What is the pelvic inlet called?
Anatomical terms of bone. [edit on Wikidata] The pelvic inlet or superior aperture of the pelvis is a planar surface which defines the boundary between the pelvic cavity and the abdominal cavity (or, according to some authors, between two parts of the pelvic cavity, called lesser pelvis and greater pelvis).
What is the junction between the greater and lesser pelvis called?
The junction between the greater and lesser pelvis is known as the pelvic inlet. The outer bony edges of the pelvic inlet are called the pelvic brim. Fig 2 – The greater and lesser pelvis. The lesser pelvis is the ‘true’ pelvis, and contains the pelvic cavity.
What is the pelvic brim of the pelvis?
The pelvic inlet is delineated by a bone crest that defines its limit (the pelvic brim), which later refers to the promontory of the sacrum.
What are the borders of the pelvic outlet?
Pelvic Outlet. The pelvic outlet is located at the end of the lesser pelvis, and the beginning of the pelvic wall. Its borders are: Posterior: The tip of the coccyx. Lateral: The ischial tuberosities and the inferior margin of the sacrotuberous ligament. Anterior: The pubic arch (the inferior border of the ischiopubic rami).
What is an inlet in biology?
: the upper opening of a bodily cavity especially : that of the cavity of the true pelvis bounded by the pelvic brim.
Does the pelvic inlet contain organs?
The pelvic cavity primarily contains the reproductive organs, urinary bladder, distal ureters, proximal urethra, terminal sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal.
Is the pelvic inlet the true pelvis?
The true pelvis contains the pelvic inlet and is a short, curved canal, deeper on its posterior than on its anterior wall. The true pelvis contains the pelvic colon, rectum, bladder, and some of the reproductive organs.
What is the difference between pelvic inlet and pelvic outlet?
The pelvic inlet is oval being widest transversely, the pelvic mid-cavity is circular, while the outlet is oval being widest anteroposteriorly.
What makes up pelvic inlet?
The pelvic inlet involves three of the four units of which the bone pelvis is composed. The pelvic brim involves the first sacral segment, the iliac and pubis portion, but not the ischium.
What organs are behind the pelvis?
The space below contains the bladder, rectum, and part of the descending colon. In females, the pelvis also houses the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
How do I open my pelvic inlet?
0:050:39Opening the Top of Your Pelvis During Labor (Inlet Opening) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo posterior pelvic tilt so tucking the button her need is gonna help open it more front to back andMoreSo posterior pelvic tilt so tucking the button her need is gonna help open it more front to back and then external rotation the femur. So knees wide. It's gonna open it more side to side.
What passes through the pelvic inlet?
As the fetus moves through the birth canal, the widest diameter of the pelvic canal changes direction from a transverse direction in the pelvic inlet, to an anteroposterior diameter in the pelvic outlet. For this reason, the fetal head must rotate as it passes through the birth canal during labor.
What are the 3 diameters of the pelvic inlet?
Antero -posterior diameters: Anatomical antero-posterior diameter (true conjugate) = 11cm. from the tip of the sacral promontory to the upper border of the symphysis pubis. ... Transverse diameters: Anatomical transverse diameter =13cm. ... (C) Oblique diameters: Right oblique diameter =12 cm.
What is the shape of the female pelvic inlet?
This results in the female inlet being large and oval in shape, while the male inlet is more heart shaped. The angle between the inferior pubic rami is acute (70 degrees) in men, but obtuse (90–100 degrees) in women. Accordingly, the angle is called the subpubic angle in men and pubic arch in women.
What bones form the pelvic inlet?
It consists of three bones; ilium, ischium and pubis. These three bones are also known as the innominate bones, pelvic bones or coxal bones.
What is pelvic outlet obstruction?
Pelvic outlet obstruction, also referred to as paradoxical puborectalis contraction , obstructive defecation , anismus , or pelvic floor dyssynergia , occurs when the puborectalis muscle fails to relax (“nonrelaxation”) or contracts further during attempted defecation.
What passes through the pelvic inlet?
As the fetus moves through the birth canal, the widest diameter of the pelvic canal changes direction from a transverse direction in the pelvic inlet, to an anteroposterior diameter in the pelvic outlet. For this reason, the fetal head must rotate as it passes through the birth canal during labor.
Which organ is not found in the pelvic cavity?
Lungs are not found in the abdominopelvic cavity. The lungs are contained in the thoracic cavity together with the heart, thymus gland, and part of the trachea and esophagus. Each of the lungs is enclosed by a membrane that creates a fluid-filled space called the pleural cavity.
What are the 3 diameters of the pelvic inlet?
Antero -posterior diameters: Anatomical antero-posterior diameter (true conjugate) = 11cm. from the tip of the sacral promontory to the upper border of the symphysis pubis. ... Transverse diameters: Anatomical transverse diameter =13cm. ... (C) Oblique diameters: Right oblique diameter =12 cm.
What region of the pelvis contains the organs of the inferior abdominal cavity?
