The main characteristics of the nebula are as follows:
- Nebulae are clouds of gas and dust in the interstellar space.
- Their size can range from millions of miles to hundreds of light years.
- They are composed primarily of hydrogen and also have other gases and dust
- Stars and planetary systems are formed from the gas and dust found inside nebulae.
- Until 1920, distant galaxies were classified as nebulae.
What does a Nebula create or do?
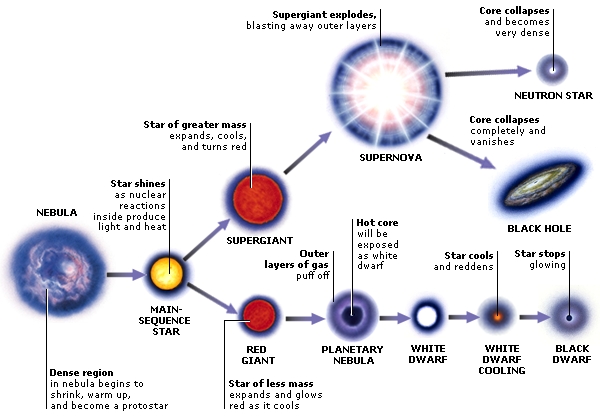
What does a planetary nebula create? Planetary Nebula: Gas and Dust, and No Planets Involved. In about 5 billion years, when the sun shucks off its outer layers, it will create a beautiful shell of diffuse gas known as a planetary nebula. What happens during the planetary nebula stage? Low-mass stars turn into planetary nebulae towards the end of their red giant phase.
What is a Nebula and how do they form?
Trending at Canaltech:
- Ômicron: 2 doses of Pfizer or AstraZeneca induce less antibodies
- This Google Play Store app has infected over 500,000 Android phones
- Who invented the internet? Discover the complete history of the Cold War to the WWW
- The sky is not the limit | Water on Mars, Einstein was right and more!
- Who created the deep web?
What happens in the formation of a Nebula?
Classical types
- H II regions, large diffuse nebulae containing ionized hydrogen
- Planetary nebulae
- Supernova remnant (e.g., Crab Nebula)
- Dark nebula
What is the most beautiful Nebula?
#4 Most Beautiful Nebulae: The Butterfly Nebula
- Distance from Earth: ~4,000 Light Years, 23,514,501,492,734,430 Miles
- Location: Scorpius Constellation
- Diameter: ~3 Light Years, 17,635,876,119,550 Miles

Is Earth inside a nebula?
0:323:24Space they are vast sometimes taking up hundreds of light-years of space. But with all that sizeMoreSpace they are vast sometimes taking up hundreds of light-years of space. But with all that size they aren't massive a nebula the diameter of the earth would only have a mass of a few kilograms.
Is nebula a gas or plasma?
Named after the Latin word for “cloud”, nebulae are not only massive clouds of dust, hydrogen and helium gas, and plasma; they are also often “stellar nurseries” – i.e. the place where stars are born. And for centuries, distant galaxies were often mistaken for these massive clouds.
How are nebulae made?
A nebula is a giant cloud of dust and gas in space. Some nebulae (more than one nebula) come from the gas and dust thrown out by the explosion of a dying star, such as a supernova. Other nebulae are regions where new stars are beginning to form. For this reason, some nebulae are called "star nurseries."
What state of matter is a nebula?
Clearly, the nebula is a gas whereas the planets and Sun are solids with some layers that are liquid (e.g., oceans) and/or gas (atmospheres).
What is a nebula made of?
The roots of the word come from Latin nebula, which means a “mist, vapor, fog, smoke, exhalation.”. Nebulae are made up of dust, basic elements such as hydrogen and other ionized gases. They either form through clouds of cold ...
When were nebulas discovered?
It wasn’t until the 17th century and advances in optics that nebulae became more observed. In 1610, Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Pieresc discovered the Orion Nebula, which was then observed in 1618 by Johann Baptist Cysat. The first detailed observations, though, waited for famous scientist Christiaan Huygens in 1659.
Who discovered the Nebula?
The first mention of it may have been in 964 by Persian astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi, who wrote about the Andromeda Galaxy, noticing “a little cloud.”.
Where is the Orion Nebula?
The Orion Nebula is one of these, located between the stars in the constellation Orion’s sword. Many others are visible through telescopes, depending on how many stars are around them to illuminate the dust clouds that form the nebulae.
What is a nebula?
A nebula ( Latin for 'cloud' or 'fog'; pl. nebulae, nebulæ or nebulas) is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen, helium and other ionized gases. Originally, the term was used to describe any diffused astronomical object, including galaxies beyond the Milky Way. The Andromeda Galaxy, for instance, was once referred to as the Andromeda Nebula ...
How big are nebulas?
He also helped categorize nebulae based on the type of light spectra they produced. Most nebulae are of vast size; some are hundreds of light-years in diameter. A nebula that is visible to the human eye from Earth would appear larger, but no brighter, from close by.
What is the name of the supernova in Taurus?
