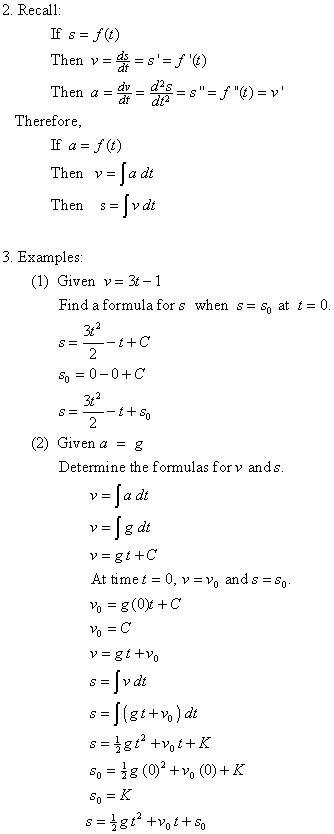
How to calculate displacement from acceleration data?
a simple way is Seismosignal. if you have an academic email, easily can receive a license from the Seismo Softawares Company. the software read the acceleration record and give you the velocity and...
What is the difference between velocity and displacement?
Displacement and Velocity Displacement is the vector difference between the ending and starting positions of an object. It may be very different from the distance the object has travelled along the way. Velocity is the rate at which displacement changes with time. It is a vector, too.
How to find displacement with a velocity time graph?
v ¯ = Δ x Δ t. In particular, if the velocity is constant, then we can rearrange this and find that displacement equals velocity times time. On a velocity vs. time graph, you'll see that the displacement is the area of the rectangle whose height is the velocity and whose width is the time interval.
How to convert velocity to acceleration?
How do you convert acceleration to velocity?
- Average Velocity. v a = (v 1 + v 0) / 2 (1)
- Final Velocity. v 1 = v 0 + a t (2)
- Distance Traveled. s = (v 0 + v 1) t / 2 (3)
- Acceleration. a = (v 1 - v 0) / t (4)
- Example - Accelerating Motorcycle.

What is displacement and velocity?
The only difference between velocity and speed is that velocity has a direction, and so is a vector quantity. Average velocity = Displacement is the distance moved in a straight line, in a given direction, from the starting point. Displacement is a vector quantity as it has size and direction.
What is acceleration and velocity?
Acceleration is a vector quantity that is defined as the rate at which an object changes its velocity. An object is accelerating if it is changing its velocity. As velocity is an example of vector, it has direction and magnitude.
How do you find displacement with velocity and acceleration?
Displacement Equations for these Calculations: Displacement (s) of an object equals, velocity (u) times time (t), plus ½ times acceleration (a) times time squared (t2). Use standard gravity, a = 9.80665 m/s2, for equations involving the Earth's gravitational force as the acceleration rate of an object.
What is displacement of acceleration?
Displacement equals the original velocity multiplied by time plus one half the acceleration multiplied by the square of time.
What is this displacement?
Displacement is defined as the change in position of an object. It is a vector quantity and has a direction and magnitude. It is represented as an arrow that points from the starting position to the final position. For example- If an object moves from A position to B, then the object's position changes.
What defines acceleration?
1a : the act or process of moving faster or happening more quickly : the act or process of accelerating rapid acceleration the acceleration of economic growth. b : ability to accelerate a car with good acceleration. 2 physics : the rate of change of velocity with respect to time broadly : change of velocity.
How do you find acceleration?
Acceleration (a) is the change in velocity (Δv) over the change in time (Δt), represented by the equation a = Δv/Δt. This allows you to measure how fast velocity changes in meters per second squared (m/s^2).
What is the formula of displacement?
Displacement = Final position – initial position = change in position.
What is acceleration unit?
Unit of acceleration is the metre per second per second (m/s2). Definition. The snewton is that force which, when acting on a mass of one kilogramme, produces an acceleration of one metre per second per second.
What is velocity constant?
To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed in a constant direction. Constant direction constrains the object to motion in a straight path thus, a constant velocity means motion in a straight line at a constant speed.
What is change velocity?
Acceleration: The rate of change of velocity is acceleration.
What is displacement velocity?
Displacement, velocity, and acceleration are measurements of a sine wave in relation to movement. During testing, a product is subject to an input vibration, and the output vibration is recorded for analysis. The movement of the output provides information on a product’s response to an external force and helps to identify the damage potential of the input.
What is acceleration in physics?
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. When a car accelerates, its velocity increases. When it decelerates, its velocity decreases. In Figure 2.1, the velocity is changing over time. What would the graph of acceleration over time look like? Consider the following:
What happens to the velocity of a wave when it passes the rest position?
In other words, when a wave passes the rest position, the velocity increases in the positive direction from negative to zero to positive velocity. ...
Why is the acceleration of a wave negative?
It increases in negative velocity until it reaches the rest position; at which point, the wave begins to slow down. During this time frame, the acceleration is negative because the velocity is increasing in a negative direction.
What is velocity in vibration testing?
Velocity refers to the rate of change in the position of a product. Speed varies during vibration testing. At the highest point, or peak, of the cycle, the product is momentarily at a standstill and the velocity is zero. Then, the product descends and picks up speed.
Do test engineers want displacement?
Test engineers are not highly interested in the displacement of a product, which is its change in position in meters. Instead, they seek acceleration over time. Before we discuss acceleration, however, we must address velocity.
How are speed and velocity related?
Speed and velocity are related, but different. Both terms indicate the rate at which an object is moving. Recall that a “rate” is any number divided by time. Speed is distance divided by time; velocity is displacement divided by time. Because distance is a scalar, speed (distance/time) is also a scalar. Direction does not matter for speed.
