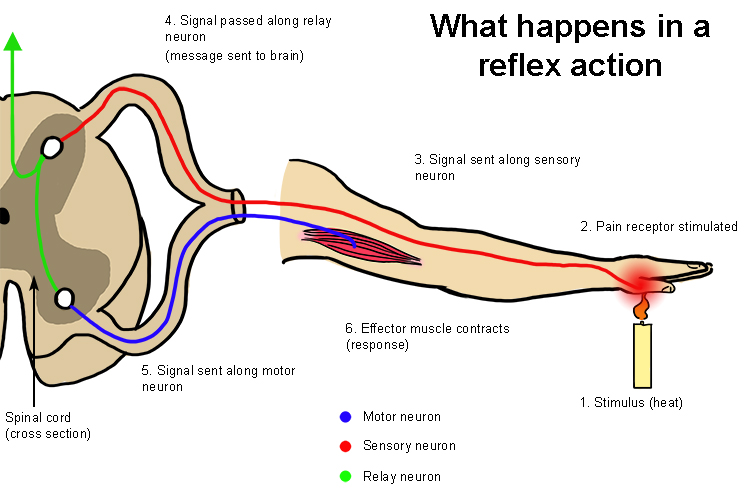
How to document normal reflexes?
- Several different positions of the limb.
- Get the patient to put slight tension on the muscle being tested. ...
- In the upper extremity, have the patient make a fist with one hand while the opposite extremity is being tested.
What is normal reflex grading?
The following are some of the normal reflexes seen in newborn babies :
- Moro reflex
- Sucking reflex (sucks when area around mouth is touched)
- Grasp reflex (Stroking the palm of a baby’s hand causes the baby to close his or her fingers in a grasp)
- Tonic neck reflex (When a baby’s head is turned to one side, the arm on that side stretches out and the opposite arm bends up at the elbow)
What causes increased reflexes?
Other causes of brisk reflexes are associated with neurological conditions, including:
- Hyperthyroidism: This condition can cause too much thyroid hormone to be released in your body. ...
- Anxiety: The adrenaline rushes caused by anxiety can cause your reflexes to be more responsive than normal.
- Lou Gehrig’s disease, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): Brisk reflexes are common with ALS. ...
What is a normal reaction for the patellar reflex?
What is a normal patellar reflex? The patellar reflex occurs when an abrupt change arises in muscle length; in this case, it is produced by the tendon stretching, which is caused when the hammer stroke is applied [3, 4]. The normal response must be a sudden leg extension.

What is a normal reflex score?
2Reflexes are graded on a scale of 0 to 4. A grade of 2 indicates normal reflexes. A grade of 3 indicates hyperreflexia; 4 indicates hyperreflexia with clonus. Decreased relexes are indicated by 1 (hyporeflexia) or 0 (no reflex elicited, even using the Jurassic maneuver.
What is a normal knee reflex?
knee-jerk reflex, also called patellar reflex, sudden kicking movement of the lower leg in response to a sharp tap on the patellar tendon, which lies just below the kneecap.
What are the 4 types of reflexes?
In our discussion we will examine four major reflexes that are integrated within the spinal cord: the stretch reflex, the Golgi tendon reflex, the withdrawal reflex and the crossed extensor reflex.
What is a good example of a reflex?
Reflexes protect your body from things that can harm it. For example, if you put your hand on a hot stove, a reflex causes you to immediately remove your hand before a "Hey, this is hot!" message even gets to your brain.
What is an abnormal reflex?
Definition. Any anomaly of a reflex, i.e., of an automatic response mediated by the nervous system (a reflex does not need the intervention of conscious thought to occur). [ from HPO]
What does it mean if you have no knee reflex?
The normal response is a 'knee jerk'. This is an example of a reflex, which is an involuntary muscular response elicited by the rubber hammer tapping the associated tendon. When reflex responses are absent this could be a clue that the spinal cord, nerve root, peripheral nerve, or muscle has been damaged.
