
Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Monitoring
- ICP (normal adults < 10 - 15 mm Hg, pediatric patients: Newborn 0.7 - 1.5mm Hg, Infant 1.5 - 6.0 mm Hg, Children 3.0 - 7.5 mmHg.
- Cerebral Perfusion Pressure (CPP) (MAP - ICP; normal 70-100 mm. ...
- Changes in ICP waveform
- Catheter insertion site to include:CSF leakage
What is the normal range of intracranial pressure ICP?
Subsequently, one may also ask, what is the normal intracranial pressure range in adults? A standing adult generally has an ICP of -10 mm Hg but never less than -15 mm Hg. In supine children, ICP is normally lower, in the range of 15 mm Hg, with infants having ICP from 5-10 mm Hg and newborns have subatmospheric pressures regardless of position.
How to treat increased ICP?
What medications are used to treat increased intracranial pressure?
- draining the excess cerebrospinal fluid with a shunt, to reduce pressure on the brain that hydrocephalus has caused.
- medication that reduces brain swelling, such as mannitol and hypertonic saline.
- surgery, less commonly, to remove a small section of the skull and relieve the pressure.
How to lower ICP?
The first-line ICP-lowering strategies that I consider (without a priority between them) include:
- Head-up positioning (15–30°),
- Hemodynamic stability aimed to maintain an appropriate cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP 50–70 mmHg according to autoregulatory status. ...
- Sedation and analgesia (propofol, 4–6 mg/kg/h and opioids, fentanyl 1–4 μg/kg/h used at the lowest dose producing ICP control. ...
How is ICP normally compensated?
How is ICP normally compensated? Compensation typically occurs by displacing or shifting CSF, increasing the absorption of CSF, or decreasing cerebral blood flow. Without these changes, ICP will rise.
What is the ICP of a healthy adult?
In a healthy adult, the ICP is usually in the range of 0 to 10 mmHg, and any pressure greater than 20mmHg is abnormal. When ICP is greater than 40mmHg, there is almost always some neurological dysfunction (impairment of consciousness, problems breathing, pupil dilation, compression of brain found on MRI) as well as impairment ...
Why does ICP shift?
The problem with increased ICP is that the fluid under pressure tends to deform the brain and pushes tissue in such a way as to cause injury to the brain itself. A MRI or CT taken at the emergency room or during follow-up care can often show shifting of the tissue because of the pressure. This is called midline shift. That is a way doctors can tell there is increased pressure, and they can also directly monitor the pressure through the skull.
Why is intracranial pressure important?
Intracranial Pressure (ICP) is a very important way of monitoring the health and outcome of the brain after injury. The brain is encased in a non-flexible cover - the skull. Therefore, if there are changes which result in increased pressure, the fluid that surrounds the brain has nowhere to go.
How long does a barbiturate coma last?
Persons can be put into a barbiturate coma, (also known as a chemically induced coma), to help alleviate the pressure as well. This can last from days to weeks.
Is it necessary to reduce ICP?
Overall, it is essential to take steps to reduce the ICP if it is in the abnormal range. Family members and the relatives who act quickly when requested by the emergency personnel or treating physicians are often blessed with better outcomes. Delays can result in additional damage.
How do you know if you have an ICP?
These are the most common symptoms of an ICP: Headache. Blurred vision. Feeling less alert than usual. Vomiting. Changes in your behavior. Weakness or problems with moving or talking. Lack of energy or sleepiness. The symptoms of ICP may look like other conditions or medical problems.
How is ICP treated?
Increased intracranial pressure is an emergency. Treatment might include:
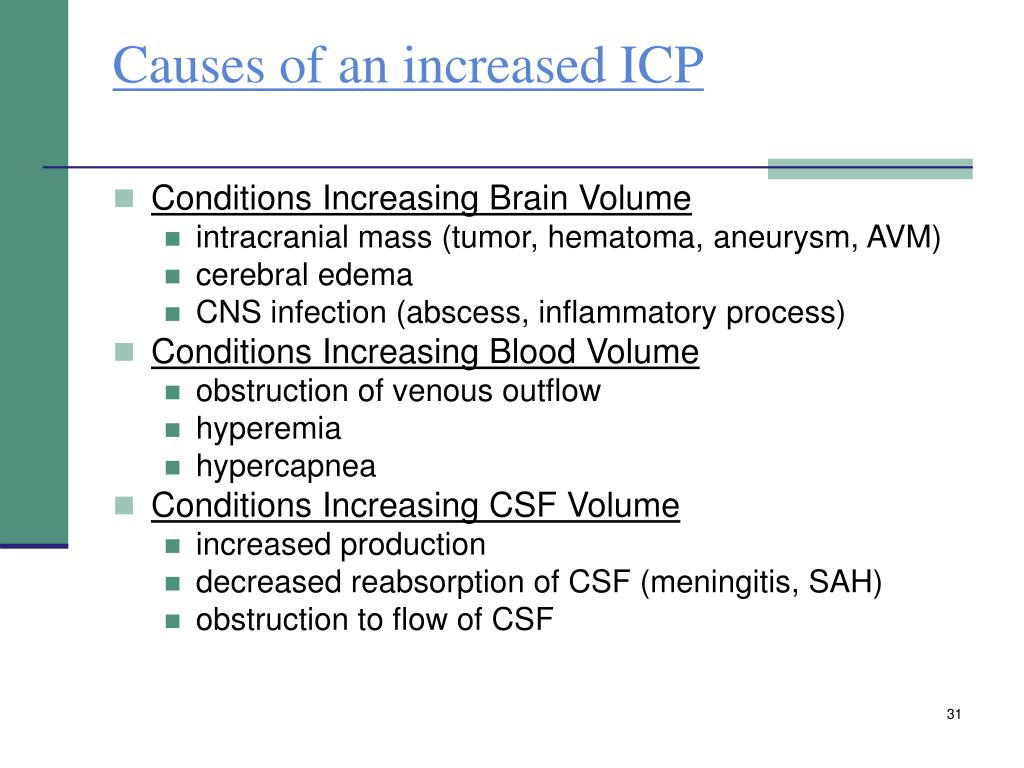
What causes ICP?
