
Transmural fibroids
Uterine Fibroids
A non-cancerous tumors in the uterus.
How to know if you have fibroids?
If you experience abnormally profuse menstrual bleeding, or if your periods last more than 7 or 8 days at a stretch, you might be suffering from fibroids. Many women disregard occasional heavy blood flow, or simply do not notice it.
Is it dangerous to remove fibroids from the uterus?
Uterine fibroids should be treated if they cause significant symptoms, and especially if there is a danger of uterine fibroids causing infertility. In the past, uterine fibroid surgery was very invasive and required the removal of the entire uterus.
Are intramural fibroids dangerous?
People with uterine fibroids have a good prognosis. Overall, intramural fibroids are not dangerous, but they can cause unpleasant symptoms like heavy periods and trouble getting or staying pregnant. Talk with your healthcare provider about which of the many available treatment options is best for you.
Do fibroid tumors move like a baby?
Rarely, a large fibroid can block the opening of the uterus or keep the baby from passing into the birth canal. In this case, the baby is delivered by cesarean birth. In most cases, even a large fibroid will move out of the fetus's way as the uterus expands during pregnancy.
What are the three types of fibroids?
There are three major types of uterine fibroids. Intramural fibroids grow within the muscular uterine wall. Submucosal fibroids bulge into the uterine cavity. Subserosal fibroids project to the outside of the uterus.
What is transmural myoma?
The transmural myoma develops in the thickness of the wall of the uterus and can reach a size that distorts the endometrium and the serous surface. It is, together with the previous one, one of the most frequent.
What are the four types of fibroids?
According to their position within the uterine wall, uterine fibroids are classified in four different types:Subserosal Fibroids. Subserosal Fibroids are located near the outer layer or serosa of the uterus. ... Submucosal Fibroids. ... Intramural Fibroids. ... Pedunculated Fibroids.
What type of fibroid is most common?
intramural fibroids – the most common type of fibroid, which develop in the muscle wall of the womb.
Can a transmural fibroid be removed?
Fibroids within the uterine cavity, we can do a Hysteroscopic Myomectomy and shave the fibroids out from the inside. Fibroids that are deep within the uterine wall, trans-mural, or subserosal, we can do laparoscopic myomectomy, where the uterine fibroids are removed and the uterine wall is repaired.
What size of fibroid should be removed?
Most experts believe that about 9-10 centimeters (about 4 inches) diameter is the largest size fibroid that should be removed laparoscopically.
What naturally kills fibroids?
Vitamins and supplements Milk and dairy may help to reduce fibroids. Dairy products contain high amounts of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus. These nutrients may help prevent growth of fibroids. Some types of vitamins may also help reduce the growth and size of fibroids.
How do I know what type of fibroid I have?
How can I find out what type of fibroids I have?Hysterosalpingogram (HSG) is a type of x-ray that allows you to see the inside of the uterus (uterine cavity). ... Transvaginal ultrasonography (TV US) is when an ultrasound wand, called a transducer, is inserted into the vagina.More items...
Can fibroids cause weight gain?
Common Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids Fibroids cause weight gain and bloating due to a hormonal imbalance or the size of the fibroid. Larger fibroids may cause a woman to gain weight in the abdomen, giving the appearance of normal belly fat. Simply put, the more a fibroid grows, the heavier it will become.
Which fibroids cause the most pain?
Back and leg pain is most common with Subserosal uterine fibroids, which grow on the outside of the uterus. If the fibroid is located on the back of the uterus, it is very close to the spinal column. If it becomes large enough it can press on or pinch the nerves in that area, causing fibroid pain.
What causes fibroids to grow rapidly?
What causes fibroids to grow? There are several factors, but what we do know is that they are under hormonal control—specifically, estrogen and progesterone—and tend to grow at a more rapid pace during the reproductive years when hormone levels are at their highest.
What size fibroid is considered large?
A large fibroid is one that is 10 cm or more in diameter. The largest fibroids can range from the size of a grapefruit to the size of a watermelon.
What is the main cause of myoma?
What causes a myoma? The cause of fibroids is not known, but their development seems to be associated with the hormone estrogen. Fibroids may appear when a person's estrogen levels are high. For example, they can grow rapidly during pregnancy and may reduce if a person takes antihormone medications.
What will happen if you have myoma?
