
The mental foramen is one of two foramina (openings) located on the anterior surface of the mandible. It is part of the mandibular canal. It transmits the terminal branches of the inferior alveolar nerve
Inferior alveolar nerve
The inferior alveolar nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve, which is itself the third branch of the trigeminal nerve. The inferior alveolar nerves supply sensation to the lower teeth.
What passes through the mental foramen?
The mental foramen is one of two foramina (openings) located on the anterior surface of the mandible. It transmits the terminal branches of the inferior alveolar nerve and vessels (the mental artery ).
Where is the foramen located?
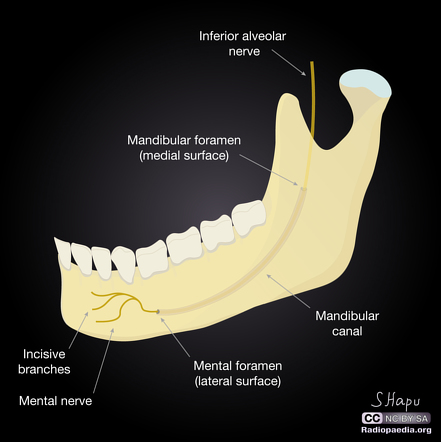
Normal variants have the foramen located anywhere between the canine and 1st molar. The mental nerve, a terminal branch of inferior alveolar nerve and the mental artery leave the mandibular canal through it 1,2.
What is the meaning of meniscal foramen?
men·tal for·a·men. The anterior opening of the mandibular canal on the body of the mandible lateral to and above the mental tubercle giving passage to the mental artery and nerve. foramen. pl. foramina [L.] a natural opening or passage, especially one into or through a bone.
Where is the incisive mental foramen located?
An incisive mental foramen is observed in 1% of the side of the mandible. The mental nerve may be anaesthetized as it leaves the mental foramen. This causes loss of sensation to the lower lip and chin on the same side. Side view of the skull.
What is the role of mental foramen?
The mental foramen is one of two foramina (openings) located on the anterior surface of the mandible. It is part of the mandibular canal. It transmits the terminal branches of the inferior alveolar nerve and the mental vessels.
How do you get a mental foramen?
The mental foramen is situated on the buccal cortex of the mandibular bone, just below the corner (chelion) of the lip on either side and in close relation to the root of the 2nd mandibular premolar tooth. It moves in a posterior direction during the development of the mandible [4].
What exits through the mental foramen?
The inferior alveolar nerve enters the mandible through the mandibular foramen, traverses the mandibular canal, and exits through the mental foramen, receiving the name of mental nerve [4]. The incisive nerve continues in the mandibular canal to innervate the premolars, canines, and incisors [1].
What is the mental foramen on a radiograph?
The mental foramen is usually the anterior limit of the inferior dental canal that is apparent on radiographs. It opens on the facial aspect of the mandible in the region of the premolars. It can pose diagnostic dilemma radiographically because of its anatomical variation which can mimic as a periapical pathosis.
What nerve goes through mental foramen?
Normal variants have the foramen located anywhere between the canine and 1st molar. The mental nerve, a terminal branch of inferior alveolar nerve and the mental artery leave the mandibular canal through it 1,2.
Where is the location of mental foramen?
The mental foramen is most commonly located between the mandibular premolars, greater than 2 mm below the apex of the second mandibular premolars. They are usually ovoid in shape with an almost equal distribution of asymmetry and symmetry.
What happens when mental nerve is damaged?
Nerve damage due to stretching, compressing, or transecting the mental nerve can cause sensory dysfunctions of the inferior lip, surrounding skin and mucosa, and teeth, including numbness, increased or decreased sensation, painful sensation, or complete loss of sensation.
Does mental nerve block teeth?
The mental nerve block provides anesthesia only to the lower lip and soft tissue of the chin. It does not anesthetize the teeth, which would require an inferior alveolar nerve block. If the foramen is not directly palpable, the anesthetic can be injected into the buccal mucosa between the 2 lower premolar teeth.
Where does the mental nerve exit?
The orifice of exit of the mental nerve, mental foramen, is most commonly located halfway between the alveolar crest and the inferior border of the mandibular bone in the vertical plane [6] and, in the horizontal plane, at the level of the apex of the second premolar or between the premolars [7].
Which periapical radiograph shows mental foramen?
Panoramic radiography can help locate the mental foramen, through which the nerve supply to the lower lip passes, and the mandibular canal during dental implantations [14].
Why does the position of mental foramen in mandible change with age?
In adults, the mental foramen is nearer to the inferior border while it moves upwards closer to the alveolar border in old age due to the loss of teeth and bone resorption [2,3] .
How do you do a mental nerve block?
Inject the local anesthetic Hold the anesthetic syringe such that the needle bevel faces the mandible. Insert the needle into the mucobuccal fold between the lower 1st and 2nd premolars. Advance the needle inferiorly, parallel to the teeth, about 0.5 to 1 cm. Do not contact bone.
Where does the mental nerve come from?
