A retroperitoneal abscess is a collection of pus in this retroperitoneal space. It can develop due to spread of an infection from adjacent organs or an infection of the blood as is seen with other types of intra-abdominal abscesses ( abscess in the abdomen ).
What are the symptoms of a peritoneal abscess?
These comprise:
- Difficulty in swallowing food, drink and saliva
- Intense pain while chewing food, along with being incapable of opening the mouth wide
- Fever and chills
- Rough and raspy voice, like in sore throat
- Headaches, alongside swollen regions in the face and neck
What causes intestinal abscess?
The causes of the development of an abscess are considered:
- The spread of infection. Pathology occurs as a result of a direct (contact) transition of the infectious process from adjacent areas, as a result of perforation, penetration of a duodenal ...
- Postoperative complications. ...
- Remote foci. ...
What causes abscess on your gums?
What’s Causing This Bump on My Gums?
- Cyst. A cyst is a small bubble filled with air, liquid, or other soft materials. ...
- Abscess. An abscess on the gums is called a periodontal abscess. ...
- Canker sore. Canker sores are small mouth ulcers that can form at the base of the gums. ...
- Fibroma. ...
- Pyogenic granuloma. ...
- Mandibular torus. ...
- Oral cancer. ...
What is the pathophysiology of abdominal abscess?
The pathophysiology of an abscess is a series of immune responses beginning with the migration of white blood cells to the infection and the separation of a fluid-filled cavity from the surrounding, healthy tissue. Some abscesses result from blocked ducts in glands, while others are caused by infected injuries, frequently by the bacterium ...

Where is a retroperitoneal abscess?
Retroperitoneal abscesses usually locate in the ilio-psoas compartment and can have varied etiologies ranging from acute spinal osteomyelitis, to Crohn disease or hematogenous spread. These abscesses will require CT guidance for drainage because of the deep location.
How do you treat retroperitoneal abscess?
Conclusion: If there is clinical evidence for a retroperitoneal abscess, sonography generally leads to further diagnostic via computed tomography. Small abscesses may be treated by antibiotics alone. Abscesses larger than 3 cm and those not responding to medical treatment should be percutaneously or surgically drained.
What is retroperitoneal infection?
Retroperitoneal infection is a secondary infection caused by inflammation, injury, or perforation of organs adjacent to the retroperitoneum. It spreads easily, is persistent, and is often misdiagnosed. Early diagnosis and active treatment considerably improve its prognosis.
What is retroperitoneal drainage?
Retroperitoneal abscesses are uncommon and are usually caused by gastrointestinal, urinary tract and, rarely, musculoskeletal infections. 1,2. The conventional treatment described is an open surgical drainage via a retroperitoneal approach with an incision on the flank.
How do you treat an intraabdominal abscess?
An intra-abdominal abscess often will need to be drained of fluid in order to heal. Typically, however, antibiotics are given along with draining the abscess. The type of antibiotic will depend on how severe your abscess is, your age, and any other conditions you may have.
Where is the retroperitoneal space?
The retroperitoneum is an anatomical space located behind the abdominal or peritoneal cavity. Abdominal organs that are not suspended by the mesentery and lie between the abdominal wall and parietal peritoneum are said to lie within the retroperitoneum. Several individual spaces make up the retroperitoneum.
What is the most common cause of retroperitoneal abscess?
Retroperitoneal abscess (RA) is an uncommon disease that is mainly caused by perinephric inflammation, infections of the gastrointestinal tract, and postoperative complications [1]. Patients usually have comorbidities, such as diabetes mellitus, malignancy, and renal failure.
How serious is retroperitoneal?
Retroperitoneal inflammation is a serious condition that can have life-threatening consequences. Serious complications can arise when inflammation affects the organs in your abdomen, such as your abdominal aorta. This is the large blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood to the lower half of your body.
How long can you live with retroperitoneal?
Approximately 10–20% of these cases are derived from the retroperitoneum with a prevalence of ∼0.3–0.4 cases/100,000 inhabitants [3]. The prognosis for patients with retroperitoneal sarcomas (RPS) is relatively poor with a 36–58% 5-year overall survival (OS) and a natural history characterized by late recurrences [4].
