
What is the function of neurohormone?
Neurohormone. The hypothalamus produces releasing hormones and neurohypophysial hormones in specialized hypothalamic neurons which extend to the median eminence and posterior pituitary. The adrenal medulla produces adrenomedullary hormones in chromaffin cells, cells which are very similar in structure to post-synaptic sympathetic...
What is the difference between hormonal stimulus and neural stimulus?
Hormonal stimuli are changes in hormone levels that initiate or inhibit the secretion of another hormone. Finally, a neural stimulus occurs when a nerve impulse prompts the secretion or inhibition of a hormone.
Is the adrenal medulla a neurohormone?
Neurohormone. The adrenal medulla produces adrenomedullary hormones in chromaffin cells, cells which are very similar in structure to post-synaptic sympathetic neurons, even though they are not neurons they are derivatives of the neural crest.
What is the difference between a releasing hormone and a neurohormone?
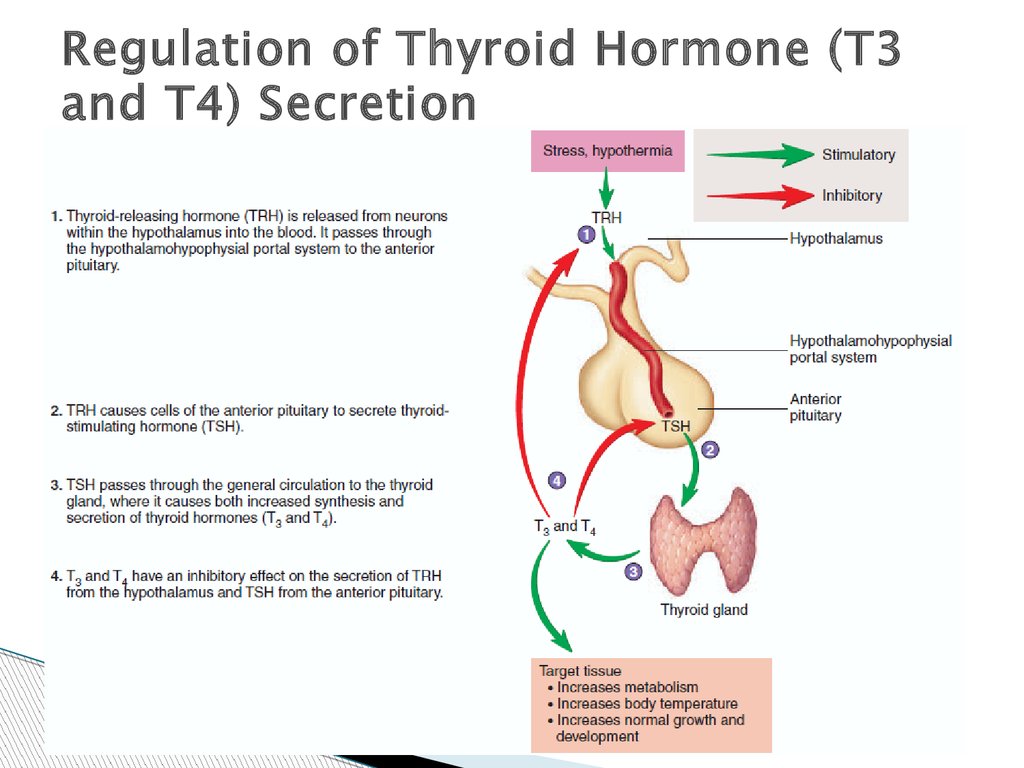
When a neurohormone increases output of a particular adenohypophysial hormone, it is called a releasing hormone ( RH ). For example, the neurohormone that increases the output of thyrotropin is called thyrotropin-releasing hormone ( TRH ).

What is neural hormone control?
Hormonal control is the secretion of hormones by the endocrine system into the bloodstream in order to produce an effect on target organs in the body, while neural control is the generation of nerve impulses by the nerve cells in the nervous system in order to produce an effect on target organs in the body.
Is oxytocin a neural hormone?
Oxytocin and vasopressin are pituitary neuropeptides that have been shown to affect social processes in mammals.
What is the difference between a hormone and a neurohormone?
Hormones are the chemical substances secreted by endocrine glands that act as chemical messengers. Neurohormones are the hormones secreted by the neuroendocrine cell known as specialized neurons.
Which is both a hormone and neurohormone?
