Symptoms
You might notice:
- Lack of pleasure. The person may not seem to enjoy anything anymore. ...
- Trouble with speech. They might not talk much or show any feelings. ...
- Flattening: The person with schizophrenia might seem like they have a terrible case of the blahs. ...
- Withdrawal. ...
- Struggling with the basics of daily life. ...
- No follow-through. ...
Causes
“People with schizophrenia may hear voices or noises; become very paranoid; believe they have unusual powers; think others control their thoughts, or vice-versa; or believe world events are connected to them,” explains psychiatrist Minnie Bowers-Smith, MD. It can be a long road to diagnosis, however. Patients — and families — are often in denial.
Prevention
What Is Hypervigilance? People who are hypervigilant are constantly on guard and prone to overreaction. They maintain an intense and sometimes obsessive awareness of their surroundings, frequently scanning for threats or routes of escape. Causes Hypervigilance is the body’s way of protecting you from threatening situations.
What are the traits of schizophrenia?
What are the 5 stages of psychosexual development?
- Stage One – Trust vs Mistrust.
- Stage Two – Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt.
- Stage Three – Initiative vs Guilt.
- Stage Four – Industry vs Inferiority.
- Stage Five – Identity vs Role Confusion.
- Stage Six – Intimacy vs Isolation.
- Stage Eight – Ego Integrity vs Despair.
What type of personality do schizophrenics have?
What is hypervigilant personality?
What are the psychosexual stages of personality development?

What is an example of schizotypal personality disorder?
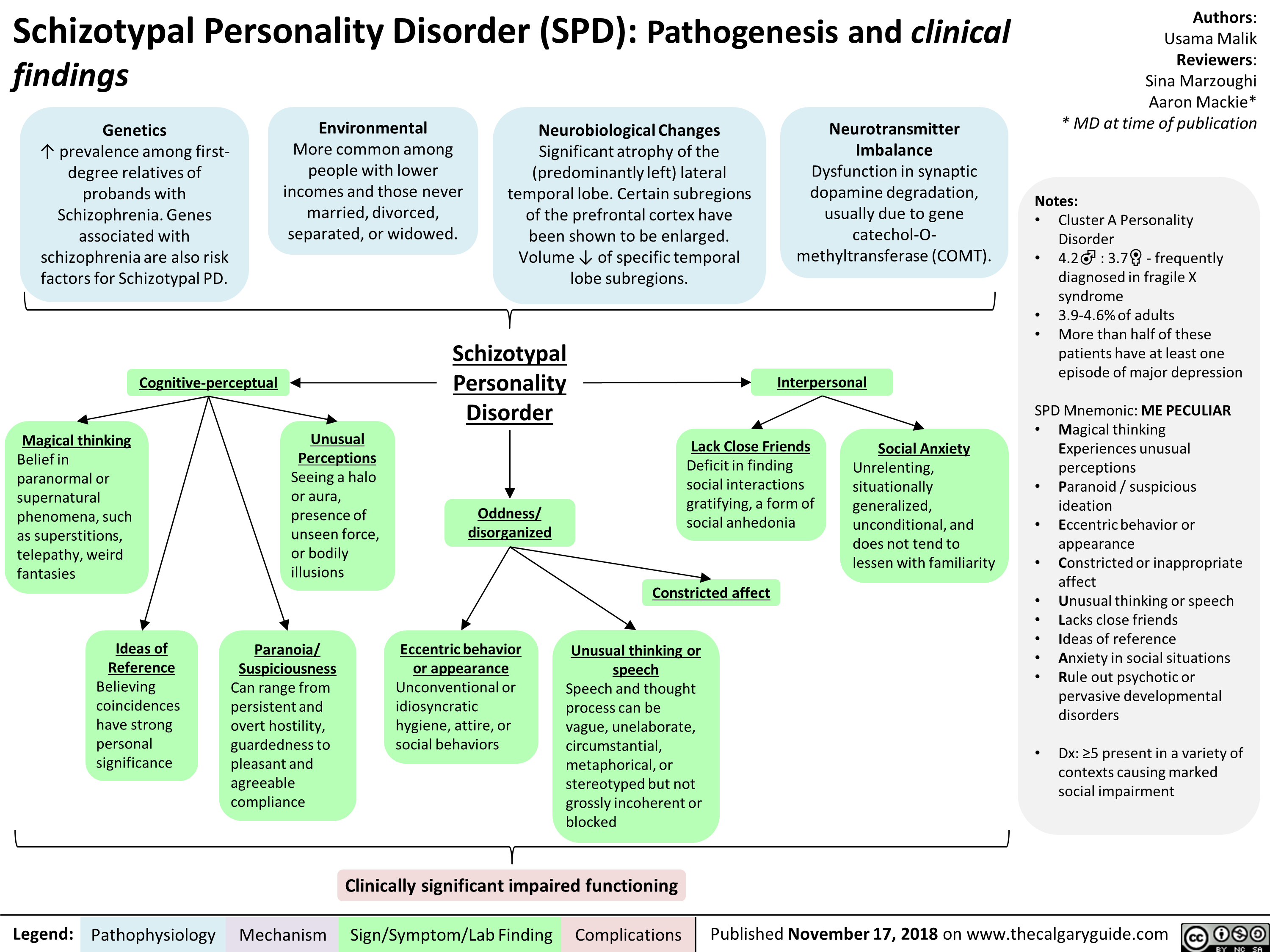
Tend to misinterpret reality or to have distorted perceptions (for example, mistaking noises for voices) Have odd beliefs or magical thinking (for example, being overly superstitious or thinking of themselves as psychic) Be preoccupied with fantasy and daydreaming. Tend to be stiff and awkward when relating to others.
What triggers schizotypal?
Schizotypal Personality Disorder Causes and Risk Factors Brain malfunction, including brain trauma. Childhood experiences including abuse or neglect. Having a parental figure who is cold or detached from you. Injury or illness before or during birth.
Is schizotypal personality rare?
Schizotypal personality disorder occurs in almost 4% of the general population in the United States. It may be slightly more common among men. Schizotypal personality disorder is less likely to resolve or lessen as people age than most personality disorders. Other disorders are often also present.
What is an example of schizoid personality disorder?
