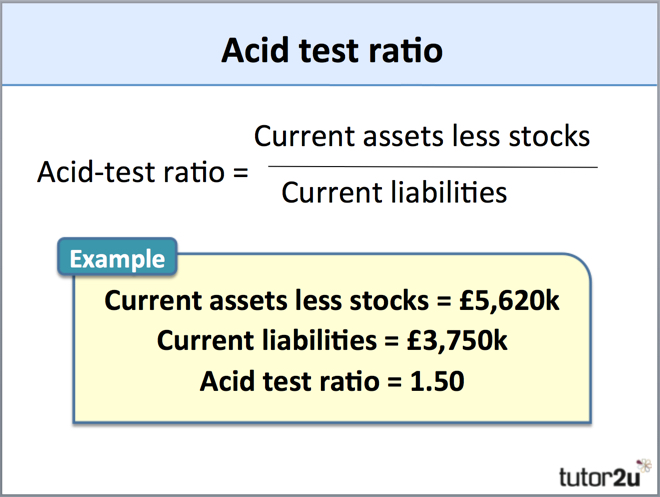
Full Answer
How do you calculate the acid test ratio?
You can determine the acid test ratio in three simple steps:
- Select the currency in which you want to perform the calculation (optional)
- Input a value for the company's liquid assets and liquid liabilities
- Click the "Calculate Acid Test Ratio" button to generate the ratio.
What is the ideal acid test ratio?
Usually 1:1 is an acceptable number for acid test ratio since it shows that the business has 1 unit of quick asset for every 1 unit of short-term obligation. A lower ratio than 1:1 indicates financial difficulty for the business.
How to improve acid test ratio?
- Sell off Inventories. This will improve Quick Ratio (Acid-Test Ratio), but not Current Ratio. ...
- Sell off Fixed Assets. Unused land and buildings as well as redundant equipment could be sold. ...
- Increase long-term loans to inject cash into the business. ...
- Sell shares. ...
- Delay payments to Creditors. ...
What is the balance equation for acid?
The chemical reaction between acid and base results in the formation of salt and water. It happens due to neutralization reaction such as. HCl + NaOH → NaCL + H 2 O. In the synthesis reactions, the final product is the combination of reactants involved in the chemical reaction such as follows ... Thus to balance equation, multiply CrCl3 with ...

How is acid-test ratio calculated?
How to Calculate the Acid-Test Ratio? To calculate the acid-test ratio of a company, divide a company's current cash, marketable securities, and total accounts receivable by its current liabilities. This information can be found on the company's balance sheet.
What ratio is acid-test ratio?
The acid-test ratio (ATR), also commonly known as the quick ratio, measures the liquidity of a company by calculating how well current assets can cover current liabilities. The quick ratio uses only the most liquid current assets that can be converted to cash within 90 days or less.
What is an example of a acid-test ratio?
For example, if a company's acid-test ratio is 2, the figure shows that the company has twice the dollar value of liquid assets than current liabilities. If the current liabilities are $100,000 and the acid-test ratio is 2, that would put the liquid assets at $200,000.
What are acid ratios?
An acid-test ratio, also known as a quick ratio, is a financial measure of a company's ability to pay off its current liabilities – that is, any debt that will need to be repaid within a year, such as credit card charges and accounts payable.
Why is acid test ratio important?
The acid test ratio is important because it measures liquidity and a company's ability to pay its bills and other short-term obligations with short-term assets quickly convertible to cash.
What is the acid test chemistry?
An acid test is any qualitative chemical or metallurgical assay which uses acid; most commonly, and historically, the use of a strong acid to distinguish gold from base metals. Figuratively, acid test is any definitive test for some attribute, e.g. of a person's character, or of the performance of product.
How do you find acid test ratio and quick ratio?
Quick ratio, or acid test ratio, is calculated by dividing current assets less inventory by current liabilities.
What does an acid test ratio of 1.2 mean?
Example of Acid Test Ratio If the company's current liabilities amount to $100,000 the acid test ratio is 1.2:1. A large acid test ratio gives creditors confidence that the company will be able to meet its current obligations when they come due.