Symptoms of Cervical Myomas Heavy bleeding can cause anemia, with fatigue and weakness. Sexual intercourse may be painful. If myomas become infected, they may cause pain, bleeding, or a discharge from the vagina. Rarely, prolapse causes symptoms such as a feeling of pressure or a lump in the pelvis.
What will happen if myoma is not treated?
If left untreated, fibroids can continue to grow in the uterus, both in size and number. *Bleeding will become heavier, and it may be accompanied by severe cramping and anaemia. *As the fibroids grow, the abdomen can swell.
Is myoma same as fibroid?
Fibroids are muscular tumors that grow in the wall of the uterus (womb). Another medical term for fibroids is leiomyoma (leye-oh-meye-OH-muh) or just "myoma". Fibroids are almost always benign (not cancerous). Fibroids can grow as a single tumor, or there can be many of them in the uterus.
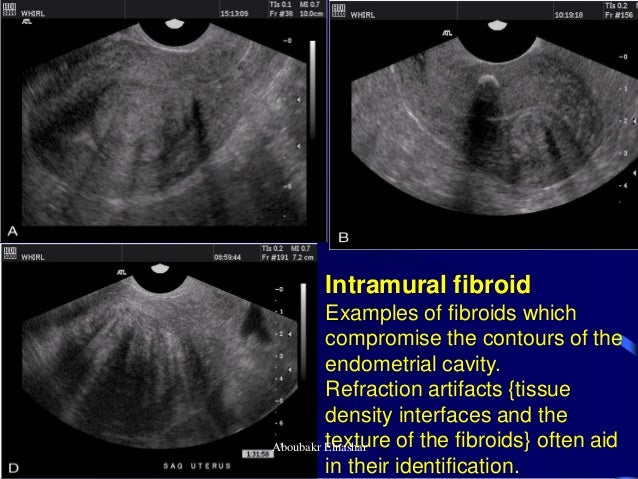
What is intramural fibroid?
What is an intramural fibroid? An intramural fibroid is a noncancerous tumor that grows between the muscles of the uterus. There are several types of intramural fibroids: anterior intramural fibroid, located in the front of the uterus. posterior intramural fibroid, located in the back of the uterus. fundal intramural fibroid, located in the upper ...
When are intramural fibroids discovered?
Typically, intramural fibroids and other types of fibroids are discovered during a routine pelvic exam or an abdominal examination.
How to treat fibroid uterus?
If you begin to experience significant symptoms, your doctor may recommend other treatment options, including: 1 Myomectomy. This surgical procedure removes the fibroid while leaving the uterus intact. 2 Hysterectomy. With this surgical procedure, your doctor will remove the entire uterus to prevent further complications from fibroids. 3 Uterine artery embolization (UAE). This technique cuts off the blood supply to the fibroid. The goal of a UAE is to reduce the size of the fibroid or completely eliminate it. 4 Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists. This treatment lowers estrogen levels and triggers medical menopause. The goal is to shrink or eliminate the fibroid.
Why do fibroids form in the middle of the uterus?
The exact cause of intramural fibroids is unknown. Many doctors believe that fibroids develop from an abnormal muscle cell in the middle layer of the uterine wall. When that cell is influenced by estrogen — the primary female hormone — it rapidly multiplies and forms a tumor.
What is the purpose of Uterine artery embolization?
This technique cuts off the blood supply to the fibroid. The goal of a UAE is to reduce the size of the fibroid or completely eliminate it. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists. This treatment lowers estrogen levels and triggers medical menopause. The goal is to shrink or eliminate the fibroid.
What is the procedure that removes the fibroid while leaving the uterus intact?
Myomectomy. This surgical procedure removes the fibroid while leaving the uterus intact.
What to do if fibroids grow in size?
Your doctor will monitor your symptoms for changes and examine you to see if the fibroids have grown in size. If you begin to experience significant symptoms, your doctor may recommend other treatment options, including: Myomectomy.
What are uterine fibroids?
When an organ develops a tumor, it will be of a tissue type normally contained within that organ. A muscular organ like the uterus makes muscle tumors. Therefore, there is nothing fibrous about fibroids. Fibroids are muscle tumors. We refer to them as myomas (“myo” means muscle; “oma” means new growth or tumor). Sometimes you will see the term leiomyoma, which refers to the fact that it is the smooth muscle of an organ as opposed to the striated muscle of the skeleton. Myomas can become malignant in less than half of 1% of cases, so myomas are generally benign, and polyps (benign growth of the endometrium) have the same low risk of malignancy.