What are some natural reflexes?
The following are some of the normal reflexes seen in newborn babies:Rooting reflex. This reflex starts when the corner of the baby's mouth is stroked or touched. ... Suck reflex. Rooting helps the baby get ready to suck. ... Moro reflex. ... Tonic neck reflex. ... Grasp reflex. ... Stepping reflex.
What are 3 reflexes in humans?
Types of human reflexesBiceps reflex (C5, C6)Brachioradialis reflex (C5, C6, C7)Extensor digitorum reflex (C6, C7)Triceps reflex (C6, C7, C8)Patellar reflex or knee-jerk reflex (L2, L3, L4)Ankle jerk reflex (Achilles reflex) (S1, S2)
What are simple reflexes?
In a two-neuron arc, simple reflexes are prompt, short-lived, and automatic and involve only a part of the body. Examples of simple reflexes are the contraction of a muscle in response to stretching, the blink of the eye when the cornea is touched, and salivation at the sight of food.
What are the 5 types of reflexes?
Both babies and adults may experience the following types of reflexes:Blinking Reflex. This type of reflex happens when the eyes blink due to sudden intense light or when they are touched.Cough Reflex. ... Gag Reflex. ... Sneeze Reflex. ... Yawn Reflex.
What are the 2 types of reflexes?
There are two types: autonomic reflex arc (affecting inner organs) and somatic reflex arc (affecting muscles). Autonomic reflexes sometimes involve the spinal cord and some somatic reflexes are mediated more by the brain than the spinal cord.
How do you check your reflexes?
0:504:12How to Test Reflexes | Merck Manual Professional Version - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTest the triceps reflex with the patient's elbow held suspended in your hand encourage her to letMoreTest the triceps reflex with the patient's elbow held suspended in your hand encourage her to let the arm hang limp palpate the triceps tendon with your thumb and strike your thumb.
What does the knee reflex test show?
The patellar reflex test is performed to determine the integrity of the neurological function, which is accomplished by hitting the patellar tendon below the knee cap with a test hammer [2].
Why do doctors test for the knee-jerk reflex?
Medical author Dr Janice Rachel Mae explains that doctors routinely use reflex tests to check if there are any problems in the nervous system involved in movement, nerve functioning or health of the connective tissue in the knee or leg.
How do I check my knee reflexes?
0:071:01Patellar Reflex Test | Knee Reflex Examination of Deep TendonsYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThis is going to be looking at l2 to l4. And to find the tendon what you want to do is locate theMoreThis is going to be looking at l2 to l4. And to find the tendon what you want to do is locate the kneecap. And then go just a little bit right below it and the best way is to have the patient extend.
Why is knee-jerk reflex important?
0:091:532-Minute Neuroscience: Knee-jerk Reflex - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe knee jerk reflex. Also known as the patellar reflex is a well-known example of a simple reflexMoreThe knee jerk reflex. Also known as the patellar reflex is a well-known example of a simple reflex arc that allows us to maintain posture. And balance.
What is a 3+ reflex?
A finding of 3+, brisk reflexes throughout all extremities is a much less significant finding than that of a person with all 2+, normal reflexes, and a 1+, diminished left ankle reflex suggesting a distinct lesion.
How to observe brachioradialis reflex?
The brachioradialis reflex is observed by striking the brachioradialis tendon directly with the hammer when the patient's arm is resting. Strike the tendon roughly 3 inches above the wrist. Note the reflex supination. Repeat and compare to the other arm.
How to observe pendular reflex?
Pendular reflexes are best observed when the patient's lower legs are allowed to hang and swing freelly off the end of an examining table. The ankle reflex is elicited by holding the relaxed foot with one hand and striking the Achilles tendon with the hammer and noting plantar flexion. Compare to the other foot.
How to do bicep reflex?