If you have schizoid personality disorder, you may be seen as a loner or dismissive of others, and you may lack the desire or skill to form close personal relationships. Because you don't tend to show emotion, you may appear as though you don't care about others or what's going on around you.
What is it like living with schizotypal personality disorder?
Individuals with schizotypal personality disorder have little capacity—and perhaps even need—for close relationships. They're often described as eccentric or bizarre. They may be suspicious and paranoid of others. They come across as “stiff” and don't seem to fit in anywhere they go.
What age does schizotypal start?
*DSM-5 states that “the features of a Personality Disorder usually become recognizable during adolescence or early adult life,” but also recognizes that “schizotypal personality disorder may be first apparent in childhood and adolescence.”
How do schizotypal people talk?
Odd thinking and speech As someone with a schizotypal personality, you may tend to use an overelaborate, vague, and metaphorical speech. For example, you may tend to use words in unusual ways or add eccentric words that aren't commonly used by others.
What famous person has schizotypal personality disorder?
Psychologists think that a number of famous creative icons, including Albert Einstein, Pablo Picasso, Vincent Van Gogh, Emily Dickinson and Isaac Newton, had schizotypal personalities.
How severe is schizotypal?
Schizotypal personality disorder is a chronic condition that requires lifelong treatment. If left untreated, the prognosis (outlook) for schizotypal personality disorder (STPD) is generally poor. It's very common for people with STPD to have other mental health conditions, including: Social anxiety disorder.
How do you love someone with schizoid?
While schizoid personality disorder is hard to treat, there are some measures loved ones can take to help a person with this condition:Avoid Judgment. Listen when a loved one shares information about their disorder and try to understand where they're coming from.Get Educated. ... Be Patient. ... Encourage Treatment.
What is a secret schizoid?
Guntrip (using ideas of Klein, Fairbairn and Winnicott) classifies these individuals as "secret schizoids", who behave with socially available, interested, engaged and involved interaction yet remain emotionally withdrawn and sequestered within the safety of the internal world.
Do Schizoids get angry?
In fact, because of a clear tendency to not experience and express strong emotions, if you have schizoid personality disorder, you rarely ever get angry or feel hatred, even when provoked.
