
Is diffusion an example of active or passive transport?
Osmosis, diffusion and facilitated diffusion are some of the examples of passive transport. Active transport requires energy for the movement of molecules whereas passive transport does not require energy for the movement of molecules.
What does passive diffusion require?
The name passive indicates that there is no energy requirement for the substance to move, laws of entropy dictate that transfer continues even if the cell is no longer metabolically active. No ATP is consumed, no gradients created. Passive diffusion never saturates, the higher the concentration difference the faster it will proceed. Increase the concentration and it continues.
What are the five types of diffusion?
Types of Diffusion:
- Self-Diffusion: Self-diffusion is the migration of atoms in pure materials. ...
- Inter-Diffusion: It occurs in binary metallic alloys. Observed in binary metal alloys such as Cu-Ni system.
- Volume Diffusion: Volume diffusion means atomic migration through the bulk of the material.
How is diffusion related to passive transport?
Diffusion is an example of passive transport by which gases like carbon dioxide and oxygen and solutes in a solution get transported. Molecules move from where they are plentiful (higher concentration) to where they are less in amount (lower concentration).
What is passive processes?
Diffusion is a passive process which means it does not require energy. Small particles diffuse faster than large ones. Eg substances like oxygen, carbon dioxide and glucose move in and out of cells by diffusion. The greater the difference in concentration, the faster the rate of diffusion.
What is an example of a passive process?
Diffusion. Diffusion is a passive process of transport. A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across the space. You are familiar with diffusion of substances through the air.
What is passive diffusion example?
Passive diffusion across the membrane continues until concentrations are identical on both sides. When the concentrations reverse, so does the direction of transport. An example is the movement of gas into and out of blood in pulmonary and systemic circulation.
What does passive process mean in biology?
Passive transport is a naturally occurring phenomenon and does not require the cell to expend energy to accomplish the movement. In passive transport, substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration in a process called diffusion.
What is the difference between passive and active diffusion?
There are two major ways that molecules can be moved across a membrane, and the distinction has to do with whether or not cell energy is used. Passive mechanisms like diffusion use no energy, while active transport requires energy to get done.
What are the types of passive diffusion?
There are four major types of passive transport are (1) simple diffusion, (2) facilitated diffusion, (3) filtration, and (4) osmosis. Simple and facilitated diffusions refer to the net movement of molecules from higher to lower concentrations.
Why is it called passive diffusion?
Without other outside forces at work, substances will move or diffuse from a more concentrated environment to a less concentrated environment. No work is performed for this to happen. Diffusion is a spontaneous process. This process is called passive transport.
What are 3 examples of passive transport?
There are three main types of passive transport: Simple diffusion – movement of small or lipophilic molecules (e.g. O2, CO2, etc.) Osmosis – movement of water molecules (dependent on solute concentrations) Facilitated diffusion – movement of large or charged molecules via membrane proteins (e.g. ions, sucrose, etc.)
How does simple passive diffusion work?
The simplest mechanism by which molecules can cross the plasma membrane is passive diffusion. During passive diffusion, a molecule simply dissolves in the phospholipid bilayer, diffuses across it, and then dissolves in the aqueous solution at the other side of the membrane.
Is diffusion an active or a passive process?
Diffusion is a passive process of transport. A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across the space.
What is the difference between active and passive process?
Active transport requires energy for the movement of molecules whereas passive transport does not require energy for the movement of molecules. In active transport, the molecules move against the concentration gradient whereas in passive transport, the molecules move along the concentration gradient.
What does active and passive process mean?
Active transport moves materials from lower to a higher concentration, while passive transport moves materials from higher to lower concentration. Active transport requires energy to proceed, while passive transport does not require the input of extra energy to occur.
What are 3 examples of passive transport?
There are three main types of passive transport: Simple diffusion – movement of small or lipophilic molecules (e.g. O2, CO2, etc.) Osmosis – movement of water molecules (dependent on solute concentrations) Facilitated diffusion – movement of large or charged molecules via membrane proteins (e.g. ions, sucrose, etc.)
What is 2 examples of a passive sentence?
In a passive sentence, the person or thing doing the action (the agent) is usually preceded by the word "by." For example: Anita was driven to the theatre by Carla. Nowadays, black kites are protected by law. The olives are stoned and crushed in this room by my son.
What are the 3 passive transport processes?
We covered three methods of passive transport: diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis, all of which are important for cellular functions. While the exact mechanisms driving each of these transport methods are different, they are united in the fact that they do not require energy.
What is passive and active example?
For example: Active voice: The cat was chasing the mouse. In this sentence, 'the cat' is the subject, 'was chasing' is the verb and 'the mouse' is the object. Passive voice: The mouse was being chased by the cat.
