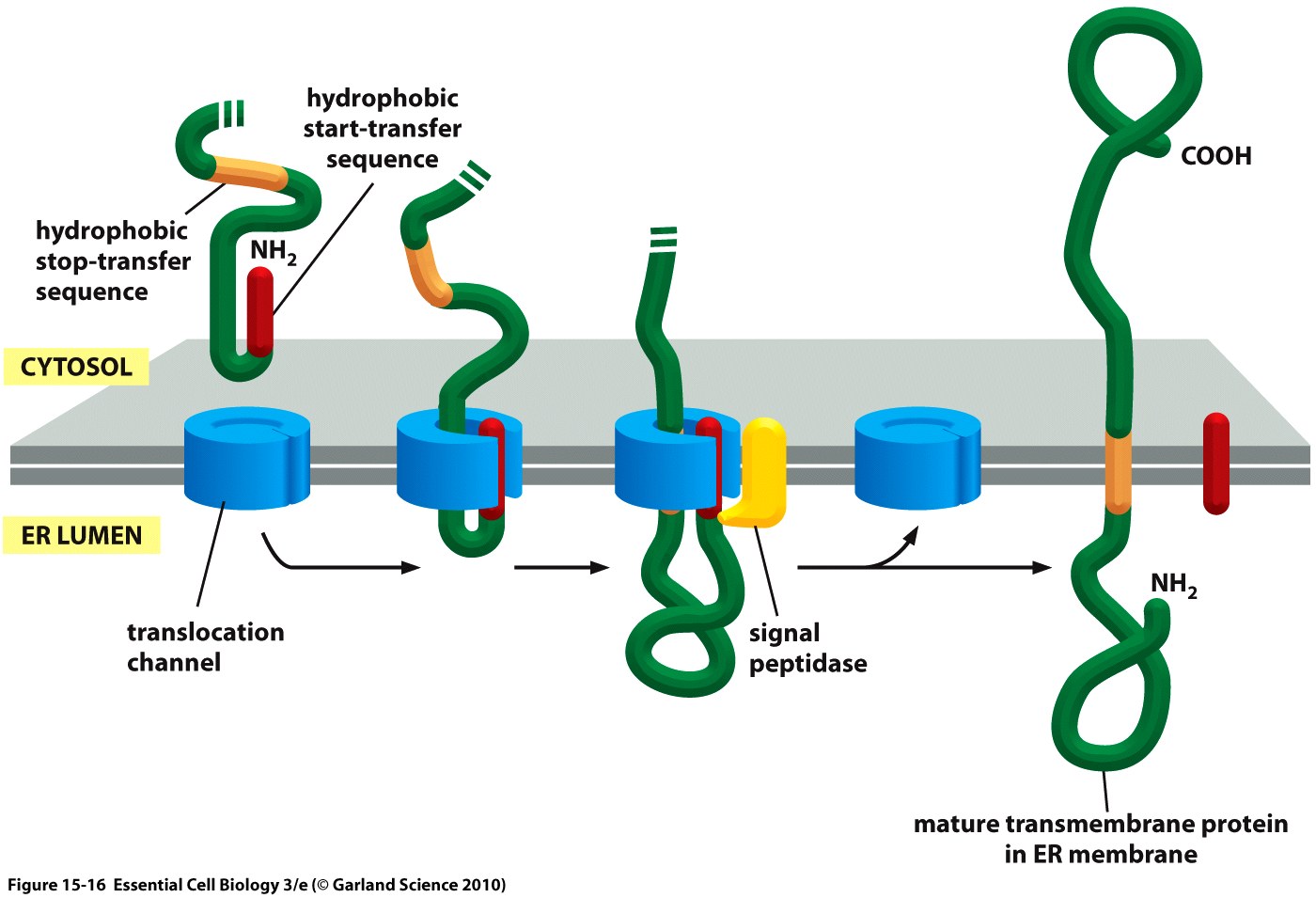
What is the start transfer sequence of a protein?