How to treat fibroids in the uterus?
Treatment options for uterine fibroids: 1) hysteroscopy to shave fibroids from inside the uterine cavity , 2) laparoscopic myomectomy to remove remove fibroids through an incision and repair of the uterine wall, 3) laparoscopic hysterectomy for large and/or multiple fibroids. Cervix and ovaries can be conserved.
What is the lining of the uterus called?
The uterus is a thick-walled muscular organ with an inside lining called the endometrium (“metri” means uterus; “endo” refers to inside lining). Although the uterus is primarily a thick-walled muscle, it is the lining that bleeds, not the uterine wall. To cause heavy uterine bleeding, fibroids need to involve, or be up against, the uterine lining. Fibroids are muscle tumors, called myomas (“myo” means muscle; “oma” means new growth or tumor). Leiomyoma refers to the smooth muscle of an organ as opposed to the striated muscle of the skeleton. Myomas are generally benign, but can become malignant in approximately 0.5% of cases.
Where are fibroids located?
Fibroids can be deep within the uterine wall (Intramural), expand from inside the uterine cavity, through the uterine wall to the outside of the uterus (Transmural). They might also be mostly on the outside of the uterus (Subserosal). Fibroids can be safely removed with minimally invasive surgery. Our goal is to manage the uterine fibroids safely with minimally invasive surgery and preserve fertility whenever possible.
How many indications are there for intervening on uterine fibroids?
There are 4 indications to intervene on uterine fibroids:
Can a fibroid tumor be morcellated?
Therefore, morcellation of uterine fibroid tumors is not an option, and Mini-laparotomy (minimal enlargement of one of the incision sites) is required to remove the specimen. I have found that as long as the procedure is accomplished by laparoscopy, and the abdominal incision is only used to remove the specimen, the patients have very minimal pain from the mini-laparotomy incision.
Can a myomectomy be done with fibroids?
Fibroids that are deep within the uterine wall, trans-mural, or subserosal, we can do laparoscopic myomectomy, where the uterine fibroids are removed and the uterine wall is repaired.
Where do intramural fibroids occur?
Intramural fibroids occur in the wall of the uterus, beneath the endometrium. 2 These are a common type of fibroid.
Where does the posterior intramural fibroid grow?
A posterior intramural fibroid grows at the back of the uterus.
How to shrink fibroids?
There are various treatments designed to shrink fibroids. Some medications that induce menopause can reduce fibroid size. Surgical procedures including embolization and myolysis can also cause fibroids to shrink, which reduces symptoms in some cases.
Why do pedunculated fibroids hurt?
No matter where they occur, pedunculated fibroids can be painful because the stalk that they grow on can twist, cutting off blood supply to the fibroid and causing shooting pain. 2
What is the procedure to cut off blood flow to the fibroids?
Uterine fibroid embolization, a procedure to cut off blood flow to the fibroids, which causes them to shrink
How common are uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are extremely common The incidence rate is unknown and varies by study, but they can be detected in up to 80% of women by 50 years of age. 1 Many people with fibroids don’t know they have them because many fibroids are asymptomatic. In other cases, fibroids can cause symptoms like heavy periods, pain, or trouble getting pregnant.
What is the best treatment for fibroid growth?
Hormonal treatments, like birth control pills and IUDs containing levonorgestrel (or progesterone), which can prevent fibroid growth and reduce symptoms like heavy bleeding
What are the changes in fibroids?
Genetic changes. Many fibroids contain changes in genes that differ from those in typical uterine muscle cells.
Where do fibroids come from?
Doctors believe that uterine fibroids develop from a stem cell in the smooth muscular tissue of the uterus (myometrium). A single cell divides repeatedly, eventually creating a firm, rubbery mass distinct from nearby tissue.
What are the three types of fibroids?
There are three major types of uterine fibroids. Intramural fibroids grow within the muscular uterine wall. Submucosal fibroids bulge into the uterine cavity. Subserosal fibro ids project to the outside of the uterus. Some submucosal or subserosal fibroids may be pedunculated — hanging from a stalk inside or outside the uterus.
What are the risk factors for uterine fibroids?
Factors that can have an impact on fibroid development include: Race. Although any woman of reproductive age can develop fibroids, black women are more likely to have fibroids than are women of other racial groups.
Why do fibroid cells shrink?