The nerves from the central nervous system develop from the neuroectoderm, while the peripheral nerves originate from the neural crest cells. Therefore, the trigeminal nerve and its branches, including the mental nerve, come from the neural crest cells.
Is the mental foramen a hole?
Mental foramen – hole on the anterior aspect of the bone below the second premolar; passageway for the mental nerve and vessels.
Why does the position of mental foramen in mandible change with age?
In adults, the mental foramen is nearer to the inferior border while it moves upwards closer to the alveolar border in old age due to the loss of teeth and bone resorption [2,3] .
What does the mental nerve control?
The mental nerve provides sensation to the front of the chin and the lower lip. It also provides sensation to some of the gums of the anterior mandibular (lower) teeth.
What is the mental foramen?
The mental foramen is one of two foramina (openings) located on the anterior surface of the mandible.
How many sides of the mandible have multiple mental foramen?
Multiple mental foramina are observed in 17% of the sides. Only (4%) of the mandibles show bilateral multiple mental foramina. The majority of the multiple foramina are unequal in size: a single large foramen while the others are small (satellite) foramina. An incisive mental foramen is observed in 1% of the sides.
Where is the mental foramen located?
The mental foramen is one of two foramina (openings) located on the anterior surface of the mandible. It is part of the mandibular canal, transmitting the terminal branches of the inferior alveolar nerve and vessels (the mental artery ). The mental foramen descends slightly in toothless individuals.
Does the mental foramen descend in toothless individuals?
The mental foramen descends slightly in toothless individuals.
What is the injection of the mandibular canal?
In the anterior aspect of the mandibular canal, injection can be made through the mental foramen to desensitize mental aspect of the mandibular nerve.
What is the name of the canal that opens to the mental artery?
the anterior opening of the mandibular canal on the body of the mandible lateral to and above the mental tubercle giving passage to the mental artery and nerve. Synonym (s): foramen mentale [TA], mental canal. Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012.
What does an asterisk on a face mean?
The asterisk (*) denotes the mental foramen on the face.
How deep is the zygoma electrode?
Some investigators support intervention surveys (Blanas et al, 2004): special needle electrode is pricked below zygoma against lower jaw temporal joint 4-4.5 cm deep by foramen ovale; the other electrode is put by mental foramen; then the time of stimulus spread is registered.
Where is the left parotid mass?
This revealed a left sided parotid mass extending posteriorly to the mandibular angle, anteriorly beyond the mental foramen and postero-superiorly to the skull base.
Which branch of the brain innervates the skin of the chin and lower lip?
Its larger terminal branch emerges from the mental foramen as the mental nerve and innervates the skin of the chin and the lower lip, while the smaller incisive branch supplies the canine and incisor teeth.
What is a Foramen?
The Latin word foramen means an aperture or opening. Most foramina are found in the facial bones and cranial bones.
What is the single foramen cecum?
Single foramen cecum; shared between the frontal crest of the temporal bone and the ethmoid bone, between the cranium and nasal cavity; emissary veins.
Where is the Paired Foramen lacerum located?
Paired foramen lacerum; the end of the shared carotid canal that begins at the carotid f. (temporal bone); located next to the sella turcica; nerve and artery of the pyterygoid canal, internal carotid artery, and emissary vein.
What is the procedure called when the parietal foramina is enlarged?
Alternatively, parietal foramina can be so enlarged that, when found in ancient remains, archeologists think that the person has undergone an early surgical procedure called trepanning or trepanation.
Which artery is acoustic meatus?
Paired internal acoustic meatus; close to the ear; facial nerve (CN VII), acoustic nerve (CN VIII), and branch of the basilar artery. Paired carotid foramen; opens into a channel (carotid canal) through which the internal carotid artery and internal carotid plexus pass. The carotid canal ends at another aperture (f. lacerum) in the sphenoid bone.
What is the cranial foramen?
Cranial Foramen. A cranial foramen allows important nervous and circulatory tissue to travel throughout the head and neck region. The following headings list the singular or paired name, location, and the structures that pass through each aperture.
What is the result of mirrored notches in multiple bone articulations that, when put together, form a?
Some foramina are the result of mirrored notches in multiple bone articulations that, when put together, form a circular hole; in this case, the information is repeated.
Overview
The mental foramen is one of two foramina (openings) located on the anterior surface of the mandible. It is part of the mandibular canal. It transmits the terminal branches of the inferior alveolar nerve and the mental vessels.
Structure
The mental foramen is located on the anterior surface of the mandible. It is directly below the commisure of the lips, and the tendon of depressor labii inferioris muscle. It is at the end of the mandibular canal, which begins at the mandibular foramen on the posterior surface of the mandible. It transmits the terminal branches of the inferior alveolar nerve (the mental nerve), the mental artery, and the mental vein.
Clinical significance
The mental nerve may be anaesthetized as it leaves the mental foramen. This causes loss of sensation to the lower lip and chin on the same side.
Additional images
• Side view of the skull.
• The skull from the front.
• Distribution of the maxillary and mandibular nerves, and the submaxillary ganglion.
• Mandibular division of the trifacial nerve.
See also
• Mandibular foramen
External links
• cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)
• Diagram at uni-mainz.de