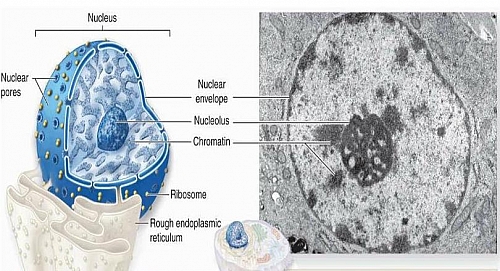
Structure Of Nucleus
- Typically, it is the most evident organelle in the cell.
- The nucleus is completely bound by membranes.
- It is engirdled by a structure referred to as the nuclear envelope.
- The membrane distinguishes the cytoplasm from the contents of the nucleus
- The cell’s chromosomes are also confined within it.
What is a cell nucleus?
Her writing is featured in Kaplan AP Biology 2016. The cell nucleus is a membrane bound structure that contains the cell's hereditary information and controls the cell's growth and reproduction. It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is commonly the most prominent organelle in a cell.
What are the properties of nucleus in biology?
Properties. The nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains the cell’s hereditary information and controls the cell’s growth and reproduction. It is generally the most prominent organelle in the cell. It is surrounded by a structure called the nuclear envelope. This membrane separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm.
What is the shape of the nucleus?
The shape of a nucleus varies from cell to cell but is often depicted as spherical. To understand more about the role of the nucleus, read about the structure and function of each of its parts.
What is the structure of nucleus and chromosomes?
The nucleus is the organelle that houses chromosomes. Chromosomes consist of DNA, which contains heredity information and instructions for cell growth, development, and reproduction. Chromosomes are present in the form of strings of DNA and histones (protein molecules) called chromatin.
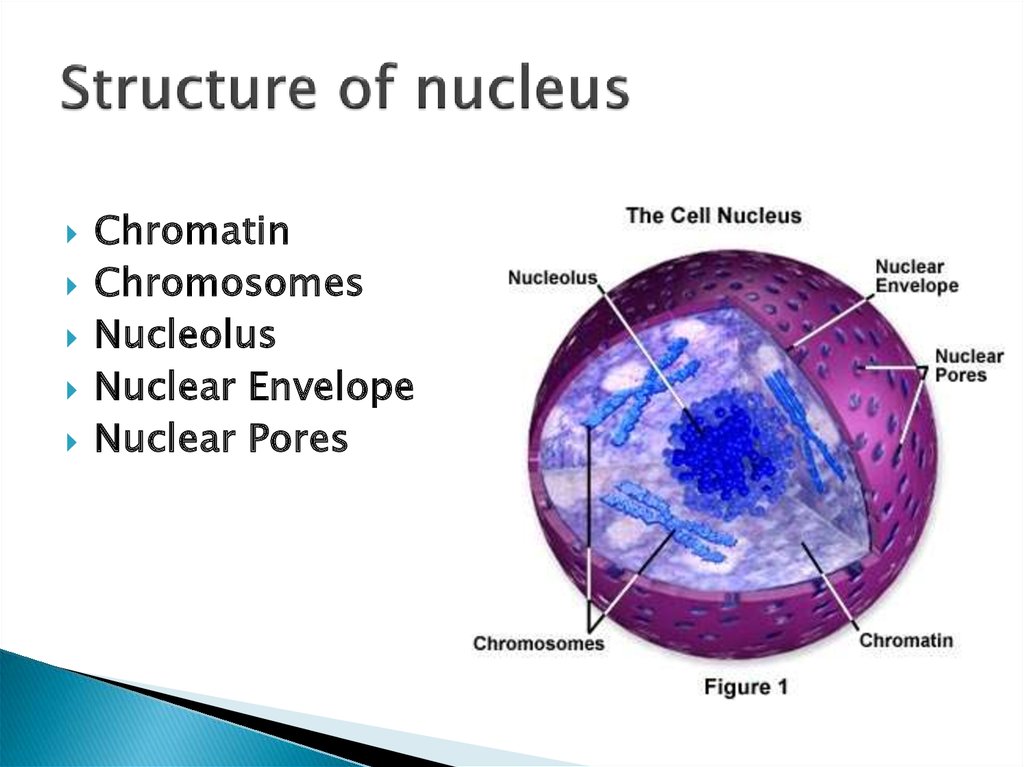
What is nucleus structure and function?