Fibroids contain more estrogen and progesterone receptors than normal uterine muscle cells do. Fibroids tend to shrink after menopause due to a decrease in hormone production. Other growth factors. Substances that help the body maintain tissues, such as insulin-like growth factor, may affect fibroid growth.
What is the material that makes cells stick together like mortar between bricks?
ECM is the material that makes cells stick together, like mortar between bricks. ECM is increased in fibroids and makes them fibrous. ECM also stores growth factors and causes biologic changes in the cells themselves. Doctors believe that uterine fibroids develop from a stem cell in the smooth muscular tissue of the uterus (myometrium).
How to reduce fibroid risk?
But, by making healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a normal weight and eating fruits and vegetables, you may be able to decrease your fibroid risk. Also, some research suggests that using hormonal contraceptives may be associated with a lower risk of fibroids. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
What is a uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are muscular growths that develop in a woman’s uterus. Also known as leiomyomas or myomas, uterine fibroids are non-cancerous tumors that are common in women of childbearing age.
Where do fibroids grow?
These are fibroids that grow into your uterine cavity, which is the open space within your uterus.
How common are fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are quite common, developing in 20-80% of women under the age of 50. You may have one fibroid or many, and they can range in size ...
How many types of fibroids are there?
There are four main types of uterine fibroids, and they’re named based on where they grow in your body. They include:
Who is the doctor for fibroid ablation?
Dr. Crockett is also skilled at Acessa, or fibroid ablation, and is one of only two doctors in the US credentialed to perform robotic-assisted Acessa fibroid procedures. When treatment is necessary, the type of treatment recommended depends on your symptoms, the type, number, and size of uterine fibroids you have, and how close you are to menopause.
Do fibroids need to be treated?
If your fibroids are causing no symptoms, they probably don’t need treatment.
Can a fibroid cause periods?
If you have uterine fibroids, you may experience one or more symptoms, or you may have no symptoms at all. Some common uterine fibroid symptoms include: Periods that are longer, heavier, or more frequent than usual. Significant menstrual pain. Bleeding between periods.
How do fibroids develop and how fast do the fibroids grow?
The uterus is made up of millions of SMOOTH MUSCLE CELLS that are uniform and grow together in sync. However, if you have THREE fibroids (aka myomas), that mean that you have three individual muscle cells that decided to grow independently and “go rogue” from the rest of the cells. Sometimes, the fibroid (s) grow slowly, and other times, the fibroids grow fast. There is both a genetic association and an ethnic association with fibroids. The fibroid (s) are stimulated by estrogen, so the fibroids may continue to grow until menopause. The first step in the rate of growth of fibroids is to perform serial pelvic ultrasounds, approximately once every year.
Can you have a vaginal delivery with fibroid?
You cannot undergo vaginal delivery because the site of the uterine incision will ALWAYS be weaker and there would be a higher risk of uterine rupture at the myomectomy incision site during the labor process.
How Large Can Fibroids Get?
According to my.cleavelandclinic.org: Fibroids may grow as a single nodule or in clusters and may range in size from 1 mm to 20 cm in diameter. A very large fibroid can even cause the uterus to expand to the size equivalent to a pregnancy heading into the 3rd trimester. Fibroids can further develop as a cluster of many small fibroids or form as one large, dominant fibroid.
How to contact Fibroid Treatment Collective?
For more information on fibroids and their symptoms, feel free to contact us at 1 (866) 479-1523 or request a free consultation online. Fibroids hurt Ingrid’s health and her sex life. Embolization freed her.
Is a uterine fibroids tumor benign?
Uterine fibroids are lumps or tumors that develop within uterine walls. Although they are tumors, they are almost always benign and not cancerous.
Can fibroids grow bigger?
Below are a few effects that can arise when fibroids grow past smaller sizes. These are just a few possible signs of a larger fibroid.
Is a fibrous tumor cancerous?
Although they are tumors, they are almost always benign and not cancerous. Cancerous fibroids occurring are very rare (less than 1 in 1,000 chance), and is known as leiomyosarcoma. Having fibroids does not increase the risk of developing leiomyosarcoma. Having fibroids does not increase the likelihood of getting other forms of cancer in the uterus.
Can a fibroid cause a pregnancy?
A very large fibroid can even cause the uterus to expand to the size equivalent to a pregnancy heading into the 3rd trimester. Fibroids can further develop as a cluster of many small fibroids or form as one large, dominant fibroid.