One of the best examples of this is the Crab Nebula, in Taurus. The supernova event was recorded in the year 1054 and is labeled SN 1054. The compact object that was created after the explosion lies in the center of the Crab Nebula and its core is now a neutron star . Still other nebulae form as planetary nebulae.
How did the planetary nebula get its name?
Planetary nebulae were given their name by the first astronomical observers who were initially unable to distinguish them from planets, and who tended to confuse them with planets, which were of more interest to them. Our Sun is expected to spawn a planetary nebula about 12 billion years after its formation.
What are some examples of nebulae?
One of the best examples of this is the Crab Nebula, in Taurus.
What happens to the cloud after a million years?
Feedback from star-formation, in the form of supernova explosions of massive stars, stellar winds or ultraviolet radiation from massive stars, or outflows from low-mass stars may disrupt the cloud, destroying the nebula after several million years.
How do supernovae occur?
A supernova occurs when a high-mass star reaches the end of its life. When nuclear fusion in the core of the star stops, the star collapses . The gas falling inward either rebounds or gets so strongly heated that it expands outwards from the core, thus causing the star to explode. The expanding shell of gas forms a supernova remnant, a special diffuse nebula. Although much of the optical and X-ray emission from supernova remnants originates from ionized gas, a great amount of the radio emission is a form of non-thermal emission called synchrotron emission. This emission originates from high-velocity electrons oscillating within magnetic fields .
What is a dark nebula?
A dark nebula is a sort of interstellar cloud that is dense to the point that it obstructs the light from objects behind it. The termination of the light is caused by interstellar dust grains situated in the coldest, densest parts of large sub-atomic clouds. Clusters of dim nebulae are related with Giant Molecular Clouds.
Why do we have planetary nebulae?
The formation of most planetary nebulae occurs due to during the last phase of the star's life, the external layers of the star are emitted by heavy stellar winds. After the vast majority of the red Goliath's climate is dispersed, the bright radiation of the hot brilliant center, called a planetary nebula nucleus (PNN), ionizes the external layers.
What is the name of the brightest cloud in the universe?
The nebula that is scarcely noticeable to the human eye from Earth would seem bigger, yet not brighter, when near it. The Orion Nebula, the brightest cloud in the ...
What is a supernova remnant?
Supernova remnant. A supernova remnant (SNR) is the structure because of the blast of a star in a supernova. The supernova leftover is limited by a growing shock wave and comprises of catapulted material extending from the blast. There are two basic ways for the formation of a supernova:
How do supernovae form?
There are two basic ways for the formation of a supernova: 1 A huge star may come up short on fuel, stopping to produce fusion energy in its center, and crumbling inward to shape a neutron star or a black hole 2 A white small star may accumulate material from a neighbour star until the point when it achieves a minimum mass and experiences a thermonuclear blast.
What is the brightest cloud in the sky?
The Orion Nebula, the brightest cloud in the sky that involves an area double the diameter of the full Moon, can be seen with the exposed eye yet was missed by early astronomers.
How are nebulas formed?
Nebula Formation: In essence, a nebula is formed when portions of the interstellar medium undergo gravitational collapse. Mutual gravitational attraction causes matter to clump together, forming regions of greater and greater density.
What is a nebula?
A nebula is a truly wondrous thing to behold. Named after the Latin word for “cloud”, nebulae are not only massive clouds of dust, hydrogen and helium gas, and plasma; they are also often “stellar nurseries” – i.e. the place where stars are born. And for centuries, distant galaxies were often mistaken for these massive clouds.
How many nebulae were there in 1781?
And in 1781, Charles Messier compiled his catalog of 103 “nebulae” (now called Messier objects), though some were galaxies and comets. The number of observed and cataloged nebulae greatly expanded thanks to the efforts of William Herschel and his sister, Caroline.
What is the difference between emission nebulae and reflection nebulae?
In contrast, Reflection Nebulae do not emit significant amounts of visible light, but are still luminous because they reflect the light from nearby stars. YouTube.
What is interstellar gas?
The interstellar gas consists partly of neutral atoms and molecules, as well as charged particles (aka. plasma), such as ions and electrons. This gas is extremely dilute, with an average density of about 1 atom per cubic centimeter.
How big are nebulae?
Most nebulae are vast in size, measuring up to hundreds of light years in diameter.
What are the two categories of nebulas?
These can be subdivided into two further categories based on their behavior with visible light – “Emission Nebulae” and “Reflection Nebulae”.
How do nebulas form?
Nature abhors empty space, after all! A nebula subsequently begins to form when a few atoms get close enough to clump together. Naturally, the more atoms that clump up, the stronger their gravitational influence then becomes.
What is a nebula in space?
December 2, 2014 Peter Christoforou FAQs, Stars 0. A nebula is mostly a cloud of gas and dust in space, and if you have more than one, they are called nebulae. Nebulae are some of the most spectacular objects in the universe, and many have been named after familiar objects, including land animals, insects, aquatic animals, birds, ...
Why do nebulae have dark areas?