The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains a cell's hereditary information and controls its growth and reproduction. It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is usually the most notable cell organelle in both size and function.
What is the structure of the nucleolus?
The nucleolus is the largest nuclear organelle and is the primary site of ribosome subunit biogenesis in eukaryotic cells. It is assembled around arrays of ribosomal DNA genes, forming specific chromosomal features known as nucleolar organizing regions (NORs) which are the sites of ribosomal DNA transcription.
Is a nucleus a structure or function?
nucleus, in biology, a specialized structure occurring in most cells (except bacteria and blue-green algae) and separated from the rest of the cell by a double layer, the nuclear membrane.
What is nucleus short answer?
A nucleus, as related to genomics, is the membrane-enclosed organelle within a cell that contains the chromosomes. An array of holes, or pores, in the nuclear membrane allows for the selective passage of certain molecules (such as proteins and nucleic acids) into and out of the nucleus.
Why is a nucleolus structure important?
The nucleolus is a spherical structure found in the cell's nucleus whose primary function is to produce and assemble the cell's ribosomes. The nucleolus is also where ribosomal RNA genes are transcribed.
What is main function of nucleolus?
The primary function of the nucleolus is in facilitating ribosome biogenesis, through the processing and assembly of rRNA into preribosomal particles.
What is the characteristics of nucleus?
1)The necleus is located at the center of an atom. 2) Necleus contains positively charged protons and neutrons which is neutral. 3) The electrons of an atom revolves around the nucleus. 4) The charge of nucleus is positive and the numbers of protons present in the nucleus is equals to the charge of necleus.
What are 3 main functions of the nucleus?
The primary functions of the nucleus are to store the cell's DNA, maintain its integrity, and facilitate its transcription and replication.
How are nucleus formed?
The vesicles first fuse to form membranes around individual chromosomes, which then fuse with each other to form a complete single nucleus.
What does the nucleolus look like?
Through the microscope, the nucleolus looks like a large dark spot within the nucleus. A nucleus may contain up to four nucleoli, but within each species the number of nucleoli is fixed. After a cell divides, a nucleolus is formed when chromosomes are brought together into nucleolar organizing regions.
What is function of nucleolus where is it located is it a permanent structure?
The nucleolus is a round body located inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. It is not surrounded by a membrane but sits in the nucleus. The nucleolus makes ribosomal subunits from proteins and ribosomal RNA, also known as rRNA.
What is the structure of nuclear membrane?
The nuclear membrane is comprised of two phospholipid bilayers. The membrane facing the cytoplasm is termed the outer nuclear membrane (ONM), and the membrane facing the nucleoplasm is termed the INM. The ONM continuously connects to the ER, and its surface, like that of the ER, is decorated with ribosomes.
What is the cell nucleus?
Updated November 06, 2019. The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains a cell's hereditary information and controls its growth and reproduction. It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is usually the most notable cell organelle in both size and function.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The key function of the nucleus is to control cell growth and multiplication. This involves regulating gene expression, initiating cellular reproduction, and storing genetic material necessary for all of these tasks. In order for a nucleus to carry out important reproductive roles and other cell activities, it needs proteins and ribosomes.
What is the nucleus membrane?
Nuclear Envelope and Nuclear Pores. The cell nucleus is bound by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. This membrane separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm, the gel-like substance containing all other organelles. The nuclear envelope consists of phospholipids that form a lipid bilayer much like that of the cell membrane.
What is the nucleoplasm?
The nucleolus and chromosomes are surrounded by nucleoplasm, which cushions and protects nuclear contents. Like the nuclear envelope, the nucleoplasm supports the nucleus to hold its shape.
What is the nuclear envelope?
The nuclear envelope consists of phospholipids that form a lipid bilayer much like that of the cell membrane. This lipid bilayer has nuclear pores that allow substances to enter and exit the nucleus, or transfer from the cytoplasm to the nucleoplasm. The nuclear envelope helps to maintain the shape of the nucleus.
What is the name of the structure that houses chromosomes?