How do schizotypal people talk?
Odd thinking and speech As someone with a schizotypal personality, you may tend to use an overelaborate, vague, and metaphorical speech. For example, you may tend to use words in unusual ways or add eccentric words that aren't commonly used by others.
What helps schizotypal?
TreatmentCognitive-behavioral therapy — Identifying and challenging negative thought patterns, learning specific social skills, and modifying problem behaviors.Supportive therapy — Offering encouragement and fostering adaptive skills.More items...•
Do schizotypal have friends?
People with schizotypal personality disorder do not have close friends or confidants, except for first-degree relatives. They are very uncomfortable relating to people. They interact with people if they have to but prefer not to because they feel like they are different and do not belong.
What is magical thinking schizotypal?
People with schizotypal personality disorder are often identified as having an eccentric personality. They might take magical thinking, superstitions, or paranoid thoughts very seriously, avoiding people whom they irrationally mistrust. They also might dress strangely or ramble in speech.
How is schizotypal personality disorder diagnosed?
The health professional, psychiatrist or psychologist will want to know when symptoms appeared, early childhood experiences, daily functioning at...
What is the difference between schizoid and schizotypal personality disorders?
Both are Cluster A disorders and are described as odd and eccentric. A big difference is that people with schizoid personality disorder are in touc...
What is the difference between schizotypal personality disorder and schizophrenia?
Schizotypal personality disorder is commonly confused with schizophrenia. However, schizophrenia is more severe as patients lose all hold of realit...
Can a person with schizotypal personality be at risk of bullying?
Yes. Teens who have a schizotypal personality are out of step socially and awkward, which can result in being bullied and teased. This dynamic fuel...
How common is schizotypal personality disorder?
About 4 percent of the American population suffers from schizotypal personality disorder. It is also somewhat more prevalent in men than women. Sch...
What is schizotypal personality disorder?
Schizotypal personality disorder (STPD) is a mental health condition marked by a consistent pattern of intense discomfort with close relationships and social interactions. People with STPD have distorted views of reality, superstitions and unusual behaviors. Their relationships are usually hindered by their symptoms.
What is the difference among schizoid and schizotypal personality disorders and schizophrenia?
Schizoid personality disorder (ScPD) is a mental health condition marked by a consistent pattern of detachment from and general disinterest in social relationships. This is distinct from schizotypal personality disorder (STPD) because people with STPD have an intense discomfort with personal relationships, not a lack of interest in them.
Who does schizotypal personality disorder affect?
Most personality disorders, including schizotypal personality disorder (STPD), begin in the teen years when personality further develops and matures.
How common is schizotypal personality disorder?
Schizotypal personality disorder is relatively rare. It affects approximately 3% to 5% of people in the United States.
What are the signs and symptoms of schizotypal personality disorder?
People with schizotypal personality disorder experience intense discomfort and distress in social situations. They have a lot of difficulties forming close relationships and maintaining them, partially due to a distorted interpretation of social interactions, as well as odd social behavior.
What causes schizotypal personality disorder?
Personality disorders, including schizotypal personality disorder, are among the least understood mental health conditions. Researchers are still trying to figure out the exact cause of them, but believe they develop due to several factors.
How is schizotypal personality disorder diagnosed?
Personality continues to evolve throughout childhood, adolescence and early adulthood. Because of this, healthcare providers don’t typically diagnose someone with schizotypal personality disorder until after the age of 18.
What is a schizotypal personality disorder?
Schizotypal personality disorder is marked by a pervasive pattern of social and interpersonal deficits. Individuals with schizotypal personality disorder have little capacity—and perhaps even need—for close relationships. They’re often described as eccentric or bizarre. They may be suspicious and paranoid of others.
Why is schizophrenia confused with schizotypal?
Schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, psychotic disorders, neurodevelopmental disorders, and other personality disorders may be confused with a schizotypal personality disorder because they have certain features in common.
What percentage of people in Norway have schizotypal personality disorder?
In community studies, the prevalence of schizotypal personality disorder ranges from .6 percent of the population in Norway to 4.6 percent in samples taken in the United States. There isn’t a single known cause for schizotypal personality disorder. It appears there is a strong genetic component, however.
