What does a particle diagram mean?
Particle Diagrams. • Elements and compounds can be represented using particle diagrams, which is a box in which colored balls are draw to represent atoms or molecules. • These diagrams can represent elements and compounds, as well as their molecular composition by the types of balls and how they are connected.
How to draw particle diagrams?
How to Draw a Particle Diagram - Liquids
- Particles fill up from the bottom of the container
- Each particle is touching at least one other particle
- Spaces between particles too small to fit another particle
- Particles form 'bridges' over gaps by leaning on other particles
- Arranged so particles cannot be squashed into a tighter space
- All particles same size
- No overlapping
What are some examples of particle physics?
- Atoms, about a billion times smaller in radius than your head, are made from electrons and atomic nuclei.
- Atoms can absorb and emit particles of light, called photons . ...
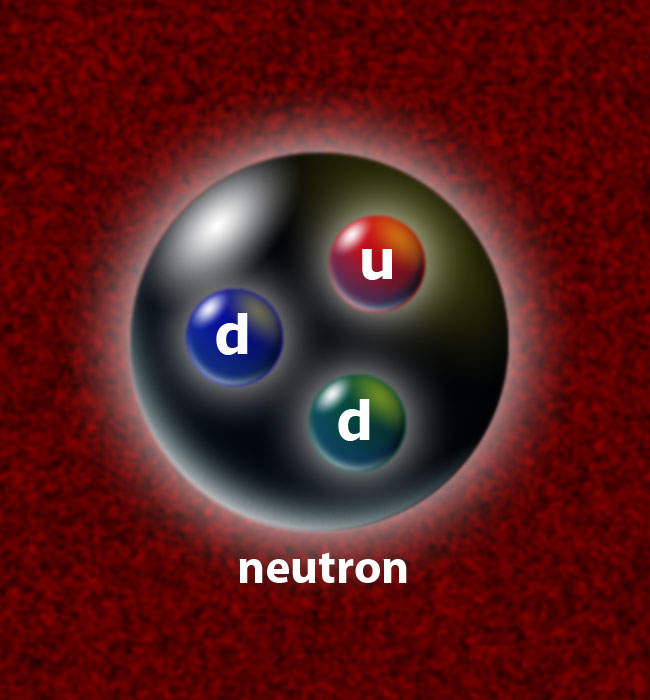
- Atomic nuclei are made from protons and neutrons, 100,000 times smaller in radius than an atom, and made from mostly up and down quarks (and anti-quarks) and gluons.
What is speed of a particle?
The speed of a particle is the distance covered by the particle per unit time. V (t)=frac {d s} {d t} V (t) = dtds Overview of Speed Of A Particle The determination of the speed of a particle is basically considered to be the most important application of derivates, in our day-to-day life.

How do you read particle diagrams?
0:132:54Rules for Drawing Particle Diagrams - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWhen we draw particle diagrams we need to show distinct countable particles we're going to relateMoreWhen we draw particle diagrams we need to show distinct countable particles we're going to relate the number of particles to the mass so if you have more particles you have more mass therefore.
What are the major components of a particle diagram?
The four main principles of the particle diagram are: Particles make up all substances. The particles are drawn to one another (some strongly, others weakly). The particles are in motion (have kinetic energy).
What does a compound particle diagram look like?
0:033:23U1:L11 Drawing Particle Diagrams - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipA particle diagram is a visual representation of the particles of a substance. With a width theMoreA particle diagram is a visual representation of the particles of a substance. With a width the particles typically represented as dots in biology class they talk a lot about diffusion.
What does the particle diagram left represent?
Each of the particle diagrams represents a chemical reaction. The left-hand side of the arrow represents the reactants, and the right-hand side of the arrow represents the products.
Why is a particle diagram important?
These diagrams can represent elements and compounds, as well as their molecular composition by the types of balls and how they are connected. Particle diagrams can represent pure substances or mixtures. The crystalline solid has a fixed shape and volume, as well as a regular repeating pattern of atoms.
What are the 4 main ideas of the particle model?
Understand the macroscopic evidence for each of the four basic principles of the particle model of matter:Matter is made of tiny particles.There is empty space between the particles.The particles are in constant motion.There are forces that act between the particles.
What do you mean by particles?
Definition of particle 1a : a minute quantity or fragment. b : a relatively small or the smallest discrete portion or amount of something. 2 archaic : a clause or article of a composition or document. 3 : any of the basic units of matter and energy (such as a molecule, atom, proton, electron, or photon)
What do the circles represent in a particle diagram?
Each circle represents a different type of particle or atom.
What is the particle theory?
The kinetic theory of matter (particle theory) says that all matter consists of many, very small particles which are constantly moving or in a continual state of motion. The degree to which the particles move is determined by the amount of energy they have and their relationship to other particles.
What are the five main points of the particle theory?
The postulates of the particle theory of matter are given as:All matter is made up of tiny particles known as atoms.Particles of matter are constantly in motion.Particles of matter attract each other.Particles of matter have spaces between them.As temperature increases, particles of matter move faster.More items...
What are the particle of matter?
Matter on Earth is in the form of solid, liquid, or gas. Solids, liquids, and gases are made of tiny particles called atoms and molecules.
What is the particle theory of matter Grade 7?
Science Background Particle Theory of Matter. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. All matter is made up of many small. particles called atoms, and they are in a continual state of motion.
What are three examples of compounds?
Water, carbon dioxide and table salt are some examples of compounds.
What is element particle?
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a subatomic particle that is not composed of other particles.
What are examples of pure elements?
Pure Element ExamplesHydrogen (H) - nonmetal.Helium (He) - nonmetal.Oxygen (O) - nonmetal.Neon (Ne) - nonmetal.Nitrogen (N) - nonmetal.Carbon (C) - reactive nonmetal.Silicon (Si) - metalloid.Magnesium (Mg) - alkaline earth metal.More items...
What is air element or compound?
Air is a mixture and not a compound because of the following reasons: Air can be separated into its constituents such as oxygen, nitrogen etc. by fractional distillation of liquid air. Air shows the properties of all the gases present in it.
What are particles attracted to?
The particles are attracted to each other (some strongly, others weakly).
What is Plasma?
Plasma is the most abundant state of matter in the universe - and yet I barely teach it to my pupils. Plasma is almost always badly defined - often as a high energy gas. This would be like defining a solid as a super-low energy gas!
What Happens to Particles at Absolute Zero?
Temperature is merely a scaled measure of this. If you cool particles enough you can get to a theoretical temperature at which the particles stop moving - this is Absolute Zero: 0 Kelvin or -273.15°C - the coldest possible temperature.
How are solids, liquids and gases related?
The properties of solids, liquids and gases are related to how their particles are arranged and how they move about. This table summarises the properties of each state and links to their particle behaviour
Can particles be compressed?
Cannot be compressed - no space for the particles to be pushed together