Hypogastric. The hypogastric region (below the stomach) contains the organs around the pubic bone. These include bladder, part of the sigmoid colon, the anus, and many organs of the reproductive system, such as the uterus and ovaries in females and the prostate in males.
What is the position of the pelvic brim?
The pelvic brim is an approximately apple-shaped line passing through the prominence of the sacrum, the arcuate and pectineal lines, and the upper margin of the pubic symphysis . Occasionally, the terms pelvic inlet and pelvic ...
Where are the diameters of the pelvis measured?
The diameters or conjugates of the pelvis are measured at the pelvic inlet and outlet and as oblique diameters.
What is the diameter of the pubic symphysis?
Extends from the upper margin of the pubic symphysis to the sacrococcygeal joint; about 110 mm. Transverse diameter. Extends across the greatest width of the superior aperture, from the middle of the brim on one side to the same point on the opposite; about 135 mm. Oblique diameter.
What does "inlet" mean in medical terms?
inlet. [ in´let] a means or route of entrance. pelvic inlet the upper limit of the pelvis minor; called also pelvic brim and superior aperture of pelvis. Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
What is the apertura pelvis superior?
apertura pelvis superior, pelvic brim Anatomy The upper opening of the minor pelvis, bounded by the crest and pecten of pubic bones, ilia arcuate lines, and anterior sacrum. Cf Pelvic outlet.
Which crest is bounded anteriorly by the pubic symphysis?
the upper opening of the true pelvis, bounded anteriorly by the pubic symphysis and the pubic crest on either side, laterally by the iliopectineal lines, and posteriorly by the promontory of the sacrum.
What is the pelvic inlet?
Introduction. The pelvic inlet, or the upper pelvic narrow, is the anatomical limit between the true pelvis below and the false pelvis above. There are tangible, genetic, and hormonal differences between the male and female pelvis related to reproductive function. In obstetrics, the pelvic inlet is the entrance door toward the birth canal.
What is the shape of the inlet?
The shape of the inlet depends on the general shape of the pelvis, according to the traditional classification of Caldwell and Moloy.[1] The dimensions of its anteroposterior, oblique, and transverse diameters vary according to the morphological type of the pelvis. The proportions of the shape of the internal pelvic spaces correspond to the proportion of the sacral area of Michaelis.
How long does it take for a pelvic ring to form?
The connections and articulations of the cartilage in the pelvis are essential for pelvic ring formation in a limited period: between 54 to 60 days after fertilization, at around eight weeks embryonic period, or 10 weeks gestation.
Where does the sigma go in the pelvis?
Sometimes even the cecum and the appendix descend into the pelvis from the right iliac fossa, near the right sacroiliac joint.
Where is the iliac bone?
Looking at the internal face of the iliac bone, one can see that the arched line ends behind the anterior angle that separates the upper and lower portions of the auricular surface, which is articulated with the sacrum. Tracing an imaginary line that continues posteriorly, the pelvic brim continues towards the posterior superior iliac spine after passing through the inferior iliac tuberosity. In this way, by analogy, the pubic tubercle and the pubic symphysis space are the anterior junction bridge of the two half parts of the pelvic inlet, while the superior posterior iliac spine (SIPS) and the space between the iliac (sacroiliac joints, and anterior and posterior ligaments) are the extremes of the posterior bridge.
Which structure most closely runs along the pelvic edge of the pelvic brim?
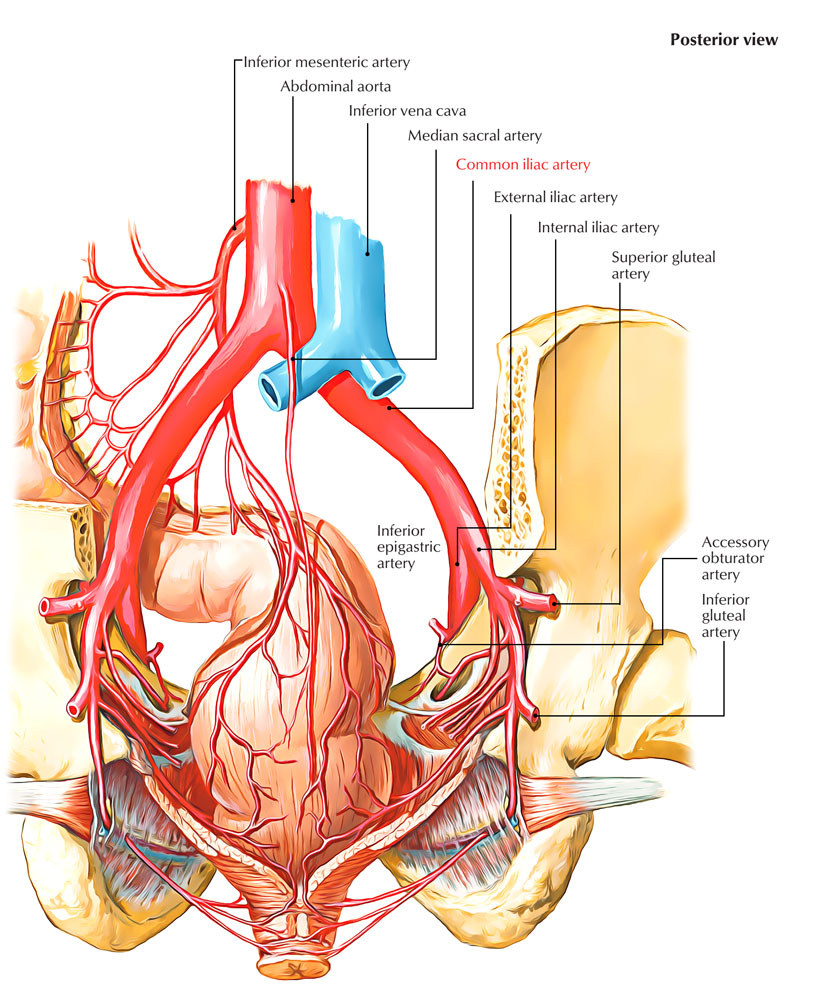
The structure that most closely runs along the pelvic edge of the pelvic brim seems to be the residual of the umbilical artery located above the obstructive vascular-nervous bundle in contact with the osseous-ligamentous plane of the pelvic inlet. The middle sacral artery originates from the abdominal aorta in the angle formed by the emergence of the common iliac arteries, then passes over the sacral promontory to descend to the coccyx. The retropubic branch of the epigastric artery (a branch of the external iliac artery) bypasses the pelvic brim in its anterior hemicycle.
