What is the function of mixed neuron?
Mixed neuron: Mixed neurons contain both Afferent axons (which carry impulses from the motor neuron to CNS) and Efferent axons (which carry impulse for the CNS to the target organs or muscles), thus mixed neurons carry impulses from the motor neurons to the CNS as well as from the CNS to the target organs.
What are neuronal and mixed neuronic tumors?
Neuronal tumors are a rare group of brain tumors made of abnormal neurons. Mixed neuronal-glial tumors are a rare group of brain tumors that have abnormal neuron cells along with glial cells. Healthcare providers who specialize in examining tumor cells under a microscope normally grade them on a scale from I to IV.
What is a mixed nerve?
Related to mixed nerve: sensory nerve nerve [nerv] a macroscopic cordlike structure of the body, comprising a collection of nerve fibersthat convey impulses between a part of the central nervous systemand some other body region. See Appendix 2-6 and see color plates. Depending on their function, nerves are known as sensory, motor,or mixed.
What are the neurons?
The neurons are specialized nerve cells that send messages within the CNS and the rest of your body. These neurons “talk” to each other by using chemical and electrical signals.

What are the mixed nerves?
Mixed cranial nerves are a group of cranial nerves that consist of sensory and motor nerve fibers. There are four such nerves in our peripheral nervous system namely the Trigeminal nerve (CN V), Facial nerve (CN VII) Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), and Vagus nerve (CN X).
What is a mixed nerve give example?
Mixed nerve has motor nerve fibres to bring muscle movemnt and sensory nerve fibres to bring sensations. Facial nerve and trigeminal nerves are the examples of mixed nerves. Facial nerve supplies to tongue and muscles of the face.So it helps in taste sensation and also facial muscle mmovement.
Why are mixed nerves called as mixed nerves?
The cell bodies of the sensory neurons are in the dorsal root ganglion, but the motor neuron cell bodies are in the gray matter. The two roots join to form the spinal nerve just before the nerve leaves the vertebral column. Because all spinal nerves have both sensory and motor components, they are all mixed nerves.
What happens in a mixed nerve?
Mixed nerves are composed of both motor and sensory fibers, and transmit messages in both directions at once. Together, the nerves make up the peripheral nervous system, as distinguished from the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
What is the function of mixed neuron?
Mixed nerves are the nerves that perform both the action of sensory nerves as well as a motor nerve. They transform electrical impulses from the central nervous system to the muscles of the body. Generally, the mixed nerves transmit impulses at the rate of 120 metres per second or 432 kilometres per hour.
What is a mixed nerve quizlet?
Mixed nerves contain both afferent and efferent axons, and thus conduct both incoming sensory information and outgoing muscle commands in the same bundle.
Are spinal nerves mixed nerves?
Spinal nerves are mixed nerves that interact directly with the spinal cord to modulate motor and sensory information from the body's periphery. Each nerve forms from nerve fibers, known as fila radiculara, extending from the posterior (dorsal) and anterior (ventral) roots of the spinal cord.
Is optic nerve a mixed nerve?
The optic nerve has been classified as the second of twelve paired cranial nerves, but it is technically part of the central nervous system, rather than the peripheral nervous system because it is derived from an out-pouching of the diencephalon (optic stalks) during embryonic development.
Are spinal nerves mixed nerves?
Spinal nerves are mixed nerves that interact directly with the spinal cord to modulate motor and sensory information from the body's periphery. Each nerve forms from nerve fibers, known as fila radiculara, extending from the posterior (dorsal) and anterior (ventral) roots of the spinal cord.
Which cranial nerve is a mixed nerve?
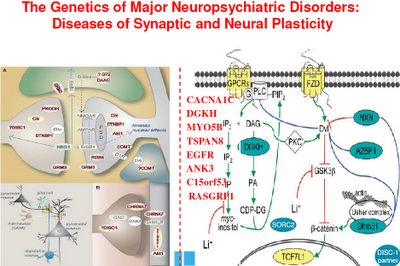
Cranial nerves III (oculomotor), IV (trochlear), VI (abducens), XI (spinal accessory), and XII (hypoglossal) are purely efferent. The remaining cranial nerves, V (trigeminal), VII (facial), IX (glossopharyngeal), and X (vagus), are functionally mixed (sensory and motor) (Figure 1A).
How are neuronal and mixed neuronal tumors treated?
How are neuronal and mixed neuronal-glial tumors treated? The standard treatment for these tumors is to remove them surgically. In many cases, treatment may only be removing the tumor. If the tumor is in a spot where it is not possible to remove it completely, radiation therapy and chemotherapy are other options.
What is a neuronal tumor?
Neuronal tumors are a rare group of brain tumors made of abnormal neurons. Mixed neuronal-glial tumors are a rare group of brain tumors that have abnormal neuron cells along with glial cells. Healthcare providers who specialize in examining tumor cells under a microscope normally grade them on a scale from I to IV.
