What does vacuole stand for?
Oct 13, 2020 · A vacuole is a membrane bound structure found in the cytoplasmic matrix of a cell. The membrane surrounding the vacuole is known as tonoplast. The components of the vacuole, known as the cell sap, differ from that of the surrounding cytoplasm. The membranes …
What is a vacuole and what is its function?
Definition of vacuole. 1 : a small cavity or space in the tissues of an organism containing air or fluid. 2 : a cavity or vesicle in the cytoplasm of a cell usually containing fluid — see cell illustration. Other Words from vacuole Example Sentences Phrases Containing vacuole Learn More About …
What is a real life example of a vacuole?
vacuole. [ văk ′yōō-ōl′ ] n. A small cavity in the cytoplasm of a cell, bound by a single membrane and containing water, food, or metabolic waste. A small space or cavity in a tissue.
What is the meaning of vacuole?
Definitions of vacuole. noun. a tiny cavity filled with fluid in the cytoplasm of a cell. see more. see less. type of: bodily cavity, cavity, cavum. (anatomy) a natural hollow or sinus within the body. …

What is a vacuole kid definition?
What is the best definition for vacuole?
1 : a small cavity or space in the tissues of an organism containing air or fluid. 2 : a cavity or vesicle in the cytoplasm of a cell usually containing fluid — see cell illustration.
What is in the vacuole?
What is a vacuole Class 8?
What are vacuoles Class 9?
What are vacuoles Class 11?
Where is the vacuole in a cell?
Do human cells have vacuoles?
Who discovered vacuole?
Who discovered vacuoles Class 9?
What is the role of vacuoles in unicellular organisms Class 9?
What is a vacuole?
What are Vacuoles? The term “vacuole” means “empty space”. They help in the storage and disposal of various substances. They can store food or other nutrients required by a cell to survive. They also store waste products and prevent the entire cell from contamination. The vacuoles in plant cells are larger than those in the animal cells.
What is the purpose of vacuoles?
The term “vacuole” means “empty space”. They help in the storage and disposal of various substances. They can store food or other nutrients required by a cell to survive. They also store waste products and prevent the entire cell from contamination. The vacuoles in plant cells are larger than those in the animal cells.
Why are vacuoles important in plant cells?
They help in the storage and disposal of various substances . They can store food or other nutrients required by a cell to survive. They also store waste products and prevent the entire cell from contamination. The vacuoles in plant cells are larger than those in the animal cells.
What do plant vacuoles store?
They can store food or other nutrients required by a cell to survive. They also store waste products and prevent the entire cell from contamination. The vacuoles in plant cells are larger than those in the animal cells. The plant vacuoles occupy more than 80% of the volume of the cell. The vacuoles may be one or more in number.
What is the structure of the vacuole?
Structure of Vacuole. A vacuole is a membrane bound structure found in the cytoplasmic matrix of a cell. The membrane surrounding the vacuole is known as tonoplast. The components of the vacuole, known as the cell sap, differ from that of the surrounding cytoplasm. The membranes are composed of phospholipids.
Where is the vacuole located?
A vacuole is a membrane bound structure found in the cytoplasmic matrix of a cell. The membrane surrounding the vacuole is known as tonoplast. The components of the vacuole, known as the cell sap, differ from that of the surrounding cytoplasm. The membranes are composed of phospholipids.
What are the components of the vacuole?
The components of the vacuole, known as the cell sap, differ from that of the surrounding cytoplasm. The membranes are composed of phospholipids. The membranes are embedded with proteins that help in transporting molecules across the membrane. Different combinations of these proteins help the vacuoles to hold different materials.
What is a vacuole?
Definition of vacuole. 1 : a small cavity or space in the tissues of an organism containing air or fluid. 2 : a cavity or vesicle in the cytoplasm of a cell usually containing fluid — see cell illustration. Other Words from vacuole Example Sentences Learn More About vacuole. Keep scrolling for more.
What is the definition of a cavity?
1 : a small cavity or space in the tissues of an organism containing air or fluid. 2 : a cavity or vesicle in the cytoplasm of a cell containing fluid.
What are some examples of starlings' escape patterns?
Recent Examples on the Web Depending on the density of the flock and speed of the predator, the starlings’ reactions can take many escape patterns, including flying outward to create a vacuole—an empty space. — Lauryn Hill, Wired, 5 Feb. 2021 The central empty spaces are vacuoles, which get larger and larger as injured cells approach death. — Sharon Begley, STAT, 3 May 2018
What is a vacuole?
vacuole. [ văk ′yōō-ōl′ ] n. A small cavity in the cytoplasm of a cell, bound by a single membrane and containing water, food, or metabolic waste. A small space or cavity in a tissue.
Where is the vacuole located?
vacuole. A cavity within the cytoplasm of a cell, surrounded by a single membrane and containing fluid, food, or metabolic waste. Vacuoles are found in the cells of plants, protists, and some primitive animals. In mature plant cells, there is usually one large vacuole which occupies a large part of the cell's volume and is filled ...
What is the vacuole?