How to determine if someone has personality disorder?
Instead, a clinician will conduct a thorough interview that gathers the history of the symptoms and assesses the impairments. The clinician also observes the individual throughout the interview to look for signs of the condition.
What are the criteria for DSM-5?
DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria. According to the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, symptoms must begin by early adulthood. In order to meet the criteria for a diagnosis, individuals must experience at least five of the following symptoms: Ideas of reference (incorrect interpretations of causal incidents or events as having an ...
Does eccentricity have a personality disorder?
Someone who is eccentric with few friends doesn’t necessarily have a schizotypal personality disorder. In order to meet the criteria for a diagnosis, the symptoms must interfere with a person’s social, occupational, or educational functioning.
Can schizotypal personality disorder be uncomfortable?
Unlike in social anxiety disorder, where an individual is likely to grow more comfortable with time, individuals with schizotypal personality disorder remain uncomfortable even when they’re interacting with the same people in ...
How to treat schizotypal personality disorder?
Treatment for schizotypal personality disorder often includes a combination of psychotherapy and medication. Many people can be helped by work and social activities that are a fit for their personality styles.
Why do people with schizotypal personality disorder seek help?
People with schizotypal personality disorder may seek help from their primary care doctor because of other symptoms, such as anxiety, depression or problems coping with frustration, or for treatment of substance misuse.
How to help a schizotypal person?
Psychotherapy may help people with schizotypal personality disorder begin to trust others and learn coping skills by building a trusting relationship with a therapist. Psychotherapy may include: Cognitive-behavioral therapy — Identifying and challenging negative thought patterns, learning specific social skills, and modifying problem behaviors.
What is the DSM-5?
Diagnosis of schizotypal personality disorder typically is based on: Symptoms listed in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), published by the American Psychiatric Association.
Does schizotypal personality disorder improve over time?
Though schizotypal personality disorder is lifelong, some symptoms may improve over time through experiences that help foster — among other positive traits — self-confidence, a belief in one's ability to overcome difficulty and a sense of social support.
Can schizotypal personality disorder be treated?
There are no medications approved by the Food and Drug Administration specifically for the treatment of schizotypal personality disorder. However, doctors may prescribe an antidepressant to help relieve or reduce certain symptoms, such as depression or anxiety. Some medications may help improve flexibility in thinking.
What is a schizotypal personality disorder?
Schizotypal personality disorder is an ingrained pattern of thinking and behavior marked by unusual beliefs and fears, and difficulty with forming and maintaining relationships. People with schizotypal personality disorder are uncomfortable with close relationships and may exhibit eccentric behavior.
What are the symptoms of a schizotypal personality?
According to the DSM-5, the symptoms include: Discomfort in social situations. Odd beliefs, fantasies or preoccupations. Odd behavior or appearance. Odd speech.
Is schizophrenia a prenatal risk factor?
The prenatal risk factors that apply to schizophrenia are also relevant to schizotypal personality disorder, including maternal exposure to certain viruses. Drug use may be a contributing factor for people already at risk of developing this disorder due to an underlying genetic predisposition.
Can schizotypal patients be treated?
Schizotypal patients rarely initiate treatment for their disorder, tending to seek relief from depressive problems instead. Some people may be helped by antipsychotic medications, but therapy is preferable for most. Because the characteristics of this disorder cannot be fundamentally altered for those with moderate to extreme cases, therapy is often aimed at helping people with this disorder establish a satisfying solitary existence.
Can distorted thinking cause anxiety?
Patients usually experience distorted thinking and avoid intimacy. They typically have few, if any, close friends, and feel nervous around strangers although they may marry and maintain jobs. The disorder, which may appear more frequently in males, surfaces by early adulthood and can exacerbate anxiety and depression.
Is schizotypal personality disorder related to schizophrenia?
As with most personality disorders, the cause of schizotypal personality disorder is unknown, but there is an increased incidence among relatives of those with the condition, as well as those whose relatives are on the schizophrenia spectrum. The prenatal risk factors that apply to schizophrenia are also relevant to schizotypal personality disorder, including maternal exposure to certain viruses.
What is a schizotypal personality disorder?