Too much cerebrospinal fluid ( the fluid around your brain and spinal cord)
Is intracranial pressure dangerous?
Key points about increased intracranial pressure (ICP) ICP is a dangerous condition. It is an emergency and requires immediate medical attention. Increased intracranial pressure from bleeding in the brain, a tumor, stroke, aneurysm, high blood pressure, brain infection, etc. can cause a headache and other symptoms.
Can ICP be prevented?
You can reduce your risk of certain underlying conditions that may lead to ICP such as high blood pressure, stroke or infection. If you have any of the symptoms, get medical attention immediately.
How many tiers of ICP elevation?
Treatment for ICP elevation can be loosely divided into three rough tiers, depending on how aggressive the treatments are (table below). Please note, however, that this is intended only as a rough cognitive rubric. It will often be appropriate to mix treatments from different tiers.
How does fever affect ICP?
A fever increases ICP by increasing the brain’s metabolic demands and need for arterial blood supply.
Why is noncommunicating hydrocephalus easier to diagnose?
Noncommunicating hydrocephalus is therefore easier to diagnose based on CT scans, because pressure differentials will cause shifts in brain tissue visible on CT.
How to measure optic nerve sheath diameter?
Optic nerve sheath diameter may be measured with ultrasound as shown in the video above.
Is papilledema accurate for ICP elevation?
Papilledema may be less accurate for immediate-onset intracranial hypertension, because it takes some time to develop. Papilledema may be useful for identifying ICP elevation in cases where the nerve sheath is borderline (e.g., between 5-6 mm wide). More on this here.
What is ICP monitoring?
Whilst ICP monitoring is most commonly used for the management of severe head trauma, its use also extends to CSF circulatory disorders, and can be either diagnostic or therapeutic (by removing CSF to reduce pressures).
What is the normal intracranial pressure?
The normal range for intracranial pressure (ICP) is 5 – 15mmHg. The average intracranial volume is 1700ml (composed of the brain 1400ml + CSF 150ml + blood 150ml), with Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) production around 500 – 600ml per day.
What are the different types of ICP monitors?
The three main types of ICP monitor are the External Ventricular Drain (EV D), the Subarachnoid Bolt , and the Epidural bolt (Fig. 2).
How is cerebral perfusion pressure calculated?
The brain can autoregulate blood flow, through cerebral vessel constriction or dilatation, in order to ensure constant flow isolated from fluctuations in systemic blood pressure*; the Cerebral Perfusion Pressure is calculated by Mean Arterial Pressure minus Intracranial Pressure.
What is the purpose of the waveforms produced from ICP monitoring?
The waveforms produced from the ICP monitoring can be used to infer the underlying pathology present. The wave forms produced are summarised in Table 1.
How to measure pressure in a CSF?
Attach the catheter to non-pressurised tubing filled with saline solution and connected to non-flush strain-gauge transducer (this will measure the pressure transmitted from CSF in the ventricles). Level the transducer to zero.
What are the physiological parameters that are measured with a probe?
These probes can often also be used to measure other physiological parameters, including temperature, lactate, and pH.
What is an ICP sensor?
As mentioned above, the 7.3 ICP sensor measures pressure from the oil rail. Over time, all that oil pressure on your ICP pushes and exerts force on the sensor’s internal components and plastic electrical connector housing. A couple hundred thousand miles of that and it’s bound to fail. When it does, the oil will cause bad electrical readings as well as corrode the sensor’s ability to send those signals.
What is 7.3 ICP?
The 7.3 ICP sends the current pressure reading to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) which in turn signals the 7.3 Injection Pressure Regulator (IPR) to add or reduce pressure.
What does it mean when ICP sensor is oily?
If there’s oil on the sensor’s female plug receptacle, its leads, or around the pigtail connector male plug, you’ve got a failed ICP sensor.
How to diagnose a failed ICP sensor?
One quick way to diagnose a failed 7.3 ICP sensor is to lift the plastic clip on the wiring connector and remove the pigtail from the sensor. If there’s oil on the sensor’s plug receptacle, its leads, or around the pigtail connector, you’ve got a failed ICP sensor.
What happens if 7.3 ICP fails?
If, or should I say when, your 7.3 ICP fails, the PCM in your truck won’t know how much pressure’s in the oil rails and it won’t be able to regulate that pressure to efficiently actuate the injectors, resulting in poor engine performance.
How much PSI should I get on 7.3?
With your engine running, pull the connector, disconnect your 7.3 ICP pigtail. This causes the PCM to deliver a default ICP value of 725 PSI at idle. As apposed to the stock setting of 500-550 PSI at idle. There should be a noticeable difference in idle when you unplug your ICP.
Where is the ICP sensor on a 7.3?
Your 7.3 diesel’s ICP sensor is located on the driver’s side cylinder head toward the front of the engine compartment … near the HPOP.