Do neuronal tumors grow slowly?
Overall, neuronal and mixed neuronal-glial tumors tend to be slow growing . Some neuronal and mixed neuronal-glial tumors happen more often in children or teens than in adults. Other types (such as the cerebellar liponeurocytoma) are more common in older adults. Almost any of these tumors can occur in people of any age.
Is a neuronal tumor benign?
Neuronal and mixed neuronal-glial tumors are a group of rare tumors that occur in the brain or spinal cord. Together, your brain and spinal cord make up your central nervous system (CNS). Many of these tumors are not cancerous (benign). Benign means that the growth does not spread to other parts of the body. But these tumors can be dangerous.
What is the name of the structure that conveys impulses between a part of the central nervous system and some other
nerve. [ nerv] a macroscopic cordlike structure of the body, comprising a collection of nerve fibers that convey impulses between a part of the central nervous system and some other body region. See Appendix 2-6 and see color plates. Depending on their function, nerves are known as sensory, motor, or mixed.
Which nerves transmit impulses from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles?
Motor nerves, or efferent nerves, transmit impulses from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles. Mixed nerves are composed of both motor and sensory fibers, and transmit messages in both directions at once.
What is the name of the nerve that sends impulses to the central nervous system?
afferent nerve any nerve that transmits impulses from the periphery toward the central nervous system, such as a sensory nerve. See also neuron. articular nerve any mixed peripheral nerve that supplies a joint and its associated structures. auditory nerve vestibulocochlear nerve; see anatomic Table of Nerves in the Appendices.
What is the name of the nerve that stimulates muscle contraction?
motor nerve a peripheral efferent nerve that stimulates muscle contraction. myelinated nerve one whose axons are encased in a myelin sheath; called also medullated nerve. peripheral nerve any nerve outside the central nervous system. pilomotor n's those that supply the arrector muscles of hair.
Which nerve stimulates the vasomotor center?
pilomotor n's those that supply the arrector muscles of hair. pressor nerve an afferent nerve whose irritation stimulates a vasomotor center and increases intravascular tension. sciatic nerve see sciatic nerve. secretory nerve an efferent nerve whose stimulation increases vascular activity.
Which nerve transmits impulses resulting in a decrease in functional activity?
inhibitory nerve one that transmits impulses resulting in a decrease in functional activity. medullated nerve myelinated nerve. mixed nerve ( nerve of mixed fibers) a nerve composed of both sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) fibers. motor nerve a peripheral efferent nerve that stimulates muscle contraction.
Which nerve produces reflex action?
excitoreflex nerve a visceral nerve that produces reflex action. fusimotor n's those that innervate the intrafusal fibers of the muscle spindle. gangliated nerve any nerve of the sympathetic nervous system. inhibitory nerve one that transmits impulses resulting in a decrease in functional activity.
What is mixed cranial nerve?
Mixed cranial nerves. Mixed cranial nerves are the cranial nerves that contain sensory and motor nerve fibers. There are four of such nerves in our peripheral nervous system ; We know that the task of learning neuroanatomy and the anatomy of the head and neck may feel insurmountable.
What is the name of the nerve that contains the motor and sensory nerves?
The trigeminal nerve (CN V) is a mixed nerve containing both general sensory (afferent) fibers and somatic motor (efferent) fibers. The fibers originate from the nuclei in the brainstem and spinal cord; principal sensory nucleus of trigeminal nerve, spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve, mesencephalic nucleus of trigeminal nerve and the motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve. CN V forms the trigeminal ganglion near the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone .
Which nerve is responsible for motor functions?
Oculomotor nerve, trochlear, mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (V3), abducens, facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus, spinal accessory and hypoglossal nerves are responsible for motor functions. Understand better the anatomy of cranial nerves with our cranial nerves quizzes and labeling exercises . According to their functions, cranial nerves are ...
How does the baroreceptor reflex work?
The baroreceptor reflex functions to maintain a person’s blood pressure and cardiac output when mean arterial pressure changes. For example, when a person suddenly stands up from a sitting or lying position, blood pressure drops; this leads to decreased firing by receptors in the carotid body and aortic arch. Signals originating in the carotid body are transmitted by the glossopharyngeal nerve, whereas signals originating in the aortic arch are transmitted by the vagus nerve. The decreased signalling rate ultimately results in disinhibition of the sympathetic nervous system, which leads to an increase peripheral vascular tone, cardiac rate, and cardiac output.
Which nerves are involved in sensory functions?
Cranial nerves have various functions; The olfactory nerve, the optic nerve, the facial nerve, the vestibulocochlear nerve, the glossopharyngeal nerve, and the vagus nerve each play roles in special sensory functions (i.e. olfaction, vision, gustation, audition, and balance). Trigeminal (all three branches) and glossopharyngeal nerves play roles in ...