GlossarynorepinephrineBoth a hormone and a neurohormone.oxytocinStimulates uterine contractions during childbirth and the flow of milk from the mammary glands.pancreatitisAn inflammation of the pancreas.parathyroidectomyThe surgical removal of one or more of the parathyroid glands.57 more rows
Which of the following is a neuro hormone?
Neurohormone is a hormone that is produced by neurosecretory cells and released by nerve impulses (e.g., norepinephrine, oxytocin, vasopressin)....Releasing and Release-Inhibiting Hormones.NeurohormoneAbbreviationProlactin release-inhibiting hormone (dopamine)PRIHCorticotropin-releasing hormoneCRH4 more rows
Is cortisol a neurohormone?
This article debates the contributory roles of the neurohormones oxytocin and cortisol for their psychobiological effects in humans. The empirical literature on these neurohormones is reviewed and suggestions for future research outlined.
Are all neurotransmitters hormones?
While the distinction between neurotransmitters and hormones is generally clear-cut, a substance can act as a neurotransmitter in one region of the brain while serving as a hormone elsewhere.
What is one way hormones are different to neurons and neurotransmitters?
Hormones are chemical signals secreted by the endocrine glands into the circulatory system which convey regulatory messages within the body. On the other hand, neurotransmitters are the brain chemicals that relay information throughout the brain and the body.
How are neurons and hormones similar but different?
Neurotransmitters and hormones are similar because they are both picked up by receptors and they are both chemicals. A difference is that neurotransmitters are still using an electric charge to be sent and hormones are triggered chemically. Another difference is that they interpret target cells in a different way.
Are pituitary hormones neurohormones?
The neurohormones in most mammals include oxytocin and vasopressin, both of which are produced in the hypothalamic region of the brain and secreted into the blood by the neurohypophysis (part of the pituitary gland).
Is adrenaline a neurotransmitter?
Epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, is both a neurotransmitter and a hormone. It plays an important role in your body's “fight-or-flight” response. It's also used as a medication to treat many life-threatening conditions.
How do I stop adrenaline anxiety?
The one and only way to get rid of adrenaline is to burn it off with cardiovascular exercise. Itʼs just like a car burning gasoline. When you do cardio your body actually burns the adrenaline up and gets rid of it! A person suffering from anxiety needs to do at least 30 minutes of cardio-vascular exercise each day.
What is the name of the hormone that is produced by neurosecretory cells and released by nerve impulses?
Neurohormone. Neurohormone is a hormone that is produced by neurosecretory cells and released by nerve impulses (e.g., norepinephrine, oxytocin, vasopressin). From: Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 2010. Download as PDF.
Which neurohormone is highly regulated by corticosteroids and prior stress?
The neurohormone CRF (in the PVN) is highly regulated by both corticosteroids and prior stress. Corticosteroids, the product of the endocrine limb of the stress response, exert a negative feedback regulation, in part by decreasing CRF mRNA in PVN hypothalamic neurons and tonic and evoked release of CRF into the median eminence (Plotsky, 1985; Plotsky et al., 1986; Plotsky and Sawchenko, 1987; Dallman et al., 1992 ). In contrast, prior stress (either repeated, chronic, or a single severe stress) generally increases CRF mRNA in PVN hypothalamic neurons and stress-evoked release of CRF ( Imaki et al., 1991; Dallman et al., 1992; De Goeij et al., 1992; Bartanusz et al., 1993 ). CRF in different nuclei is differentially regulated by corticosteroids and stress ( Swanson and Simmons, 1989; Imaki et al., 1991, 1992; Makino et al., 1994, 1995; Palkovits et al., 1998 ). For example, adrenalectomy and corticosteroids have reciprocal effects on CRF mRNA in PVN neurons, which are opposite to those on CRF mRNA in the CNA. Differential regulation is also seen with a single session of footshock or hypoosmotic challenge, which selectively increase CRF expression in neurons of Barrington’s nucleus ( Imaki et al., 1991, 1992 ).
What is neurohormone axe?
Neurohormone axes typify complex feedback systems in which two or more model variables (e.g., secretion and clearance) are required to account for the nonlinear behavior of the system output ( neurohormone concentrations over time). For example, episodic fluctuations in blood concentrations of a neurohormone are controlled jointly by neurohormone ...
How are episodic fluctuations in blood concentrations of a neurohormone controlled?