Schizotypal personality disorder ( STPD ), also known as schizotypal disorder, is a mental and behavioural disorder.
What is a schizotype?
The term "schizotype" was first coined by Sandor Rado in 1956 as an abbreviation of " schizo phrenic pheno type ". STPD is classified as a cluster A personality disorder, also known as the "odd or eccentric" cluster.
What is STPD in psychology?
Schizotypal personality disorder ( STPD ), also known as schizotypal disorder, is a mental and behavioural disorder. DSM classification describes the disorder specifically as a personality disorder characterized by thought disorder, paranoia, a characteristic form of social anxiety, derealization, transient psychosis, and unconventional beliefs.
How difficult is it to treat schizotypal personality disorder?
It is difficult to gain rapport with people who suffer from STPD due to the fact that increasing familiarity and intimacy usually increase their level of anxiety and discomfort.
What is the ICd 10 for schizophrenia?
The World Health Organization 's ICD-10 uses the name schizotypal disorder ( F21 ). It is classified as a clinical disorder associated with schizophrenia, rather than a personality disorder as in DSM-5.
Is schizotypal personality disorder a cluster A disorder?
In terms of comorbidity with other personality disorders, schizotypal personality disorder has high comorbidity with schizoid and para noid personality disorder, the other two 'Cluster A' conditions. It also has significant comorbidity with borderline personality disorder and narcissistic personality disorder.
Can STPD be treated in a group?
Group therapy is recommended for persons with STPD only if the group is well structured and supportive. Otherwise, it could lead to loose and tangential ideation. Support is especially important for schizotypal patients with predominant paranoid symptoms, because they will have a lot of difficulties even in highly structured groups.
Facts About Schizotypal Personality Disorder
Schizotypal personality disorder (STPD) is a chronic mental illness that involves eccentric mannerisms in the way someone behaves, looks, talks, and thinks.
STPD Symptoms
People with STPD often struggle to maintain close relationships with people outside their immediate family. They may also find it hard to “fit in” at work or school.
Causes and Risk Factors
There is no single known cause of STPD. 12 Researchers have identified several possible factors that may contribute to the development of STPD, including:
DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria
According to the criteria in the DSM-5, someone must have five or more of the following symptoms to be diagnosed with STPD:
STPD Treatment
A mental health therapist can diagnose you with STPD using the criteria in the DSM-5. They may perform other assessments, such as a physical or neurological examination, to rule out any other possible underlying causes for your symptoms. 1
Situational Coping Strategies
Because STPD is usually a long-lasting condition, it can be difficult to treat. In addition to treatments like psychotherapy or medication, many people with STPD are able to improve their symptoms with social skills training. 12
Summary
Schizotypal personality disorder is a long-lasting mental health condition that involves odd and eccentric patterns of behavior, thinking, and appearance. Many people with STPD feel socially isolated and find it hard to develop close relationships with people outside their immediate families.
Which personality disorder is more likely to be a schizotypal personality disorder?
People with bipolar disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, borderline personality disorder, and narcissistic personality disorder are also at higher risk of having schizotypal personality disorder.
How do you know if you have schizotypal personality disorder?
The first is a decreased capacity to form close relationships, which can cause a person severe discomfort. The second is experiencing distortions in one’s thinking or perceiving of events. The third is exhibiting eccentric behavior.
Why do psychiatrists evaluate people for schizotypal personality disorder?
A psychiatric evaluation can help a doctor or mental health professional rule out other diagnoses and determine whether there are co-occurring conditions that also need to be treated. Because so many people with schizotypal personality disorder also experience depression, they are at increased risk of suicide.
What is the condition called when you have strange patterns of thinking and behavior?
Sometimes, however, a person will begin to experience strange patterns of thinking and behaving and struggle to form relationships with others. This condition is a chronic mental illness known as schizotypal personality disorder (SPD).
Why is it so hard to find employment with schizotypal personality disorder?
The eccentric behaviors and beliefs that accompany schizotypal personality disorder can make it difficult for a person to find or maintain employment. They might show up to work dressed inappropriately or experience paranoid fears when dealing with customers or other coworkers.
How to tell if someone is paranoid?