Is acid test ratio and current ratio the same?
Current Ration vs Acid Test Ratio The current ratio measures the ability to pay off current liabilities by using current assets. Acid test ratio measures the ability to pay off current liabilities using current assets excluding inventory.
Why does acid test ratio decrease?
A low or decreasing acid test ratio generally suggests that a company is struggling to maintain or grow sales, paying their bills too quickly, collecting receivables too slowly or over-leveraged.
How do you calculate acid test ratio in Excel?
Acid-Test Ratio = Cash + Short Term Investments + Current Receivables –Inventory –Prepaid Expenses / Current LiabilitiesAcid-Test Ratio = 60,000 + 5,000 + 3,000 –1,500 / 33,000.Acid-Test Ratio = 2.01.
What is the formula of gearing ratio?
Gearing ratio formula The most common way to calculate gearing ratio is by using the debt-to-equity ratio, which is a company's debt divided by its shareholders' equity – which is calculated by subtracting a company's total liabilities from its total assets.
What are the items on a balance sheet?
The following items can all be found on a company’s balance sheet#N#Balance Sheet The balance sheet is one of the three fundamental financial statements. The financial statements are key to both financial modeling and accounting.#N#: 1 Cash and cash equivalents are the most liquid current assets on a company’s balance sheet, such as savings accounts, a term deposit with a maturity of fewer than 3 months, and T-bills#N#Treasury Bills (T-Bills) Treasury Bills (or T-Bills for short) are a short-term financial instrument issued by the US Treasury with maturity periods from a few days up to 52 weeks.#N#. 2 Marketable securities are liquid financial instruments that can be readily converted into cash. 3 Accounts receivables are the money owed to the company from providing customers with goods and/or services. 4 Current liabilities are debts or obligations due within one year.
Why is cash flow ratio used in conjunction with acid test?
or cash flow ratio are commonly used in conjunction with the acid-test ratio to provide a more complete and accurate estimation of a company’s liquidity position. The ratio excludes inventory from the calculation because inventory is not generally considered a liquid asset.
What does a ratio of 2 mean?
A ratio of 2 implies that the company owns $2 of liquid assets to cover each $1 of current liabilities. However, it’s important to note that an extremely high quick ratio (for example, a ratio of 10) is not considered favorable, as it may indicate that the company has excess cash that is not being wisely put to use growing its business. A very high ratio may also indicate that the company’s accounts receivables are excessively high – and that may indicate collection problems.
What is current asset?
Current assets are assets that can be reasonably converted into cash within a year. Inventories are the value of materials and goods held by a company with the intention of selling them to customers. The logic here is that inventory can often be slow moving and thus cannot readily be converted into cash.
What is acid test ratio?
The acid-test ratio is used to indicate a company’s ability to pay off its current liabilities. Current Liabilities Current liabilities are financial obligations of a business entity that are due and payable within a year. A company shows these on the.
What is the most liquid current asset on a company's balance sheet?
These statements are key to both financial modeling and accounting. : Cash and cash equivalents are the most liquid current assets on a company’s balance sheet, such as savings accounts, a term deposit with a maturity of fewer than 3 months, and T-bills.
What are the different types of assets?
Types of Assets Common types of assets include current, non-current, physical, intangible, operating, and non-operating. Correctly identifying and. are to cover its current liabilities. Current Liabilities Current liabilities are financial obligations of a business entity that are due and payable within a year.
What Does the Acid-Test Ratio Tell You?
The acid-test, or quick ratio, shows if a company has, or can get, enough cash to pay its immediate liabilities, such as short-term debt. For most industries, the acid-test ratio should exceed 1. If it's less than 1 then companies do not have enough liquid assets to pay their current liabilities and should be treated with caution. If the acid-test ratio is much lower than the current ratio, it means that a company's current assets are highly dependent on inventory. On the other hand, a very high ratio could indicate that accumulated cash is sitting idle, rather than being reinvested, returned to shareholders, or otherwise put to productive use.
How to Calculate the Acid-Test Ratio?
To calculate the acid-test ratio of a company, divide a company’s current cash, marketable securities, and total accounts receivable by its current liabilities. This information can be found on the company’s balance sheet.