What does the word retroperitoneal mean?
(REH-troh-PAYR-ih-toh-NEE-ul) Having to do with the area outside or behind the peritoneum (the tissue that lines the abdominal wall and covers most of the organs in the abdomen).
What organs are in the retroperitoneal area?
The retroperitoneal space contains the kidneys, adrenal glands, pancreas, nerve roots, lymph nodes, abdominal aorta, and inferior vena cava.
What is the treatment of retroperitoneal cyst?
Treatment of choice is, complete excision with, if necessary, the resection of a portion of the adherent bowel. Marsupialization and partial excision of the cyst are less satisfactory procedures. Retroperitoneal cyst can be excised by using a transperitoneal flank approach.
What is the difference between peritoneal and retroperitoneal?
Peritoneal Cavity: That part of the abdomen surrounded by peritoneum. It is a potential space between the parietal and visceral layers of peritoneum. Retroperitoneal Space: The area behind (posterior to) the peritoneum. Retroperitoneal organs are located in this space.
What causes retroperitoneal fluid?
Retroperitoneal fluid may be caused by hemorrhage or leakage of urine from the kidneys or ureters (Figure 2-6, N). Gas or air from a pneumomediastinum is occasionally seen outlining structures in this region.
How serious is an abdominal abscess?
An untreated abdominal abscess can be life threatening. In some cases it may grow, causing damage to nearby organs and blood vessels. Bacteria can also enter the bloodstream, spreading to other organs and tissues. This spread can be fatal.
How long does it take to heal from an abdominal abscess?
Your abscess will be treated with antibiotics, drainage of the pus, or both. At first, you will likely receive care in the hospital. You will be given antibiotics to treat the abscess. You will take them for up to 4 to 6 weeks.
Can abscess be treated without surgery?
Unlike other infections, antibiotics alone will not usually cure an abscess. In general an abscess must open and drain in order for it to improve. Sometimes draining occurs on its own, but generally it must be opened with the help of a warm compress or by a doctor in a procedure called incision and drainage (I&D).
Why are kidneys called retroperitoneal?
The kidneys are considered “retroperitoneal” organs, which means they sit behind a lining in the abdominal cavity, unlike all other abdominal organs.
What is a retroperitoneal cyst?
Retroperitoneal cystic teratomas are cystic tumors composed of well-differentiated derivations from at least two of the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm). Most patients are female, and the tumor is commonly diagnosed in newborns, who are usually asymptomatic (,6).
What part of the colon is retroperitoneal?
The ascending colon, descending colon, rectum, and anal canal are retroperitoneal structures.
How long can you live with retroperitoneal?
Approximately 10–20% of these cases are derived from the retroperitoneum with a prevalence of ∼0.3–0.4 cases/100,000 inhabitants [3]. The prognosis for patients with retroperitoneal sarcomas (RPS) is relatively poor with a 36–58% 5-year overall survival (OS) and a natural history characterized by late recurrences [4].
What is the treatment of retroperitoneal cyst?
Treatment of choice is, complete excision with, if necessary, the resection of a portion of the adherent bowel. Marsupialization and partial excision of the cyst are less satisfactory procedures. Retroperitoneal cyst can be excised by using a transperitoneal flank approach.
How is retroperitoneal mass treated?
Complete surgical resection is the only potential curative treatment modality for retroperitoneal sarcomas and is best performed in high-volume centres by a multidisciplinary sarcoma team. Local recurrence occurs in a large proportion of patients.
Is retroperitoneal mass curable?
For patients with retroperitoneal sarcoma, surgery is still the only chance for cure. However, these are not straightforward operations at all. Because of their large size and the limited space in the rest of the abdomen, these tumors often touch, compress, displace or outright invade major organs and blood vessels.
What is retroperitoneal abscess?