Start transfer sequences. These are of two types: N-terminal signal peptide sequence - a cluster of about 8 hydrophobic amino acids at the N-terminal end of a protein. This sequence remains in the membrane and is cleaved off of the protein after transfer through the membrane. Internal start transfer sequence.
What is internal start transfer sequence?
Internal start transfer sequence. Similar to a signal sequence, but located internally (not at the N terminal end of the protein). It also binds to the SRP and initiates transfer. Unlike the N-terminal signal sequence, it is not cleaved after transfer of the protein.
What are the different types of transfer sequences?
Start transfer sequences. These are of two types: Signal peptide sequence - contains a cluster of about 8 -14 hydrophobic amino acids at the N-terminal end of a protein. This is the same as the signal peptide sequence mentioned above. Start transfer sequence.
What is the difference between start and stop transfer signal?
Start transfer sequence. Similar to a signal sequence, but located internally (not at the N terminal end of the protein). It also binds to the SRP and initiates transfer. Unlike the N-terminal signal sequence, it is not cleaved after transfer of the protein. Stop transfer signal.

Are start transfer sequences hydrophobic?
Start transfer sequences. These are of two types: Signal peptide sequence - contains a cluster of about 8 -14 hydrophobic amino acids at the N-terminal end of a protein. This is the same as the signal peptide sequence mentioned above.
What is the stop transfer sequence?
A polypeptide sequence of a nascent membrane protein that prevents its translocation into a transfer vesicle and permits its insertion into a membrane.
What is the ER signal sequence?
The ER signal sequence is guided to the ER membrane by at least two components: a signal-recognition particle (SRP), which cycles between the ER membrane and the cytosol and binds to the signal sequence, and an SRP receptor in the ER membrane.
What is the pathway of a newly synthesized protein?
So, the correct answer is 'Rough ER →→ Golgi apparatus →→ Cell membrane'.
What happens to the signal sequence of ER lumen proteins?
The signal sequence is cleaved as the polypeptide chain crosses the membrane, so the amino terminus of the polypeptide chain is exposed in the ER lumen.
What is the pathway in which a protein moves through the Endomembrane system?
What is the correct sequence for secreted protein movement through the endomembrane system? See Section 7.5 (Page 158) . Correct. Synthesized proteins move first to the RER, then through the Golgi for processing, and then travel to various destinations via vesicles.
What is transit sequence?
A signal peptide (sometimes referred to as signal sequence, targeting signal, localization signal, localization sequence, transit peptide, leader sequence or leader peptide) is a short peptide (usually 16-30 amino acids long) present at the N-terminus (or occasionally nonclassically at the C-terminus or internally) of ...
How do signal sequences work?
Signal sequences are located on the N-terminus of some proteins and enable those proteins to find their correct location outside the cell membrane. The signal sequence tags the protein for transport through the cell membrane and out of the cell.
What is the N-terminal signal sequence?
Signal sequences are N-terminal extensions of nascent polypeptide chains that mediate protein targeting to the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
Which is the correct pathway of a protein through a cell?
Although the protein itself is not made until the mRNA transcript leaves the nucleus to find a ribosome in the cytosol or on rough endoplasmic reticulum, the most correct choice is A) nucleus, ribosome, Golgi apparatus.
How does a newly made protein travel through and out of the cell?
Protein cargo moves from the ER to the Golgi, is modified within the Golgi, and is then sent to various destinations in the cell, including the lysosomes and the cell surface. The Golgi processes proteins made by the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) before sending them out to the cell.
How are proteins transported out of the cell?
From the endoplasmic reticulum, proteins are transported in vesicles to the Golgi apparatus, where they are further processed and sorted for transport to lysosomes, the plasma membrane, or secretion from the cell.
Is stop transfer sequence hydrophobic?
A hydrophobic sequence may trigger opening of the pore sideways, so protein slides out of pore, laterally, into lipid bilayer. These hydrophobic sequences are usually called 'stop-transfer' sequences and/or 'anchor' sequences.