What is passive diffusion?
Passive diffusion is the simplest, unregulated method for a substance to cross the membrane. Substances of the right size and chemical class (small, non-polar, uncharged particles) pass through the membrane unassisted by taking advantage of imperfect nature of the phospholipid bilayer.
What factors influence passive diffusion?
Factors influencing passive diffusion. In passive diffusion, the only method of transport without membrane proteins, the flow rate depends on several factors. First, the higher the concentration difference the greater the flow, the relationship is directly proportional. If you want more substance to enter the cell, ...
Why is the phospholipid bilayer a natural divider between intracellular and extracellular fluids?
Because of its highly organized structure, with fatty acid chains of phospholipids pointing inward and alcohol heads pointing outwards , the phospholipid bilayer is a natural divider between intracellular and extracellular fluids.
How does passive diffusion affect the structure of a bilayer?
The number and localization of “kinks” in fatty acids impact diffusion by altering membrane topology. More double bonds being present and located closer to glycerol end of phospholipids (closer to the surface) create more space, and as a whole, the membrane is more loosely held together or less rigid so to speak. This is a positive situation when it comes to passive diffusion. That should explain the importance of polyunsaturated fatty acids in our diets.
How do chemotherapy drugs cross the membrane?
Certain drugs such as chemotherapy drugs must cross the membrane in order to work. The most efficient way to accomplish this is by engineering them as membrane diffusible molecules. Most of the chemotherapy drugs of natural origin or developed are small hydrophobic molecules. We can mention that a cell has defensive mechanisms to clear them out of the cells – ABC type pumps, discussed in a later chapter.
How does CO2 move through the blood barrier?
Carbon dioxide, more concentrated in the tissues drifts into blood, through membranes of capillary endothelium, until it reaches equilibrium with CO2 diluted in blood. In pulmonary circulation, the concentration gradient reverses and CO2 drifts to the air in alveoli where the concentration is lower. Despite very small differences in concentration driving the exchange, as there is always some CO2 on both sides of the barrier, it is quite efficient.
How does oxygen exchange work?
Similarly, oxygen exchange is assisted by oxygen binding to hemoglobin and continuous increase of “driving” gradient in the pulmonary circulation. In systemic circulation higher affinity of myoglobin for oxygen, or simply oxygen use in metabolic reactions, keep the flow going.
How does diffusion work?
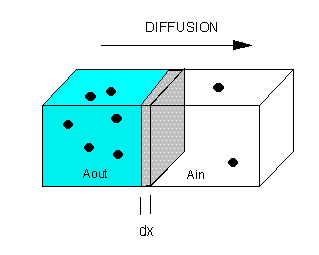
Diffusion is a passive process of transport. A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across the space. You are familiar with diffusion of substances through the air. For example, think about someone opening a bottle of perfume in a room filled with people. The perfume is at its highest concentration in the bottle and is at its lowest at the edges of the room. The perfume vapor will diffuse, or spread away, from the bottle, and gradually, more and more people will smell the perfume as it spreads. Materials move within the cell’s cytosol by diffusion, and certain materials move through the plasma membrane by diffusion ( Figure 1 ). Diffusion expends no energy. Rather the different concentrations of materials in different areas are a form of potential energy, and diffusion is the dissipation of that potential energy as materials move down their concentration gradients, from high to low.
Why does diffusion slow down as the density of a solvent increases?
The molecules slow down because they have a more difficult time getting through the denser medium.
Why do molecules diffuse more slowly?
Mass of the molecules diffusing: More massive molecules move more slowly, because it is more difficult for them to move between the molecules of the substance they are moving through; therefore, they diffuse more slowly.
What is the most direct form of membrane transport?
The most direct forms of membrane transport are passive. Passive transport is a naturally occurring phenomenon and does not require the cell to expend energy to accomplish the movement. In passive transport, substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration in a process called diffusion.
Does diffusion expend energy?
Diffusion expends no energy. Rather the different concentrations of materials in different areas are a form of potential energy, and diffusion is the dissipation of that potential energy as materials move down their concentration gradients, from high to low.
Does each substance diffuse according to the concentration gradient?
Each separate substance in a medium, such as the extracellular fluid, has its own concentration gradient, independent of the concentration gradients of other materials. Additionally, each substance will diffuse according to that gradient.
What is passive diffusion?