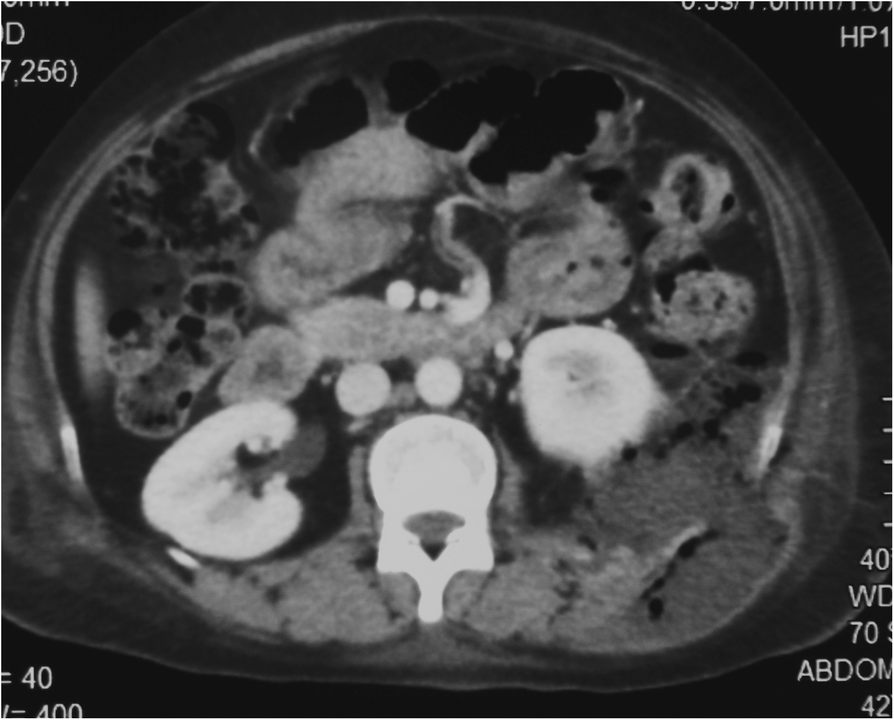
Retroperitoneal abscess is an unusual type of abscess in surgical practice. It is often underdiagnosed due to the insidious onset of symptoms and its location in the retroperitoneal space making it hard to be assessed via the regular abdominal examination. It is most often due to Genitourinary infection ( Pyelonephritis) or gastrointestinal cause (i.e Inflammatory Bowel Syndrome ). CT & MRI are the cornerstones for diagnosis . Treatment is usually focused on surgical drainage either through open or percutaneous approaches usually accompanied with the use of IV antibiotics .
When was retroperitoneal abscess first described?
Retroperitoneal abscess was first described by Grassi and Serge in 1887.
What happens if you get an abscess and it shrinks?
If the body defenses are successful in eliminating the infection, the granulation tissue continues to grow and the abscess continues to shrink in size until it is only a scar.
What are the risk factors for a retroperitoneal abscess?
Any condition compromising the immune system is a risk factor for developing retroperitoneal abscess. The following were the risk factors in observed patients.
Why is abdominal pain not localized?
Abdominal pain : Not localized due to the unusual site of the abscess.
Is a retroperitoneal abscess secondary or primary?
A retroperitoneal abscess is usually secondary to spread from other primary site either through hematogenous or by contiguous spread.
Can a septic focus cause a retroperitoneal abscess?
Any septic focus can theoretically lead to retroperitoneal abscess. These are the primary foci in order of frequency of causing retroperitoneal abscess.
What causes a retroperitoneal abscess?
Other causes of abscesses in the retroperitoneum include traumatic duodenal injury and IPAs.
Where is a retroperitoneal abscess located?
Retroperitoneal Abscess. Retroperitoneal abscesses usually locate in the ilio-psoas compartment and can have varied etiologies ranging from acute spinal osteomyelitis, to Crohn disease or hematogenous spread. These abscesses will require CT guidance for drainage because of the deep location.
Why do you need CT guidance for abscesses?
These abscesses will require CT guidance for drainage because of the deep location. If the abscess involves the psoas muscle in the abdomen and the iliacus in the pelvis, it is often sufficient to place a catheter in the iliacus muscle as there is extensive communications between the iliacus and psoas muscles.
What factors should be considered when deciding the best approach for the management of retroperitoneal abscesses?
These include time since injury, clinical presentation and hemodynamic stability of the patient, as well as concurrent injuries or illnesses.
What is renal abscess?