Chromatin. The nucleus houses chromosomes containing DNA. DNA holds heredity information and instructions for cell growth, development, and reproduction. When a cell is "resting", or not dividing, its chromosomes are organized into long entangled structures called chromatin .
What is the gelatinous substance within the nuclear envelope?
Nucleoplasm is the gelatinous substance within the nuclear envelope. Also called karyoplasm, this semi-aqueous material is similar to cytoplasm in that it is composed mainly of water with dissolved salts, enzymes, and organic molecules suspended within.
What is the role of the nucleus in the cell?
The nucleus controls and regulates the activities of the cell (e.g., growth and metabolism) and carries the genes, structures that contain the hereditary information. Nucleoli are small bodies often seen within the nucleus. The gel-like matrix in which the nuclear components are suspended is the nucleoplasm.
Which organelle contains the genetic information necessary for cell growth and reproduction?
One major organelle, the nucleus, contains the genetic information necessary for cell growth and reproduction. Each cell contains only one nucleus, whereas other types of organelles are present in multiple copies in the cellular contents, or cytoplasm. Organelles include mitochondria, which are responsible for the energy transactions necessary for…
What is the name of the molecule that encodes the information for one protein?
Information in DNA is transcribed, or copied, into a range of messenger ribonucleic acid ( mRNA) molecules, each of which encodes the information for one protein (in some instances more than one protein, such as in bacteria).
Where is mRNA translated?
The mRNA molecules are then transported through the nuclear envelope into the cytoplasm, where they are translated, serving as templates for the synthesis of specific proteins. For more information on these processes, see transcription; translation. Britannica Quiz. Parts of a Cell Quiz.
Do cells have nuclei?
A cell normally contains only one nucleus. Under some conditions, however, the nucleus divides but the cytoplasm does not. This produces a multinucleate cell ( syncytium) such as occurs in skeletal muscle fibres. Some cells—e.g., the human red blood cell —lose their nuclei upon maturation. See also cell.
What is the structure of the nucleus?
The nucleus is a cell organelle which is spherical and is present in all the eukaryotic cells. Nucleus is referred to as the control centre of the eukaryotic cells. It also helps in the coordination of both the genes and the gene expression.
What is the nucleus responsible for?
Nucleus is responsible for the hereditary characteristics of organisms. It is also responsible for the synthesis of protein, cell division, growth and cell differentiation. The nucleolus stores proteins and RNA. Transcription takes place in the nucleus wherein the messenger RNA is produced for the synthesis of proteins.
What is the role of the nucleolus in eukaryotic cells?
The nucleolus has an implied or indirect role in the synthesis of protein by producing ribosomes.
What is the outer layer of the nuclear membrane?
The outer layer of the nuclear membrane is joined with the endoplasmic reticulum of the cell. A liquid-filled space, also called the perinuclear space occurs between the two layers of the nuclear membrane.
How does the nucleus get into the cytoplasm?
The nucleus gets through the cytoplasm or the remaining of the cell via openings known as nuclear pores. These nuclear pores are responsible for the exchange of the larger molecules between the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
What is the nucleoplasm?
Nucleoplasm is also known as karyoplasm and is referred to as the matrix which is present inside the cell nucleus. The nuclear membrane differentiates the nuclear constituents from the cytoplasm. Just as the cell membrane, the nuclear envelope contains phospholipids which tend to form a lipid bilayer. The envelope helps in maintaining the shape of ...
What is the function of the nucleus envelope?
The envelope helps in maintaining the shape of the nucleus of the cell and also assisting in the coordination of the flow of the molecules that go into and out of the nucleus via the nuclear pores. The nucleus of the cell consists of DNA which controls the form, growth, and function of the cell. The nucleus can be compared to ...
Why do we need a nuclear envelope?
A nuclear envelope encloses the nucleus to keep it separate from surrounding materials in the cell. Sometimes substances need to move into or out of the nucleus, and this is possible because there are little holes in the nuclear envelope called nuclear pores. Inside the nucleus is at least one dark-colored mass called a nucleolus. DNA occupies most of the rest of the space inside a nucleus. DNA is genetic material that has the instructions necessary to build proteins. Proteins are responsible for helping with most activities in a cell.
What is mRNA in biology?
mRNA is messenger RNA. It carries instructions for making a protein.
