a logic model?
They ensure, as far as possible, that ‘implementation’, ‘mechanisms of impact’, ‘outcomes’ and ‘context’ are separated in a logic model because these are conceptually distinct. An evaluator will probably have different research questions about these different aspects of the intervention and may want to use different methods to answer these questions
What is the logic model of evaluators?
Based on this logic model, an evaluator might collect programme records and observational data on the quantity, quality and content of the drama sessions delivered to children, and interview families about their changing attitudes towards food (including questions about the causal relationship between the drama sessions and their attitudes towards food). By collecting data on these aspects of the logic model, the evaluator is able to explore main aspects of the ‘theory of change’ of the intervention.
Why are logic models criticised?
Logic models have also been criticised for representing interventions as linear and mechanistic, and for overplaying the predictability of an intervention. For example, they tend to give the impression of steady change over time, whereas change may occur in jumps at certain points or problems may initially get worse before they get better.
When should logic models be developed?
Ideally, logic models should be developed during intervention development, or in the early stages of planning an evaluation, so that they can be used to inform the design of the process evaluation and data collection. However, researchers can develop a logic model to describe an intervention at any stage of an evaluation, including retrospectively - for example, the EPODE (Ensemble Prévenons l’Obésité Des Enfants or Together let’s prevent childhood obesity) logic model.
What is logic model?
logic model captures the logical flow and linkages that exist in any program. Even in cases where the theory of a program has never been made explicit, the. logic model approach can help to uncover, articulate, present and examine a. program’s theory.
How does program theory help in program development?
The role of program theory in developing, operating and evaluating programs is gaining increased emphasis in recent years. A clear grasp of a program's theory can contribute to the successful performance of many important developmental and evaluative tasks along its life span. Although there is growing recognition of the importance of program theory in the development and evaluation of programs, it should be noted that this is not a simple task. Programs are often complex, comprising many different types of interlinking components. What is needed is a relatively simple instrument that can help the practitioner explicate and present program theory, by guiding and structuring the process. The logic model is such a tool, whose purpose is to describe and articulate program theory. Drawing upon examples from the authors' work with both nonprofit and governmental organizations, this paper presents potential uses of the logic model tool in explicating program theory for a variety of purposes throughout the life span of programs: for assessing the feasibility of proposed programs and their readiness for evaluation, for program development, for developing performance monitoring systems, and for building knowledge.
What is systematic planned practice?
Systematic planned practice is a framework that guides worker decision making at critical junctures of the treatment process, facilitates evaluation, and creates conditions for using professional knowledge in making practice decisions. The approach also provides a framework for case supervision and for enhancing professional accountability.
How does a library affect quality of life?
A big data study examining 10 years of North Carolina public library data found that per capita print book circulation had predictive, positive, and statistically significant relationships with five quality of life factors including a community’s level of educational attainment, per capita and median household income, and number of jobs. Altogether, five public library factors were found to have positive impact on six community quality of life variables. These results support the role libraries serve as community anchors in positively impacting quality of life. The use of predictive analytics and the study’s findings can be used in advocating for the value of public libraries.
Is program theory a simple task?
Although there is growing recognition of the importance of program theory in the development and evaluation of programs, it should be noted that this is not a simple task. Programs are often complex, comprising many different types of interlinking components.
What is a logic model?
Logic models are linear, progressing step by step—typically from inputs to activities to outcomes— and an effect never precedes a cause.
Why do we need logic models?
Logic models and theories of change help programs organize and illustrate their activities and goals. Funders often require these illustrations to help them understand exactly what a proposed initiative intends to do and what change is expected to come of it. For program evaluators, understanding a program’s intended progression from intervention (activities) to outcomes (goals) drives evaluation-question and evaluation-plan development.
Is a logic model descriptive?
Though logic models ideally include a section for contextual factors and assumptions, these are not detailed within each part of the model and are often left out altogether. A theory of change includes these factors, where appropriate, throughout the model. As such, a logic model is descriptive while a theory of change is explanatory.

Introduction to Logic Models
- A logic model is a graphic which represents the theory of how an intervention produces its outcomes. It represents, in a simplified way, a hypothesis or ‘theory of change’ about how an intervention works. Process evaluations test and refine the hypothesis or ‘theory of change’ of the intervention represented in the logic model. The design of, and t...
Creating A Useful Logic Model
- Ideally, process evaluations are ‘theory based’ evaluations, where the evaluation is supported by the underpinning theory of how the intervention works (see Process Evaluation section). The logic model should draw on and summarise this theory. In some cases, an intervention manual may also be useful to specify critical aspects related to the implementation/delivery of the interventio…
Features of Good Logic Models
- They do not include detail about absolutely everything that happens in an intervention, but summarise the aspects that are critically important in explaining how the intervention produces the changes that it is aiming to achieve. Therefore, it is important when creating a logic model to decide what these critical aspects are. They ensure, as far as possible, that ‘implementation’, ‘me…
Limitations of Logic Models
- Logic models tread a fine line between being simple, easy to understand and use, and reflecting the complexity of the real world. A good logic model will include the critical aspects of an intervention that contribute to its outcomes. In practice, these may be hard to identify in advance, and therefore the logic model may not include every factor that explains outcomes. On the othe…
Categorising Aspects of Logic Models
- In practice, it can sometimes be tricky to define and agree on which category (such as ‘implementation’ or ‘context’) an aspect of a logic model falls into. There are no standard definitions for what counts as ‘implementation’, a ‘mechanism of impact’, ‘context’ or ‘outcome’ as these will vary depending on the study. For example, a school may be part of the context for a ch…
Developing A Logic Model For Exploratory Interventions
- If you have designed an intervention, you will have some hypothesis about how it is expected to produce change to resolve the problem you are trying to address. This hypothesis can form the basis of a logic model. However, there may be some aspects of how the intervention might work or processes that may occur which due to large gaps in knowledge are genuinely unknown. For …
References
- Anderson A (2005): The community builder’s approach to theory of change: a practical guide to theory development. New York: The Aspen Institute roundtable on community change. Coffman J (1999): Learning from logic models: an example of a family/school partnership program. Harvard Family Research Project. De Silva and others (2014): Theory of change: a theory-driven approac…
Acknowledgements
- This work was partially funded by the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) School for Public Health Research, the NIHRCollaboration for Leadership in Applied Health Research and Care of the South West Peninsula (PenCLAHRC) and by Public Health England. However, the views expressed are those of the authors. Written by Sarah Morgan-Trimmer, Jane Smith, Krysta…