A person also must have experienced five of the following symptoms: 1 Lack of close friends outside of immediate family 2 Eccentric or unusual beliefs or mannerisms 3 Belief in superpowers (i.e. telepathy) or superstitions 4 Excessive social anxiety associated with paranoid fears 5 Paranoid thoughts or doubts about others’ loyalty 6 Interpreting harmless events as having a personal meaning 7 Dressing in an unkempt or odd manner 8 Sensing an absent person is present 9 Strange or rambling speech patterns 10 Flat or limited emotional responses
Can a person with schizophrenia develop schizophrenia?
However, a person who exhibits symptoms of SPD earlier in life may go on to develop schizophrenia.
What Is Schizotypal Personality Disorder?
Schizotypal personality disorder is one of a group of conditions informally called "eccentric" personality disorders. People who have these disorders often seem odd or peculiar to others. They also may show unusual thinking patterns and behaviors.
What are the problems of people with personality disorders?
Their rigid personality traits can cause problems and interfere with many areas of life, including social and work.
Can a person with schizophrenia develop schizophrenia?
In rare cases, people with schizotypal personality disorder may go on to develop schizophrenia. Schizotypal Personality Disorder Causes. Your genes may play a role in schizotypal personality disorder. It’s more common in relatives of people with schizophrenia and usually starts in early adulthood.
Can a person with schizophrenia have a hallucination?
People who have schizophrenia are disconnected from reality. They may have delusions and see or hear things that aren’t there (hallucinations). But people who have schizotypal personality disorder don’t. In rare cases, people with schizotypal personality disorder may go on to develop schizophrenia.
Is schizophrenia a brain disorder?
In this way, schizotypal personality disorder can seem like a mild form of schizophrenia, a serious brain disorder that distorts the way a person thinks, acts, expresses emotions, perceives reality, and relates to others. People who have schizophrenia are disconnected from reality.
Do people with personality disorders have a problem?
Unlike people with anxiety disorders, who know that they have a problem but can’t control it, people with personality disorders generally are not aware that they have a problem and do not believe that they have anything to control.
Can a doctor test for personality disorder?
If you have symptoms, your doctor will ask about your medical history and may do a physical exam. There are no lab tests to diagnose personality disorders, but your doctor might use other tests to rule out physical illness as the cause of the symptoms.
What is a schizotypal personality disorder?
Schizotypal personality disorder definition. STPD is a type of personality disorder. This classification means that it affects a person’s behavior and causes them to think, feel, or relate to others in a way that deviates from what society considers normal. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders ...
What is the difference between schizophrenia and STPD?
The main difference between STPD and schizophrenia is that people with schizophrenia frequently experience characteristic psychotic symptoms, while those with STPD do not. The symptoms of psychosis include losing a sense of reality, which may involve hallucinations and delusions.
What is STPD in the DSM-5?
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) groups personality disorders into three broad clusters that it refers to as A, B, and C. STPD is a cluster A personality disorder. According to Mental Health America, these disorders involve behaviors that may seem odd or eccentric to others. A person with STPD may have peculiar ...
What is STPD in a relationship?
The symptoms may manifest as odd manners of speaking or dressing, strange beliefs, and difficulty forming relationships. STPD is a personality disorder, meaning that it affects a person’s behavior and their way of thinking. The name relates to the condition being a personality disorder that exists on the schizophrenia spectrum.
What is STPD cluster?
Summary. STPD is a cluster A personality disorder, which means that people with the condition find it difficult to relate to others. In particular, people with STPD display behaviors that society may consider to be odd or eccentric.
What are the criteria for STPD?
A doctor will only diagnose STPD if a person meets five of the nine criteria that the DSM-5 sets out. These criteria are: 1 ideas of reference, which are false beliefs that random events directly relate to a person 2 odd beliefs or magical thinking 3 unusual perceptual experiences and bodily illusions 4 odd thinking and speech 5 suspiciousness or paranoid ideation 6 inappropriate reactions or a lack of expressive range and emotional intensity 7 behavior or appearance that others likely see as odd, eccentric, or peculiar 8 lack of close friends 9 constant and excessive social anxiety that may relate to paranoid fears
What is the prevalence of STPD?
Evidence suggests that the prevalence of STPD may vary among different populations and range from 0.6% to 4.6%. Trusted Source.