What does it mean when a company has an acid test ratio of less than 1?
If the acid-test ratio is much lower than the current ratio, it means that a company's current assets are highly dependent on inventory.
What is the acid test?
The acid-test, or quick ratio, compares a company's most short-term assets to its most short-term liabilities to see if a company has enough cash to pay its immediate liabilities, such as short-term debt.
How long does it take for an acid test to convert to cash?
Another key difference is that the acid-test ratio includes only assets that can be converted to cash within 90 days or less, while the current ratio includes those that can be converted to cash within one year.
Why is the acid test ratio more useful than the current ratio?
The acid-test ratio is more useful in certain situations than the current ratio, also known as the working capital ratio, since it ignores assets such as inventory, which may be difficult to quickly liquidate.
Why use acid test ratio?
In certain situations, analysts prefer to use the acid-test ratio rather than the current ratio (also known as the working capital ratio) because the acid-test method ignores assets such as inventory, which may be difficult to quickly liquidate. The acid test ratio is thus a more conservative metric.
Why use acid test ratio?
There are many advantages and uses of Acid-test ratio formula and they are as follows-. The acid-test formula provides an appropriate picture of liquidity of the company. It is most useful when the proportion of illiquid current assets to total current assets is high.
Why is a high liquidity ratio good?
If a company has a higher ratio better the company liquidity will be which result in better overall financial health. But if the ratio is very high it is also not favorable as it may possible company has excess cash but the company is not using it in a beneficial manner and it is also possible that the company’s receivable is too high and the company is not able to collect the same which imply collection problem in a company.
What is the acid test ratio of HML?
So, the acid-test ratio of HML Pvt. Ltd is 1.86 which means it has lot of liquid assets and has high liquidity.
What is the acid test?
The acid-test ratio is generally used to evaluate an enterprise’s overall short term solvency or liquidity position. In simple language, it measures the capability of the company to pay its debt with its current asset. Current assets are assets that can be converted to cash within 90 days.
What is current asset?
Current assets are assets that can be converted to cash within 90 days. Many times it is desirable to know the more immediate position or instant debt paying ability of a firm than that indicates by the current ratio for this acid-test ratio is used. It is relating the most liquid assets to current liabilities.
Is cash receivable a current asset?
In this formula, cash receivable is considered as a current asset but it may possible company will not able to collect the fund against it.
Does acid test ratio include inventory?
There are some issues with acid-test ratio they are as follows-. Acid-test ratio alone is not sufficient to find liquidity of the company. As acid-test ratio does not include inventory it will not provide a clear picture as it may possible company have high inventories.
Why is the acid test ratio more conservative than the current ratio?
The acid-test ratio is more conservative than the current ratio because it doesn't include inventory, which may take longer to liquidate.
How does the ATR measure liquidity?
The acid-test ratio (ATR), also commonly known as the quick ratio , measures the liquidity of a company by calculating how well current assets can cover current liabilities. The quick ratio uses only the most liquid current assets that can be converted to cash within 90 days or less.
What are the assets that can be converted into cash?
Current assets or all assets that can be converted into cash within one year: 1 Cash and cash equivalents 2 Marketable securities 3 Accounts receivable
How to calculate quick ratio?
The quick ratio is calculated by totaling cash and equivalents, accounts receivables, and marketable investments, and dividing the total by current liabilities as shown below:
Where to find acid test ratio?
The Acid Test. All of the information necessary to calculate the acid-test ratio can be found on a company's balance sheet and includes the following: Current assets or all assets that can be converted into cash within one year: Current liabilities or a company's debts or obligations that are due within one year:
What is the purpose of the acid test?
The acid-test, or quick ratio, involves assessing a company's balance sheet to see whether it has enough funding on hand to cover its current debt. It is seen as more useful than the often-used current ratio since the acid-test excludes inventory, which can be hard to quickly liquidate.
Is it important to include multiple ratios in financial statements?
It's important to include multiple ratios in your analysis and compare each ratio with companies in the same industry.
What is the Acid Test Ratio?