Renal abscess or infected renal cyst that fails to improve with broad-spectrum antibiotics or a large infected renal or retroperitoneal fluid collection that requires drainage.
What causes an epidural abscess in the lumbar region?
Hematogenous spread from other sites of infection (e.g., skin, soft tissue, bone, respiratory or urinary tract) is the major source of spinal epidural abscess. Direct extension from local osteomyelitis or retropharyngeal, retroperitoneal, or abdominal abscess can also occur. 70a Spinal fracture, 100 penetrating injury, spinal surgery, and local invasive procedure (e.g., lumbar puncture, steroid injection, 101 epidural analgesia 102) have been identified as possible causes. Other mechanisms include: complication of meningitis, fistula in Crohn disease, 103 midline neuroectodermal defects (e.g., dermal sinus), and intradural tumors (e.g., lipoma). In almost one-third of reported cases, the pathogenesis is unknown.
What is the most common site of osteomyelitis in Crohn's disease?
The iliac bone and sacrum are the most frequent sites of osteomyelitis in patients with Crohn's disease. They are almost invariably the result of an adjacent pelvic abscess or enteric fistula. Accordingly, osteomyelitis is usually diagnosed on cross-sectional imaging when the abscess is identified. CT findings in osteomyelitis include cortical bone destruction, intraosseous gas, increased attenuation of the bone marrow, narrowing of the medullary cavity, serpentine drainage tracts, and the presence of an involucrum or sequestrum. On MRI, the marrow space of the involved bone demonstrates decreased signal on T1-weighted images and increased signal on T2-weighted images. Cortical destruction or thickening and edema or abscess formation in the soft tissues can also be demonstrated on MRI.
What is the best treatment for retroperitoneal abscess?
Several factors should be considered when deciding the best approach for the management of retroperitoneal abscesses resulting from duodenal pathology. These include time since injury, clinical presentation and hemodynamic stability of the patient, as well as concurrent injuries or illnesses. Any approach should accomplish drainage of the retroperitoneal abscess cavity and address the primary pathology of the duodenum.34–36 Possible surgical approaches include primary repair and drainage with or without pyloric exclusion versus a more aggressive approach of a pancreaticoduodenectomy. Successful percutaneous drainage also has been reported. 35 Nutritional support is important as enteral feeding will be precluded in the postoperative period. 34,36
What is renal abscess?
Renal abscess or infected renal cyst that fails to improve with broad-spectrum antibiotics or a large infected renal or retroperitoneal fluid collection that requires drainage.
How to treat psoas abscess?
Psoas abscesses are managed by drainage and antibiotic therapy. Except in the case of a known prior infection, empiric antibiotic therapy should cover S. aureus, the most common etiologic agent. Drainage has been accomplished by percutaneous US-guided aspiration or catheter drainage. 46,47 Retroperitoneoscopy and open operative approaches have been used when percutaneous drainage is not successful.
Can percutaneous abscess drainage cure renal abscesses?
Percutaneous abscess drainage can be expected to cure approximately 72% of renal and related retroperitoneal abscesses. This is a significant improvement compared to the results of surgical drainage and is due to the use of cross-sectional imaging techniques for evaluation, which allows the diagnosis of abscesses earlier in their development; needle aspiration to confirm the nature of a fluid collection; and also the efficacy of percutaneous drainage techniques.
What is a spontaneous retroperitoneal abscess?
Spontaneous retroperitoneal abscess as the first clinical manifestation of a non-functioning retroperitoneal paraganglioma.
Where is an abscess located?
An abscess located between the peritoneum and the posterior abdominal wall. It may arise from an abscess in the kidney or from the spread of an intraperitoneal infection posteriorly. See also: abscess. Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners.
What is the term for inflammation of the retroperitoneum?
Retroperitoneal inflammation is also known as retroperitonitis.
What causes retroperitoneal inflammation?
Retroperitoneal inflammation can happen when harmful bacteria come in contact with the organs in the retroperitoneal space or the lining that encloses your abdominal cavity . Possible causes of retroperitoneal inflammation include:
What is the space between the intestines and the back?
In less complicated terms, it’s the space in your abdomen between your abdominal cavity (the area where your intestines are) and your back. It houses several major organs, including: kidneys. bladder. abdominal aorta. adrenal glands. Inflammation often happens in response to an infection.