For example, episodic fluctuations in blood concentrations of a neurohormone are controlled jointly by neurohormone secretory event frequency, amplitude, duration, and waveform, as well as by neurohormone disappearance rates from the blood (1, 2 ).
Which area of the hypothalamus releases neurohormones?
The neurohormones released by the axons of the hypophysiotropic area of the hypothalamus can either increase or decrease the synthesis and secretion of hormones of the adenohypophysis. When a neurohormone increases output of a particular adenohypophysial hormone, it is called a releasing hormone ( RH ).
What gland produces melatonin?
The neurohormone melatonin is secreted by the pineal gland. Melatonin derives from serotonin, which is first N -acetylated, then O -methylated to lead to N -acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine or melatonin, which is directly released into the general circulation. 11 This synthesis occurs only during the night in all species, regardless of diurnal or nocturnal activity. 12-15 Norepinephrine released during the night stimulates the beta-adrenergic receptors present on the pinealocytes and hence the synthesis of the enzyme N -acetyltransferase, which is synthesized and activated only during the night, and finally drives the rhythmicity of melatonin secretion ( Fig. 36-2 ). 16-18
Which neurohormone increases the output of thyrotropin?
For example, the neurohormone that increases the output of thyrotropin is called thyrotropin-releasing hormone ( TRH ). When a neurohormone lowers the secretion of a particular adenohypophysial hormone, it is termed a release-inhibiting hormone ( RIH ).
What is Hormonal Control?
Hormonal control refers to the secretion of hormones by the endocrine system into the bloodstream from glands throughout the body in order to produce an effect on target organs in the body. A hormone is a chemical substance produced by a gland. They are always transported into different parts of the body through the bloodstream.
What is Neural Control?
Neural control refers to the phenomenon where nerve cells in the nervous system generate electrochemical impulses in order to produce an effect on target organs in the body. Neurons are the building blocks of the communication system of the body. Neurons allow signals to move between the brain and various parts of the body.
What are the Similarities Between Hormonal and Neural Control?
Hormonal and neural control are two mechanisms that are essential for communication in the human body.
What is the Difference Between Hormonal and Neural Control?
Hormonal control is the secretion of hormones by the endocrine system into the bloodstream in order to produce an effect on target organs in the body, while neural control is the generation of nerve impulses by the nerve cells in the nervous system in order to produce an effect on target organs in the body.
Summary – Hormonal vs Neural Control
Communication throughout the human body takes place through two main mechanisms: hormonal and neural control. They are very important for controlling the functions of the human body.
Overview
A neurohormone is any hormone produced and released by neuroendocrine cells (also called neurosecretory cells) into the blood. By definition of being hormones, they are secreted into the circulation for systemic effect, but they can also have a role of neurotransmitter or other roles such as autocrine (self) or paracrine (local) messenger.
The hypothalamus releasing hormones are neurohypophysial hormones in specialized hypothala…
Releasing hormones
Releasing hormones also known as hypophysiotropic or hypothalamic hormones are synthesized by different kinds of specialized neurons in the hypothalamus. They are then transported along neuronal axons to their axon terminals forming the bulk of the median eminence, where they are stored and released into the hypophyseal portal system. They then rapidly reach the anterior pituitary where they exert their hormonal action. The residual hormones pass into the systemic ci…
Neurohypophysial hormones
Neurohypophysial hormones are synthesized in the magnocellular secretory neurons of the hypothalamus. They are then transported along neuronal axons within the infundibular stalk to their axon terminals forming the pars nervosa of the posterior pituitary, where they are stored and released into the systemic circulation. The synthesis, control, and release of those hormones is co-regulated by hormonal, local and synaptic signals. Neurohypophysial hormones include:
Adrenomedullary hormones
Adrenomedullary hormones are catecholamines secreted from the adrenal medulla by chromaffin cells, neurosecretory cells connected to the central nervous system. The synthesis, storage (in chromaffin cells) and release of catecholamines is co-regulated by synaptic input from their respective pre-synaptic sympathetic neurons, as well as hormonal and local inputs. The adrenomedullary hormones are:
Enteric neurohormones
Enterochromaffin cells in the epithelia lining the lumen of the digestive tract secrete serotonin, while enterochromaffin-like cells at the stomach glands secrete histamine. Their synthesis, storage, and release of hormones is co-regulated by hormonal, local and nervous inputs.
See also
• Natural neuroactive substance