Passive diffusion is the transport of a molecule across a lipid bilayer membrane according to its electrochemical potential gradient without the assistance of additional transporter molecules. This process can be studied in pure lipid membranes, although it is acknowledged that the properties of even relatively pure lipid patches in native membranes are altered by the high density of neighboring protein molecules. The physical and functional properties of membranes can be modeled with varying levels of detail and mathematical complexity. The simplest model represents the membrane as a single semipermeable barrier separating two uniform aqueous compartments. Transport is characterized by a single reversible rate constant. A more complex model represents the membrane as an intervening third compartment of 25-30 A thickness with properties equivalent to a bulk organic solvent. Transport is modeled as a reversible partition of molecules from the donor aqueous phase into the membrane compartment and rate-limiting release of the solute from the organic membrane phase into the receiving compartment. This model yields a rate equation of the same form as the Michaelis-Menten equation in enzyme kinetics. Although such kinetics are observed for mediated membrane transport, they are not typically observed for simple diffusive transport. A more sophisticated model adds barriers of high charge density and high dielectric constant on either side of the organic compartment to represent the phospholipid head groups. Still other models may incorporate unstirred diffusion layers extending into the aqueous compartments. These models reveal different points of view about what constitutes the most important rate-determining barrier to bulk transport.
What are the simulations of the membrane bilayer?
Molecular dynamics simulations (12, 13) have provided a provocative image of passive diffusion of solute molecules within the membrane bilayer (Figure 14.2). These simulations illustrate the rapid but restricted mobility of the lipid side chains, and demonstrate that the membrane hydrophobic region is not particularly well modeled by bulk solvent properties. They suggest the spontaneous formation of voids and transient channels within the membrane and the ability of small molecules and ions to diffuse within the membrane by hopping among these voids (~8-A jumps on a 5-psec time scale).
What is the process of diffuse?
No work is performed for this to happen. Diffusion is a spontaneous process. This process is called passive transport.
What is passive transport?
Passive transport is the diffusion of substances across a membrane. This is a spontaneous process and cellular energy is not expended. Molecules will move from where the substance is more concentrated to where it is less concentrated. "This cartoon illustrates passive diffusion. The dashed line is intended to indicate a membrane ...
What molecules can't pass through the phospholipid bilayer?
Some molecules and ions such as glucose, sodium ions, and chloride ions are unable to pass through the phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes. Through the use of ion channel proteins and carrier proteins that are embedded in the cell membrane, these substances can be transported into the cell .
What type of transport allows molecules to cross membranes?
In other cases, the protein changes shape, allowing molecules to pass through. Mariana Ruiz Villarreal. Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that allows substances to cross membranes with the assistance of special transport proteins.
What affects the rate of diffusion of different substances?
Although the process is spontaneous, the rate of diffusion of different substances is affected by membrane permeability. Since cell membranes are selectively permeable (only some substances can pass), different molecules will have different rates of diffusion.
What is diffusion in science?
Diffusion is the tendency of molecules to spread into an available space. This tendency is a result of the intrinsic thermal energy (heat) found in all molecules at temperatures above absolute zero. A simplified way to understand this concept is to imagine a crowded subway train in New York City. At rush hour most want to get to work ...
How do ion channels work?
The ion channels are regulated by the cell and are either open or closed to control the passage of substances into the cell. Carrier proteins bind to specific molecules, change shape, and then deposit the molecules across the membrane. Once the transaction is complete the proteins return to their original position.
What is passive transport?
Passive transport, also known as passive diffusion, is a process by which an ion or molecule passes through a cell wall via a concentration gradient, or from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. It’s like moving from the train to the platform of a subway station, or stepping out of a crowded room.
What is the difference between passive and active transport?
Like physical activity, active transport requires energy. Passive transport, on the other hand, needs no energy at all.
Why can ethanol molecules perform simple diffusion?
C is correct. Ethanol molecules can perform simple diffusion because they are smaller than most membranes. The process would take longer if they were larger, and would make the effects of alcohol far less intense.
Why do neurons need passive transport?
The fact that neurons – or brain cells – rely on passive transport to communicate is easy to miss, partly because of how complicated we make them out to be. Crazily enough, the spindly web of synapses ( brain activity) in our head relies on two ions, sodium (Na +) and potassium (K + ), which work along a gradient.
Why is the large intestine not active transport?
A is correct. The large intestine performs filtration, because it removes vitamins and minerals (in liquid form) from solid waste. It cannot be active transport because it does not require energy. It is neither osmosis nor facilitated diffusion because it relies on neither equilibrium nor integral proteins. 3.
Why does water pass through raisin?
Water passes through the raisin’s membrane not only to reach a less-concentrated interior, but also to make the grape “equal” to its outside environment. This process can happen with other fruits and vegetables, as well, as long as the produce has undergone some form of dehydration.