What tests are done to check for retroperitoneal space?
Your doctor will assess your symptoms. Then they will typically order an ultrasound, abdominal X-ray, CT scan, or MRI. These imaging tests will help reveal any abnormalities in the retroperitoneal space. This will allow your doctor to assess your condition.
How do antibiotics help with infection?
Antibiotics can help prevent inflammation caused by infection . The type of antibiotic prescribed and the length of your treatment will depend on the severity of the infection and the suspected bacteria.
What can cause bacteria to enter the retroperitoneal space?
A ruptured appendix, stomach ulcers, or a perforated colon can allow bacteria into your retroperitoneal space .
Is retroperitoneal space a serious condition?
It has a high mortality rate. However, early diagnosis and treatment can improve your outlook. The retroperitoneal space is the space between your peritoneum and your posterior abdominal wall.

Overview
Historical Perspective
- Retroperitoneal abscess was first described by Grassi and Serge in 1887.
- Dr. Hugh Cabbot presented the first case of retroperitoneal abscess in a case report in 1922.
Classification
- Retroperitoneal abscess may be classified according to the location in the retroperitoneal space into 5 categories : 1. Perinephricabscess 2. Upper retroperitonealabscess 3. Pelvicabscess 4. Combined retroperitoneal and pelvicabscess 5. Lٍٍocalized musculoskeletalabscess
Pathophysiology
- Pathogenesis
1. A retroperitoneal abscess is usually secondary to spread from other primary site either through hematogenous or by contiguous spread. 2. The bacteria causing the abscess depends on the primary site. When the bacteria invades the retroperitoneal tissue, toxins released from it destro… - Microscopic findings
1. The Abscess consists of a mixture of inflammatory cellstogether with debris tissue. 2. From the surrounding wall grows some capillaries to form granulation tissue. 3. If the body defenses are successful in eliminating the infection, the granulation tissue continues to grow and the absces…
Causes
- Retroperitoneal Abscess may be caused by : 1. E. Coli or Proteus spp (if the primary site is the urinary tract) 2. Multibacterial & anaerobes(if gastrointestinal tract (GIT) is the primary source) 3. Staphylococcus aureus (if from distant septic focus) 4. Tuberculosis (if secondary to Pott’s disease)
Epidemiology and Demographics
- Retroperitoneal abscess is far less common than intraperitoneal abscesses. 1. Males are slightly more susceptible than females. 2. Increased incidence between third and sixth decades. 3. Most common cause in developing countries is spread from distant septic focus. 4. Most common causes in developed countries are Renal and GIcauses.
Risk Factors
- Any septic focus can theoretically lead to retroperitoneal abscess. These are the primary foci in order of frequency of causing retroperitoneal abscess. 1. Renalinfections: 1. Spread from the urinary tract is the most common cause. 1. Gastrointestinaldiseases: 1. Spread from the gastrointestinal tract is the second common cause (e.g. perforated appendix, perforated colon c…
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
- Natural history
If left untreated, retroperitoneal abscess may cause septicemia with very high incidence of morbidity and mortality. - Complications :
Most complications result from septicemiawhich presents late in the disease. 1. Pneumonia and respiratory failure type 1 is the most common complication with very high mortality. 2. Recurrent Abscessafter drainage. 3. Renal Failure 4. DVT 5. Small Bowel Obstruction 6. Arterial Thrombosi…
Diagnosis
- History
1. A detailed history should be obtained from the patient presenting with insidious onset of abdominal pain. 2. Common causes should be investigated (Kidney and gastrointestinal diseases) especially in the presence of any of the risk factors (e.g. DM and corticosteroidadministration). - Symptoms [1]:
Given that the presentation is usually insidious, nonspecific beside that it’s an unusual condition .. the diagnosis is usually delayed.
Physical Exam
- General Appearance
The patient is usually fatigued & looking ill due to the preexisting risk factor. In advanced cases with septicemia, the patient may be drowsy with decreased level of consciousness. - Vital signs
1. Fever 2. Tachycardia 3. Tachypnea 4. Hypotension (if patient is presenting with shock)