What does the Translocon do?
The translocon complex acts as a switching station: Secretory proteins are allowed to pass straight through into the ER lumen or the bacterial periplasm (secretion), while TM segments of membrane proteins are shunted into the membrane bilayer.
Why is the secretory pathway important?
The secretory pathway provides a route for the cell to handle things that might not be good to have in the cytoplasm, and/or are most useful when kept concentrated in a specialized compartment with their desired interacting partners.
How do transmembrane proteins get into the plasma membrane?
In other cases, the signal peptide or another stretch of hydrophobic amino acids gets embedded in the ER membrane. This creates a transmembrane (membrane-crossing) segment that anchors the protein to the membrane.
How do transmembrane proteins get anchored in the membrane?
How do transmembrane proteins get anchored in the membrane? A hydrophobic sequence may trigger opening of the pore sideways, so protein slides out of pore, laterally, into lipid bilayer. These hydrophobic sequences are usually called 'stop-transfer' sequences and/or 'anchor' sequences.
What happens to the extracellular domain after a protein reaches the plasma membrane?
After the protein reaches the plasma membrane, the extracellular domain is detached from the rest of the protein and attached to lipid. (Proteins to be anchored to the plasma membrane on the inside are made on cytoplasmic ribosomes.) See Becker if you are curious about the details.
What is the SP loop?
a. SP probably forms loop not arrow. Loop enters channel (translocon) in membrane. SP loop is probably what opens (gates) the channel on the cytoplasmic side.
Where do proteins enter the ER?
Note: In unicellular organisms, soluble proteins destined for the ER lumen often enter the ER after they are finished (post-translational import).
Which enzyme is required to move amphipathic lipids from one leaflet (P side) of membrane to?
Flipping: Enzymes ('flippases' = transporters) are required to move amphipathic lipids from one leaflet (P side) of membrane to other leaflet (E side). If lipids are moved preferentially from one side of membrane to the other, transport is active and requires ATP.
What is an I/O transfer sequence?
An example of an I/O transfer sequence is a write-read operation , which is a bus write operation followed by a bus read operation. A client peripheral device driver might use this type of sequence to write to a function-select register in an SPB-connected peripheral device, and then read the value of the selected device function. These two transfers can be of different lengths. For example, the write operation might transfer one byte of data, and the read operation might transfer many bytes of data.
Why do I need to implement I/O transfer sequence?
A client might need to implement this type of I/O transfer sequence if a later transfer in the sequence has a dependency on an earlier transfer. For example, the first read might indicate how many more bytes to subsequently read or write. If no such dependency exists, however, the client should send an IOCTL_SPB_EXECUTE_SEQUENCE request to the SPB controller driver, which can perform the sequence more efficiently.
Which request is faster, less prone to errors, and significantly decreases the time during which other clients are locked out?
Whenever possible, a client should use the IOCTL_SPB_EXECUTE_SEQUENCE request , which is faster, is less prone to errors, and significantly decreases the time during which other clients are locked out of the bus. However, a client can use the IOCTL_SPB_LOCK_CONTROLLER and IOCTL_SPB_UNLOCK_CONTROLLER requests if it must look at the value that is read during one of the transfers in the sequence before it can initiate a later transfer in the sequence. In this case, careful design is required to avoid locking other clients out of the bus for longer than is necessary, and a badly designed peripheral driver can degrade overall system performance.
Does SpbCX follow an EvtSpbControllerIoSequence callback?
SpbCx never precedes an EvtSpbControllerIoSequence callback with an EvtSpbControllerLock callback, and it never follows an EvtSpbControllerIoSequence callback with an EvtSpbControllerUnlock callback.
Is EvtSpbControllerIoSequence required for Windows 8?
Implementation of an EvtSpbControllerIoSequence function is strongly recommended, and might become a requirement for Windows 8.
Can IOCTL_SPB_EXECUTE_SEQUENCE I/O be specified?