What is displacement in geometry?
Displacement is a vector quantity, and only depends on the starting and ending points of the object. Distance is a scalar quantity, and so a longer route taken will cause the object to have a greater distance. Question 2.
How to find velocity change?
You cannot tell velocity directly, though you can find the change in velocity. To find the change in velocity, find the area between the curve and the x-axis. You cannot tell displacement from an acceleration vs. time graph, though you can make predictions about how displacement is changing.
Why does distance increase?
Because distance is a scalar, distance increases whenever an object moves in any direction. Displacement is a vector: Direction matters! A moving object can gain or lose displacement depending on its direction, but a moving object always gains distance. Displacement’s advantage is that it shows distance between initial and final position, ...
Does direction matter for speed?
Direction does not matter for speed. Unlike distance, which always increases or stays the same, speed can increase or decrease over time. Like distance, speed is never negative. Because displacement is a vector, velocity is also a vector. Acceleration is any change in velocity.
What is the difference between acceleration and velocity?
Velocity is the rate at which your displacement is changing; it's how fast you're moving, and in what direction. And acceleration is the rate at which your velocity is changing, measured in meters per second per second (or meters per second squared).
What is displacement in kinematics?
Those terms are ones people often get mixed up, so let's go through them carefully. Displacement is the change in position of an object or person , measured in meters. Displacement is a vector, which means that it has magnitude (size) and direction.
What is kinematics in science?
So an important step in understanding the world is understanding movement, and that's what kinematics is all about. Kinematics is the study of motion, without addressing any of the forces that cause the motion.
What is the study of motion?
Kinematics is the study of motion, without addressing any of the forces that cause the motion. In kinematics, we simply talk about how things move: how their position changes, how fast they go, and how that speed itself changes. We map out motion using graphs, numbers, and calculations.
When do race cars accelerate?
Race cars can accelerate rapidly at the beginning of a race. People tend to accidentally use acceleration when they mean velocity. 'That guy's accelerating fast' might be true if they're talking about a race car in the first few seconds of a race, but not if the car's moving at 200 miles per hour already.
Can displacement be measured relative to origin?
That's because displacement can be measured relative to a fixed origin, or alternatively it can be measured relative to where you started. Maybe you started at the coordinate (11,0) and ended at the coordinate (7,0).
Is displacement a vector?
Displacement is a vector, which means that it has magnitude (size) and direction. For example, 50 miles is considered to be a distance, but 50 miles north of the origin is a displacement. Displacement ignores the path you took, and only considers the start and end points. It is said to be 'path independent'.
Distance
Distance is the magnitude of the total movement from the start point or a fixed point.
Displacement
The displacement of a moving position relative to a fixed point. Displacement gives both the distance and direction that a particle is from a fixed point.
Velocity
The average velocity of a particle is the rate of change of its position with respect to time. If the particle moves forwards, then its velocity is positive, and if the particle moves backwards, then its velocity is negative.
Speed
Instantaneous speed is the magnitude of instantaneous velocity and is always positive, regardless of its direction either forwards or backwards.
Acceleration
The average acceleration of a particle during a time interval is the rate of change of its velocity with respect to time.
Kinematic Equations from Integral Calculus
Let’s begin with a particle with an acceleration a (t) which is a known function of time. Since the time derivative of the velocity function is acceleration,
Example 3.17
A motorboat is traveling at a constant velocity of 5.0 m/s when it starts to accelerate opposite to the motion to arrive at the dock. Its acceleration is
Check Your Understanding 3.8
a ( t) = ( 5 – ( 10 1 s) t) m s 2. (a) What is the velocity function? (b) What is the position function? (c) When is the velocity zero?
What is acceleration in math?
Acceleration is a vector which shows the direction and magnitude of changes in velocity. Its standard units are meters per second per second, or meters per second squared. Average acceleration is the total change in velocity (magnitude and direction) over some extended period of time, divided by the duration of that period.
What is the difference between instantaneous velocity and average velocity?
The average velocity of an object is the total displacement during some extended period of time , divided by that period of time. Instantaneous velocity, on the other hand, describes the motion of a body at one particular moment in time.
Is velocity a vector?
Velocity is a vector which shows the direction and rate of motion. The standard units of velocity are meters per second. Speed and velocity are not the same thing: speed is a scalar, whereas velocity is a vector. One must use different rules when combining speeds and combining velocities.
Learning Objectives
Derive the kinematic equations for constant acceleration using integral calculus.
Kinematic Equations from Integral Calculus
Let’s begin with a particle with an acceleration a (t) is a known function of time. Since the time derivative of the velocity function is acceleration,
Example
A motorboat is traveling at a constant velocity of 5.0 m/s when it starts to decelerate to arrive at the dock. Its acceleration is a(t) = −1 4tm/s2 a ( t) = − 1 4 t m/ s 2.
Check Your Understanding
A particle starts from rest and has an acceleration function 5−10tm/s2 5 − 10 t m/s 2. (a) What is the velocity function? (b) What is the position function? (c) When is the velocity zero?
Conceptual Questions
When given the acceleration function, what additional information is needed to find the velocity function and position function?
Problems
The acceleration of a particle varies with time according to the equation a(t) = pt2 −qt3 a ( t) = p t 2 − q t 3. Initially, the velocity and position are zero. (a) What is the velocity as a function of time? (b) What is the position as a function of time?
Additional Problems
Professional baseball player Nolan Ryan could pitch a baseball at approximately 160.0 km/h. At that average velocity, how long did it take a ball thrown by Ryan to reach home plate, which is 18.4 m from the pitcher’s mound? Compare this with the average reaction time of a human to a visual stimulus, which is 0.25 s.