What is DNA replication?
DNA replication is a process of duplicating or doubling a cell's genetic material. DNA replication must occur before a cell can reproduce.
What is the process of using DNA in a gene to make a product, such as a protein?
Gene expression is the process of using the DNA in a gene to make a product, such as a protein. Every cell in your body has the same genes, but only some are used to make proteins. Only these genes are considered to be expressed, or turned on. It is these active genes that give a cell its specific function and shape.
What is the control center of the brain?
The brain is your body's control center. The nucleus is a cell's control center. The nucleus oversees many processes that occur inside a cell. Let's take a look at some of them more closely.
How many genes are in DNA?
Your DNA is organized into about 20,000 genes, basically instruction manuals for our bodies. Without all of these genes, your body would not be able to make proteins. Proteins are absolutely necessary to make sure everything in your body is working properly. The nucleus helps protect your very important DNA. More specifically, the nuclear envelope keeps your genes separate from the other structures inside a cell.
What is the structure of a nucleus?
The structure of a nucleus encompasses the nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, chromosomes, and nucleolus.
What is Nucleus?
The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains the cell’s hereditary information and controls the cell’s growth and reproduction.
What is the space between the nucleus and the cytoplasm?
Such nuclear pores are the sites for the exchange of large molecules (proteins and RNA) between the nucleus and cytoplasm. A fluid-filled space or perinuclear space is present between the two layers of a nuclear membrane.
How many nuclei does an eukaryotic cell have?
In general, a eukaryotic cell has only one nucleus. However, some eukaryotic cells are enucleated cells (without a nucleus), for example, red blood cells (RBCs); whereas, some are multinucleate (consists of two or more nuclei), for example, slime molds. The nucleus is separated from the rest of the cell or the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane.
What is the outer layer of the cell membrane?
The outer layer of the membrane is connected to the endoplasmic reticulum. Like the cell membrane, the nuclear envelope consists of phospholipids that form a lipid bilayer. The envelope helps to maintain the shape of the nucleus and assists in regulating the flow of molecules into and out of the nucleus through nuclear pores.
What is the control center of a cell?
As the nucleus regulates the integrity of genes and gene expression , it is also referred to as the control center of a cell.
What is the structure of a chromosome?
Chromosomes are present in the form of strings of DNA and histones (protein molecules) called chromatin. When a cell is “resting” i.e. not dividing, the chromosomes are organized into long entangled structures called chromatin.
What is the nucleus?
The nucleus is a membrane bound organelle found in the majority of eukaryotic cells. It is the largest organelle of the eukaryotic cell, accounting for around 10% of its volume. It houses the genome, and through gene expression, it co-ordinates the activities of the cell.
What is the nucleus envelope?
The nucleus is completely surrounded by the nuclear envelope. This consists of both an inner and outer membrane which run parallel to each other. The envelope is perforated by small gaps known as the nuclear pores. These pores are around 100nm wide in true diameter, however due to the presence of central regulatory proteins the true size of the gap is around 9nm.
What is cell compartmentalization?
Cell compartmentalisation: The presence of a selectively permeable nuclear envelope separates the contents of the nucleus from that of the cytoplasm.
What is the chromatin of DNA?
Chromatin describes DNA that is complexed with proteins. The primary protein components of chromatin are histones, which are highly basic proteins that associate readily with DNA. Histones combined with DNA form nucleosomes, which are the subunit of chromatin. Specifically, a nucleosome describes a segment of DNA associated with 8 histone proteins. By associating with histones, DNA is more compact and able to fit into the nucleus.
What is the function of the nuclear envelope?
Larger molecules such as larger proteins and nucleic acid are unable to pass through these pores, and so the function of the nuclear envelope is to selectively separate the contents of the nucleus from that of the cytoplasm.
What is the mechanical support for the nucleus?
Mechanical support for the nucleus is provided by the nuclear lamina. This is a protein mesh, which is more organised on the internal surface on the nucleus than on the cytoplasmic surface.
Is the nucleus a membrane-bound organelle?
The nucleus is a relatively large and spherical membrane-bound organelle. The nucleus itself is comprised of distinct components, and understanding their structure allows a deeper understanding of their function.