The client can specify the entire sequence in an IOCTL_SPB_EXECUTE_SEQUENCE I/O control request. This request enables the SPB controller driver to use whatever hardware-specific performance optimizations are available to perform the transfer sequence. For more information, see Single-Request Sequences.
Which type of loop enters the channel in the membrane?
b. SP probably forms loop not arrow. Loop enters channel (translocon) in membrane. SP loop is probably what opens (gates) the channel on the cytoplasmic side.
How do transmembrane proteins get anchored in the membrane?
How do transmembrane proteins get anchored in the membrane? A hydrophobic sequence may trigger opening of the pore sideways, so protein slides out of pore, laterally, into lipid bilayer. These hydrophobic sequences are called 'stop-transfer' sequences and/or 'anchor' sequences.
What happens to the extracellular domain after a protein reaches the plasma membrane?
After the protein reaches the plasma membrane, the extracellular domain is detached from the rest of the protein and attached to lipid. (Proteins to be anchored to the plasma membrane on the inside are made on cytoplasmic ribosomes.) See Becker if you are curious about the details.
Which direction do transport vesicles move?
a. Transport vesicles move primarily forward (anterograde) -- towards trans face. For an animation of this process, see here.
Where is protein released into the ER?
Protein is released into lumen of ER
Is every start/stop sequence an SP?
Every SP is also a "start transfer sequence" but not every start/stop sequence is necessarily an SP. To act as an SP, a sequence must bind to the SRP. If a hydrophobic sequence does not bind the SRP, it will not direct ribosomes to the ER. e.
Which argument to start method might cause a confusion regarding the term parent used in inheritance versus the parent sequence that starts?
The second argument to start method is parent which might cause a confusion regarding the term parent used in inheritance versus the parent sequence that starts the main sequence. To try out an example, we'll create a child sequence of base_seq with a print statement in each of its methods and spawn that from the test case.
What is the default value of call_pre_post in a sequence?
Within our test case, we'll call the start method of our sequence base_seq. Note that the default value of call_pre_post argument of the start method is 1 and hence the pre_body and post_body tasks of that sequence will be called.
What is the second argument to start method?
The second argument to start method is parent which might cause a confusion regarding the term parent used in inheritance versus the parent sequence that starts the main sequence. To try out an example, we'll create a child sequence of base_seq with a print statement in each of its methods and spawn that from the test case.
Does child2_seq execute its own methods?
It can be seen that child2_seq also executed its own methods after which child1_seq execution is resumed.
What is an emergency system?
These systems are intended to automatically supply illumination, power, orboth, to designated areas and equipment in the event of failure of the normal supply or in the event of accident to elements of a system intended to supply, distribute, and control power and illumination essential for safety to human life.
What is time delay on EPS?
6.2.5 Time Delay on Starting of EPS. A time-delay device shall be provided to delay starting of the EPS. The timer shall prevent nuisance starting of the EPS and possible subsequent load transfer in the event of harmless momentary power dips and interruptions of the primary source.
Types of I/O Transfer Sequences
- A client can initiate an I/O transfer sequence in one of these ways: 1. The client can specify the entire sequence in an IOCTL_SPB_EXECUTE_SEQUENCE I/O control request. This request enables the SPB controller driver to use whatever hardware-specific performance optimizations are available to perform the transfer sequence. For more information, see Single-Request Sequence…
Single-Request Sequences
- To improve performance, your SPB controller driver should implement an EvtSpbControllerIoSequence callback function to handle IOCTL_SPB_EXECUTE_SEQUENCErequests. This approach adds some complexity to the SPB controller driver but avoids requiring the client to perform an I/O transfer sequence as a series o…
Client-Implemented Sequences
- A client of an SPB controller driver can explicitly perform an I/O transfer sequence as a series of simple reads and writes. The client can be either a kernel-mode driver or a user-mode driver that controls a peripheral device that is attached to the bus. Before the first transfer in the sequence, the client sends an IOCTL_SPB_LOCK_CONTROLLER reque...