The biceps reflex is elicited by placing your thumb on the biceps tendon and striking your thumb with the reflex hammer and observing the arm movement. Repeat and compare with the other arm.
What nerves are involved in the triceps reflex?
The triceps reflex is mediated by the C6 and C7 nerve roots, predominantly by C7. With the lower leg hanging freely off the edge of the bench, the knee jerk is tested by striking the quadriceps tendon directly with the reflex hammer. Repeat and compare to the other leg.
How to test plantar reflex?
The plantar reflex (Babinski) is tested by coarsely running a key or the end of the reflex hammer up the lateral aspect of the foot from heel to big toe. The normal reflex is toe flexion. If the toes extend and separate, this is an abnormal finding called a positive Babinski's sign.
What does a positive Hoffman response mean?
Repeat this manuever multiple times on both hands. A positive Hoffman response is indicative of an upper motor neuron lesion affecting the upper extremity in question.
What does "reflex small" mean?
1: Reflex small, less than normal; includes a trace response or a response brought out only with reinforcement
Why are reflexes used in physical examination?
Several types of reflexes can be tested as part of a physical examination and these all reveal something about the status of the elements of the nervous system that contribute to their functioning . They have been used for over a century as part of a routine neurological examination due to their safety, low cost, predictive value, and ability to be performed rapidly, even without specialized equipment.
What scale is used to grade reflexes?
Reflexes are graded based on amplitude. Various scales have been used to grade reflexes. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) Muscle Stretch Reflex Scale is frequently used and empirically supported[6]:
What is the term for deep tendon reflexes?
This article will focus on the “deep tendon reflexes” which are more appropriately named — and will be referred to herein — as muscle stretch reflexes (MSR).
What are the different types of reflex hammers?
The most commonly used specialized reflex hammers are grouped into 3 types by the shape of the head: triangular/tomahawk shaped (Taylor), T-shaped (Tromner, Buck), or circular (Queen Square, Babinski). Each is effective at provoking reflexes, with the Taylor being possibly less favorable at eliciting more stubborn (hyporeflexia) reflexes. [2]
How to test for bicep reflex?
This may require supporting the distal component of the joint (for instance, when testing the biceps reflex, the elbow will naturally hang limply at nearly 180 degrees of extension but can be supported to approximately 90 degrees while remaining fully relaxed by placing it on the patient’s thigh if seated, or by supporting it in a clinician’s arm). The infant’s heads should be positioned midline when assessing any reflex.
What nerve is the jaw jerk?
The jaw jerk is conceptualized in a similar manner. There is an afferent signal in the form of proprioceptive signals being transmitted along the mandibular nerve to the mesencephalic nucleus of the trigeminal nerve. These pseudounipolar neurons send bilateral projections to the efferent motor neurons (in the motor nuclei of the trigeminal in the pons) which sends the motor impulse out to the masseter muscles to contract on both sides of the jaw. The modulating upper motor neuron innervation comes from the corticobulbar rather than the corticospinal tract.
What is reflex exam?
Reflex Exam (Deep Tendon Reflexes) The reflex exam is fundamental to the neurological exam and important to locating upper versus lower motor neuron lesions. There are five deep tendon reflexes and a number of superficial and visceral reflexes covered here.
Can you evaluate reflexes?
Reflexes are useful for the general internist to perform, but you can’t evaluate them if …. You don’t have a hammer. You don’t use proper technique, in which case the reflex will appear to be absent when it is present. If you don’t know what abnormalities to expect and what they mean.
Is grading reflexes useful?
We are not big believers in grading reflexes ( grading muscle power is much more useful). Nevertheless, if you need something beyond “absent,” “present,” “brisk,” or “hyperactive” then use below. If you have a hyperactive reflex don’t forget to look for clonus.
What reflex is used in neurological examination?
Applying the extensor digitorum reflex to neurological examination.
What does "small reflex" mean?
1: Small reflex, less than normal, or obtained with reinforcement
What is the DTR in neurology?