How often does pelvic morphology change?
It seems that the pelvic morphology changes every two decades due to a form of re-modeling, general bone reshaping.[16] . For women, the pelvic form, which has the largest internal diameters, is present between 20 and 40 years: the age of sexual maturity and pregnancy with lower risk.
Where is the pelvic girdle located?
The Pelvic Girdle. The pelvic girdle is a ring-like bony structure, located in the lower part of the trunk. It connects the axial skeleton to the lower limbs. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the pelvic girdle – its bony landmarks, functions, and its clinical relevance.
Which pelvis is the true pelvis?
Fig 2 – The greater and lesser pelvis. The lesser pelvis is the ‘true’ pelvis and contains the pelvic cavity.
What is the boundary between the greater pelvis and the lesser pelvis?
The pelvic inlet marks the boundary between the greater pelvis and lesser pelvis. Its size is defined by its edge, the pelvic brim. The borders of the pelvic inlet: Posterior - sacral promontory (the superior portion of the sacrum) and sacral wings (ala).
What are the bones of the pelvic girdle?
Structure of the Pelvic Girdle. The bony pelvis consists of the two hip bones (also known as innominate or pelvic bones), the sacrum and the coccyx. Sacrococcygeal symphysis – between the sacrum and the coccyx. Pubic symphysis – between the pubis bodies of the two hip bones.
What is the term for the joint between the pubis and hip bones?
Pubic symphysis - between the pubis bodies of the two hip bones.
What is the iliopectineal line?
Iliopectineal line – the combined arcuate and pectineal lines. This represents the lateral border of the pelvic inlet.
What is a false pelvis?
Greater pelvis (false pelvis) – located superiorly, it provides support of the lower abdominal viscera (such as the ileum and sigmoid colon). It has little obstetric relevance.
What is the pelvic inlet?
During vaginal childbirth, the baby passes through the birth canal, which runs through your pelvic cavity. The pelvic inlet is at beginning of the birth canal. The four different pelvis shapes are: Gynecoid. This is the most common type of pelvis in females and is generally considered to be the typical female pelvis.
What is the function of the pelvic area?
It has several important functions, including: supporting the weight of your upper body. acting as a connection point for your lower limbs, as well as various muscles. helping you stand, walk, or run. protecting the organs located in or around the pelvic area.
Why is it so hard to give birth with a platypelloid pelvis?
Platypelloid. The shape of the platypelloid pelvis can make a vaginal birth difficult because the baby may have trouble passing through the pelvic inlet. Many pregnant women with a platypelloid pelvis need to have a C-section.
Why does my pubis hurt?
It’s often caused by repeated stress to the area through activities like playing sports. Pelvic fractures. This is when there’s a break in one of the bones of your pelvis.
What to do if you are pregnant and have concerns about pelvis shape?
If you’re pregnant or planning to become pregnant and have concerns about how your pelvis shape might affect childbirth, speak with your doctor. They can examine your pelvis to help get an idea of how it’s structured.
Why is labor so difficult with an Android pelvis?
The narrower shape of the android pelvis can make labor difficult because the baby might move more slowly through the birth canal. Some pregnant women with an android pelvis may require a C-section. Anthropoid. The elongated shape of the anthropoid pelvis makes it roomier from front to back than the android pelvis.
What are some examples of health conditions that can affect your pelvis?
Several health conditions can affect your pelvis and the surrounding muscles. Some examples include: Pelvic floor dysfunction. This is when the muscles of your pelvic floor have trouble coordinating to help you go to the bathroom. It can lead to incontinence and pain in your pelvis or lower back.