Where does the CN IX originate?
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) Glossopharyngeal nerve is another multimodal nerve. It originates from the brainstem and leaves the skull through the jugular foramen. Its fibers originate from four nuclei; nucleus ambiguus, inferior salivatory nucleus, nuclei of solitary tract and spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve.
Where does the facial nerve originate?
The former originates from the motor nucleus of facial nerve, while the latter stemms from the nuclei of solitary tract, spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve and the superior salivatory nucleus.
Types of Neurons
There are many different types of neurons, and they all have special functions in the brain, spinal cord, and muscles that control our body. 1 These different types of neurons are highly specialized. Some neurons are responsible for taste while others sense pain.
Sensory Neurons
Sensory neurons help us feel and explore the world around us. Major senses such as touch and pain can help us to move safely through the world.
Motor Neurons
Motor neurons control the movement of the body. These neurons coordinate our muscles and ensure that our arms and legs move together.
Interneurons
Interneurons are the most abundant neurons in the body. They act as the signal controllers within the body, relaying important information from one end of the nervous system to the other.
Neuronal Anatomy
Neurons are the basic cellular unit of the nervous system. Neurons have different components that play integral roles in their ability to receive and transmit signals through the body.
Summary
Neurons are responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body, a process that allows us to move and exist in the world around us. Different types of neurons include sensory, motor, and interneurons, as well as structurally-based neurons, which include unipolar, multipolar, bipolar, and pseudo-unipolar neurons.
A Word From Verywell
Neurons and their various complexities can seem like a daunting topic to understand. However, knowing that distinct types of neurons play different roles within the body can help you develop a basic understanding of the nervous system's structure.

What Are Neuronal and Mixed Neuronal-Glial Tumors?
- Neuronal and mixed neuronal-glial tumors are a group of rare tumors that occur in the brain or spinal cord. Together, your brain and spinal cord make up your central nervous system (CNS). Many of these tumors are not cancerous (benign). Benign means that the growth does not spread to other parts of the body. But these tumors can be dangerous. They ...
What Causes Neuronal and Mixed Neuronal-Glial Tumors?
- Experts do not yet know what causes neuronal and mixed neuronal-glial tumors to develop. Some theories suggest links to gene mutations, environmental toxins, or infections (such as by viruses). But, the possible risk factors for these tumors are not clear.
What Are The Symptoms of Neuronal and Mixed Neuronal-Glial Tumors?
- Where the tumor is located in the brain and its size determine what symptoms you may have. A neuronal or a mixed neuronal-glial tumor may cause symptoms related to the part of the brain that it grows in. In general, symptoms may include: 1. Seizures (often the first symptom) 2. Headache 3. Nausea and vomiting 4. Dizziness and balance problems 5. Trouble walking 6. Eye problems …
How Are Neuronal and Mixed Neuronal-Glial Tumors Diagnosed?
- Healthcare providers often take a health history, asking about your recent symptoms, past health problems, and your family health history. You will need a thorough physical exam, including a nervous system exam. Your healthcare provider will likely check your coordination and reflexes and do several nervous system tests. If a healthcare provider suspects a brain tumor, he or she …
How Are Neuronal and Mixed Neuronal-Glial Tumors Treated?
- The standard treatment for these tumors is to remove them surgically. In many cases, treatment may only be removing the tumor. If the tumor is in a spot where it is not possible to remove it completely, radiation therapy and chemotherapy are other options. You can work with your care team to talk about the best treatment plan for you. You will likely need regular follow-ups with yo…
What Are Possible Complications of Neuronal and Mixed Neuronal-Glial Tumors?
- Seizures are the most common nervous system symptoms. In some cases, the tumor may be blocking drainage of the cerebrospinal fluid from your brain. This causes a buildup of fluid and increases the pressure within your brain. If this happens, you may need surgery to insert a tube to drain excess fluid and lower the pressure. After removal of the tumor, this problem often goes a…
Key Points About Neuronal and Mixed Neuronal-Glial Tumors
- Neuronal and mixed neuronal-glial tumors are rare tumors of the brain or spinal cord. These tumors include abnormal nerve cells. Some key points include: 1. Most of these tumors are low grade (grade I or grade II) and tend to grow slowly. 2. The first symptoms may be seizures. Headaches, nausea, or other symptoms may occur. 3. Surgery to remove the tumor is often the …
Next Steps
- Tips to help you get the most from a visit to your healthcare provider: 1. Know the reason for your visit and what you want to happen. 2. Before your visit, write down questions you want answered. 3. Bring someone with you to help you ask questions and remember what your healthcare provider tells you. 4. At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis, and any new medicines, treatm…