A vacuole has a broad definition, and includes a variety of membrane-bound sacs. The membranes are composed of phospholipids, but each organism may use slightly different phospholipids. Embedded in the membranes are proteins, which can function to transport molecules across the membrane or give it structure.
What is the function of the vacuole?
Vacuole Definition. A vacuole is an organelle in cells which functions to hold various solutions or materials. This includes solutions that have been created and are being stored or excreted, and those that have been phagocytized, or engulfed, by the cell. A vacuole is simply a chamber surrounded by a membrane, ...
What is the structure of a vacuole?
Vacuole Structure. A vacuole has a broad definition, and includes a variety of membrane-bound sacs. The membranes are composed of phospholipids, but each organism may use slightly different phospholipids. Embedded in the membranes are proteins, which can function to transport molecules across the membrane or give it structure.
What is the vacuole in a plant cell?
This vacuole is surrounded by the tonoplast, a type of cytoplasmic membrane that can stretch and fills itself with a solution known as cell sap. The vacuole also fill itself with protons from the cytosol, creating an acid environment inside of the cell.
Why do we need a vacuole?
A vacuole is used whenever a large amount of substance is taken in through endocytosis, or excreted through exocytosis. Many cells, plant and animal, take in substances and must store them separate from the cytosol. This could be because the substances are reactive, in which case they will cause unwanted reactions.
How do plants use their vacuoles?
Plants use their vacuoles for a second function, which is of utmost importance to all plants. The vacuole, when completely filled with water , can become pressurized and exert a force on the cell walls . Although the force in each cell is small, this turgor pressure allows the cells to create a form, and stand up to wind, rain and even hail. Although woody plants create additional proteins and fibers that help them stand tall, many non-woody plants can reach a height of several feet on turgor pressure alone.
Does garlic contain allicin?
This molecule, allicin, is produced when the enzyme alliinase and the substrate alliin are mixed. However, allicin doesn’t exist until a garlic cell is crushed. The allinase is found in the cytosol.
What is the function of a vacuole?
Especially in protozoa (single-celled eukaryotic organisms), vacuoles are essential cytoplasmic organs ( organelles ), performing functions such as storage, ingestion, digestion, excretion, and expulsion of excess water.
What are the organelles in a plant cell?
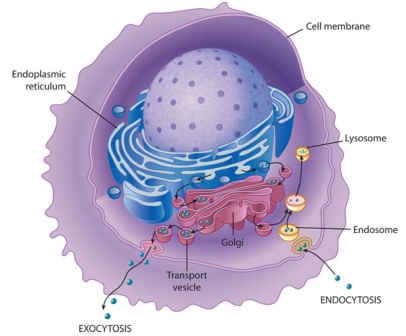
Plant cells contain membrane-bound organelles, including fluid-filled spaces, called vacuoles, that play an important role in maintaining the rigidity of a plant. Endocytosis and exocytosis are fundamental to the process of intracellular digestion. Food particles are taken into the cell via endocytosis into a vacuole.
What are the secondary metabolites in plants?
Potent secondary metabolites, such as tannins or various biological pigments, are also sequestered in the vacuoles in plants, fungi, algae, and certain other organisms to protect the cell from self-toxicity. plant cell. Plant cells contain membrane-bound organelles, including fluid-filled spaces, called vacuoles, ...
What is the function of lysosomes in the cell?
Lysosomes attach to the vacuole and release digestive enzymes to extract nutrients. The leftover waste products of digestion are carried to the plasma membrane by the vacuole and eliminated through the process of exocytosis. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Britannica Quiz. Parts of a Cell Quiz.
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
What is the function of the vacuole?
The main vacuole function is to store substances, typically either waste or harmful substances, or useful substances the cell will need later on.
What is the structure of a vacuole?
Vacuoles have a simple structure: they are surrounded by a thin membrane and filled with fluid and any molecules they take in. They look similar to vesicles, another organelle, because both are membrane-bound sacs, but vacuoles are significantly larger than vesicles and are formed when multiple vesicles fuse together.
What is the function of the contractile vacuole?
The contractile vacuole prevents this by contracting and expelling water from the cell. Some protists have one contractile vacuole ...
What is the function of vacuoles in animal cells?
Structure and Function of Vacuoles in Animal Cells. Vacuoles in animal cells mostly store substances; they aren’t needed as much for breaking down substances because lysosomes, another organelle in animal cells, do that. Animal cell vacuoles are typically small, and each cell can contain multiple vacuoles.
What do vacuoles store?
Vacuoles can store different substances depending on the type of cell they are in. For example, in fat cells, vacuoles will often store large amounts of lipids. Vacuoles in animal cells also help with the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis.
What are the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis?
Vacuoles in animal cells also help with the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis. Endocytosis is when substances that can’t passively move through the cell membrane are actively transported into the cell. These substances can include anything from nutrients to toxins to cell debris. Exocytosis is the opposite;
How many vacuoles are in a plant cell?
Unlike animal cells, plant cells typically contain only one vacuole per cell (often referred to as a “central vacuole”), and the vacuole they contain is much larger than those in animal cells. Plant cell central vacuoles take up an enormous percentage of the cell, sometimes over 90% of cell space, although 30-50% is more common.