The DTR is used to assess the integrity of the motor system. They also provide information on the condition of upper and lower motor neurons. The DTR depends on the integrity of both the upper motor neuron and the lower motor neuron. If a patient has an injury or a disease involving a lower motor neuron (nerve roots or peripheral nerves), a decrease or loss of the reflex will be noted. If the lesion or injury involves the upper motor neuron (brain, brainstem, or spinal cord), an increased reflex will be present. In severe chronic cases, usually associated with spasticity, clonus can be seen. It is common in stroke, spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, and multiple sclerosis.[20] It can also occur after ingesting a large amount of serotonergic drugs.
How to perform patellar reflex?
For the tricep reflex, the patient's arm should be held and suspended by the examiner at 90 degrees. Gravitational force is usually sufficient. The patellar reflex is performed with the patient sitting and legs hanging free over the chair's edge. If no visible response occurs, the examiner places his hand over the patient's ipsilateral quadriceps muscle and tries to feel a contraction; the Jendrassik maneuver helps elicit this reflex. The same position is used for the ankle reflex. Tapping the Achilles tendon will elicit a response.
What causes an absent reflex in the ankle?
If the reflex is absent, other findings are usually present secondary to the lower motor neuron disease. They include muscle atrophy, weakness, and sometimes fasciculations. If it is an isolated reflex deficit, it is most commonly the result of a root lesion, a peripheral nerve injury or entrapment, or a mononeuropathy.[21] If several reflexes are involved, peripheral neuropathy is the probable etiology. Bilateral absent ankle jerk usually indicates a peripheral neuropathy, but a cauda equina syndrome can also produce it. [21]
What causes reflexes to decrease?
Decreased reflexes present in lower motor neuron lesions, including nerve root lesions with radiculopathy and peripheral nerve lesions. Diabetes and hypothyroidism slow down the response of the DTR. If absent when initially tested, the response can be elicited with repetitive tapping of the tendon; however, this maneuver sometimes causes extinguishment of the reflex. Muscle disease may cause the reflex to become diminished as the muscle fiber can not respond adequately. A patient with a spinal cord injury presenting spinal shock can have hyporeflexia. Cerebellar disease can also produce hyporeflexia. If the reflexes decrease bilaterally, it is often a normal finding.
What is the role of stretch reflex?
[14][18] It probably plays an important role in maintaining muscle tone and upright posture. The cerebral cortex and possible brainstem nuclei produce influence in the muscle spindle through the gamma motor neurons. [13][15][17][19] Dorsal spinocerebellar tracts carry the information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum.
What is the gag reflex?
The gag reflex is a natural reaction to prevent a person from choking or eating something unpleasant. A gag reflex. Trusted Source. , or pharyngeal reflex, is a normal bodily response. It prevents swallowing by contracting the pharynx. The pharynx.
What is the purpose of gag reflex?
The main purpose of a gag reflex is to contract the throat to prevent a person from choking.
What are the two types of stimuli that trigger gag reflexes?
Two types of stimuli can trigger a gag reflex: somatogenic and psychogenic.
How to desensitize a gag reflex?
A person may desensitize their gag reflex by accustoming the trigger point in their mouth to touch. One technique that a person can try is taking their toothbrush and slowly moving it toward the back of their tongue until they feel close to gagging. They can then brush that area for 15–30 seconds.
How long does it take to stop gag reflex?
It may also take years of physical and mental retraining to stop a gag reflex. However, it is possible that some people have no gag reflex, have a higher threshold to physical trigger points, or are yet to face a sensation extreme enough to cause them to gag.
Does acupuncture help with gag reflex?
A 2015 study suggests that acupuncture may help alleviate a sensitive gag reflex in a short time.
Can physical stimuli be separate events?
Physical and mental stimuli can be separate events or happen at the same time. A person may, therefore, also gag due to certain sights, sounds, and smells .