Which term refers to the tendency of a fluid to pass through a membrane into a solution where the solvent?
Osmosis – The tendency of a fluid to pass through a membrane into a solution where the solvent concentration is higher, thus equalizing the concentrations of materials on either side of the membrane. Ion – An electrically-charged atom or group of atoms.
What is Diffusion?
Diffusion is the process of movement of molecules under a concentration gradient. It is an important process occurring in all living beings. Diffusion helps in the movement of substances in and out of the cells. The molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration until the concentration becomes equal throughout.
What is diffusion in science?
Causes of Diffusion. Diffusion is a natural and physical process, which happens on its own, without stirring or shaking the solutions. Liquid and gases undergo diffusion as the molecules are able to move randomly. The molecules collide with each other and change the direction.
What is facilitated diffusion?
Facilitated diffusion is a passive movement of molecules across the cell membrane from the region of higher concentration to the region of lower concentration by means of a carrier molecule.
What is the process of moving a substance through a semipermeable membrane?
A process in which the substance moves through a semipermeable membrane or in a solution without any help from transport proteins. For example, bacteria deliver small nutrients, water and oxygen into the cytoplasm through simple diffusion.
What is the role of diffusion in life?
In all living species, diffusion plays an important role in the movement of the molecules during the metabolic process in the cells.
Which type of membrane allows only specific ions and molecules to pass through?
A selectively permeable membrane is the one that allows only specific ions and molecules to pass through, while it obstructs the movement of others. Osmosis: It is the movement of solvent molecules from the region of lower concentration to the region of higher concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
What are the factors that affect the rate and extent of diffusion?
These factors include: Temperature. Area of Interaction. Size of the Particle. The steepness of the concentration gradient.
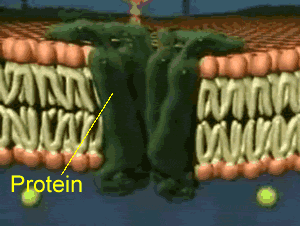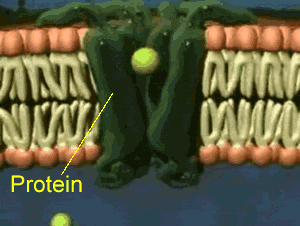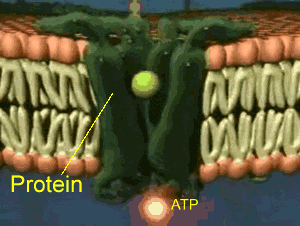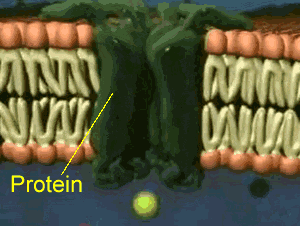
How Is Diffusion Passive?
- In passive transport mechanisms, any kind of energy or ATP molecules from a cell is not required for the movement of substances across the plasma membrane. In the diffusion process, substances to be transported move from their higher concentration zone to the lower concentration zone means according to their concentration gradient until the concentration of t…
Is Facilitated Diffusion A Passive Transport?
- The facilitated diffusion process is a type of diffusion process in which molecules move across the plasma membrane with the help of channel proteins embedded within the cell membrane. With the concern to the question is facilitated diffusion a passive transport or not? The answer is yes, The facilitated diffusion process is a passive diffusion transport mechanism. It means in thi…
Why Is Facilitated Diffusion A Passive Transport?
- The facilitated diffusion process is a passive transport mechanism which transports water or polar molecules across the plasma membrane. The facilitated diffusion process is a passive mode of transportation because in this process any kind of energy through cellular ATP hydrolysis is not required for the movement of substances across the plasma mem...
Is Simple Diffusion Passive Or Active Transport?
- Simple diffusion is a kind of diffusion process in which molecules move from their higher concentration zone to lower concentration zone according to their concentration gradient without requiring any help from other molecules. With the concern to the question is simple diffusion process passive or active transport mechanisms? The answer is that a simple diffusion proces…
Why Is Simple Diffusion Passive Or Active Transport?
- The simple diffusion process is a typical passive transportmechanism within the cell. Just like any other passive transport mechanism, the simple diffusion process does not require any energy or ATP molecules from the surrounding environment for the movement of the substances. The concentration gradient or chemical gradient influences the molecules to move from their higher …
Conclusion
- As a whole, we can say that the diffusion process is a very efficient cellular transport mechanism which moves molecules according to their concentration gradient. Here we try to find out the answer to the question: is diffusion passive or not? We also mention some most common facts related to the diffusionprocess. Hope this article on whether diffusion is passive or not will be he…