As they recombine they emit longer wavelengths in the red part of the spectrum, which gives them their distinctive red colour. These types of nebulae often appear to have dark areas as their clouds of dust block the light. Many nebulae have components of both reflection and emission, including the Trifid Nebula.
What is the dark nebula?
Also known as Dark Nebula, the shapes they form are very irregular, with the largest varieties visible to the naked eye as dark patches, such as the Coalsack Nebula which obscures parts of the bright Milky Way.
Which type of nebula absorbs light?
Many nebulae have components of both reflection and emission, including the Trifid Nebula. – Absorption Nebulae: This type nebula absorbs or obscures the light coming from sources behind them, including stars and bright nebulae, a famous example of which is the Horsehead Nebula.
What happens when a star blows up?
Every once in a while a star blows up. It runs out of hydrogen or helium fuel, it gets too big, collapses and then goes boom – don’t worry our Sun is stable for about another 5 billion years. The resulting explosion sends out material and shock waves that can disturb the nebulae causing it to form more stars.
What are some examples of planetary nebulas?
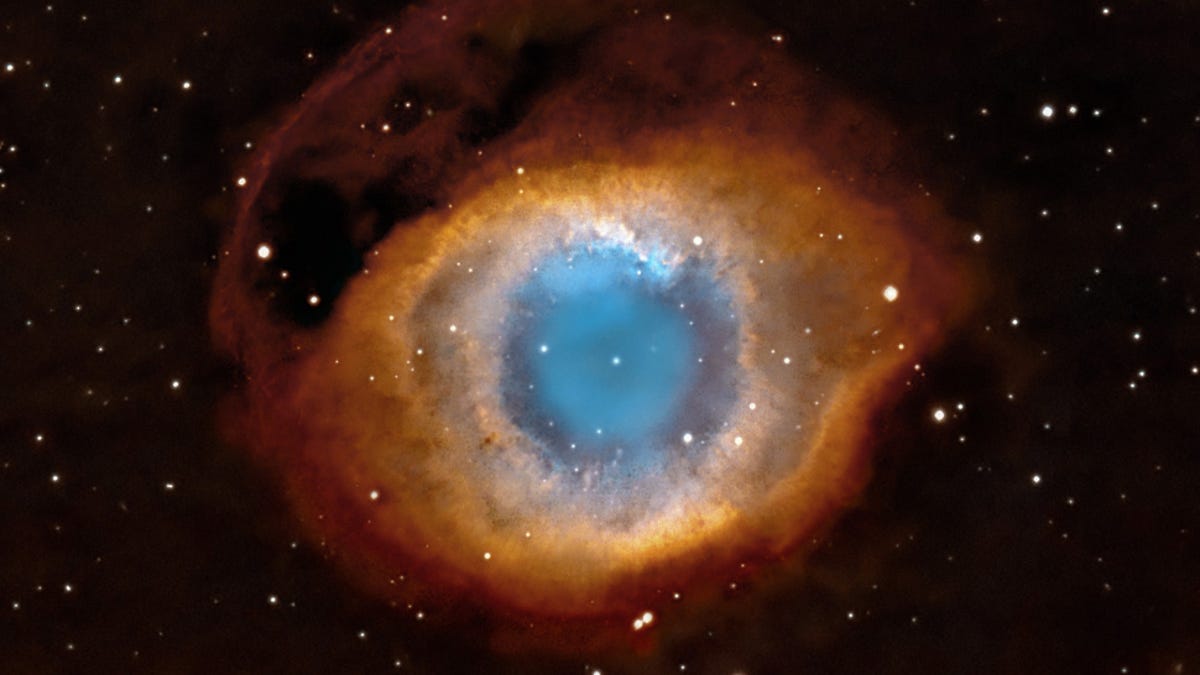
One of the best examples of a planetary nebula is the Ring Nebula (M57) in Lyra, with other beautiful examples including the Helix Nebula in Aquarius, and the Eskimo Nebula in the constellation of Gemini.
Overview
Observational history
Formation
Types
Examples
A nebula (Latin for 'cloud' or 'fog'; pl. nebulae, nebulæ or nebulas ) is a distinct body of interstellar clouds (which can consist of cosmic dust, hydrogen, helium, molecular clouds; possibly as ionized gases). Originally, the term was used to describe any diffused astronomical object, including galaxies beyond the Milky Way. The Andromeda Galaxy, for instance, was once referred to as the Androm…
See also
Around 150 AD, Ptolemy recorded, in books VII–VIII of his Almagest, five stars that appeared nebulous. He also noted a region of nebulosity between the constellations Ursa Major and Leo that was not associated with any star. The first true nebula, as distinct from a star cluster, was mentioned by the Persian astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi, in his Book of Fixed Stars (964). He noted "…
External links
There are a variety of formation mechanisms for the different types of nebulae. Some nebulae form from gas that is already in the interstellar medium while others are produced by stars. Examples of the former case are giant molecular clouds, the coldest, densest phase of interstellar gas, which can form by the cooling and condensation of more diffuse gas. Examples of the latter case ar…