The acid test ratio (or quick ratio) is a formula used to determine a company’s ability to pay their bills on time, by comparing their shortest-term assets to their shortest-term liabilities and seeing if they have enough cash to pay for those immediate liabilities.
What Does Acid Test Mean?
According to the Merriam-Webster Dictionary, the term acid test was coined in 1854 “from the use of nitric acid to determine the gold content of jewelry.” Merriam-Webster defines acid test as a “severe or crucial test.”
What is an Acid Test Ratio Interpretation of Results?
With an acid test ratio of at least 1, a company should have adequate liquidity to pay current liabilities when payments are due. The higher the acid test ratio number, the more cash and near-cash liquid assets a company has.
Why is the Acid Test Ratio Important?
The acid test ratio is important because it measures liquidity and a company’s ability to pay its bills and other short-term obligations with short-term assets quickly convertible to cash.
How Do You Calculate the Acid Test Ratio Formula?
The accounting formula for acid test ratio (also known as quick ratio) is:
Acid-Test Ratio Example
The following table shows a calculation in Excel using the acid test ratio formula. The numbers are from financial statements. You can find a template or acid ratio test calculator online.
Acid Test Ratio vs Current Ratio
In comparing financial ratios, the acid test ratio vs current ratio, the acid test ratio formula excludes current assets like inventory and prepaid assets.
What Is the Acid Test Ratio?
Let us first start with knowing what is acid test ratio in financial terms. An acid test ratio, in financial terms, is a type of liquidity ratio that measures a company's ability to meet its current financial obligations. For a healthy financial position of a company, the acid test ratio is 1:1.
The Formula of Acid Test Ratio
The acid test ratio can be calculated as liquid assets divided by current liabilities. Another way to calculate is to substitute inventories and prepaid expenses from current assets to calculator liquid assets and divide them by the current liabilities.
Acid Test Ratio Example
Following is an extract of the balance sheet for an illustrative Company, ABC Ltd., for the purpose of this example -
Interpretation of The Acid Test Ratio
If a company has an acid test ratio of less than 1, it indicates that the company has insufficient liquid assets to pay off its current financial obligations.
Difference Between Acid Test Ratio and Current Ratio
Both current and acid test or quick ratio measures the company’s ability to pay off its current short-term debts and financial obligations as and when they become due for payment. However, the acid test ratio considers liquid assets for measuring the company’s financial soundness, which is considered more conservative than the current ratio.
Drawbacks of Acid Test Ratio
There are a lot of benefits of using the acid test ratio as a financial analytical tool. There are certain drawbacks as well. Here are a few of them -
What happens if your acid test ratio is less than 1?from freshbooks.com
If your acid test ratio is less than 1, your company does not have enough liquid assets to pay their current liabilities.
What does it mean when a company has a low acid test?from freshbooks.com
A low or decreasing acid test ratio generally suggests that a company is struggling to maintain or grow sales, paying their bills too quickly, collecting receivables too slowly or over-leveraged. On the other hand, a high or increasing acid test ratio indicates a company has faster inventory turnover and cash conversion cycles.
How to calculate acid test ratio?from freshbooks.com
Then divide current liquid assets by total current liabilities to calculate the acid test ratio.
What does it mean when acid test ratio is lower than current ratio?from freshbooks.com
Acid test ratios that are much lower than the current ratio means that current assets are highly dependent on inventory. This is not always a bad sign, as some business models are dependent on inventory. Retail stores might have a very low acid test ratio without necessarily being in financial danger.
What is the best determinant of liquidity?from wikiaccounting.com
Quick ratio can best the best determinant of liquidity measures within a company. As a matter of fact, it can be seen as a measure to validate the organization’s ability to meet its day to day expenses and other short-term liabilities like accounts payable and accrued interest expenses.
Why is an acid test ratio higher than 1?from freshbooks.com
An acid test ration greater than 1 is considered healthy and is important for external stakeholders like creditors, lenders, investors and capitalists. Here are three ways to improve a company’s acid test ratio:
Why do corporations discard unproductive assets?from wikiaccounting.com
These assets need to be identified and then discarded in order to get cash against those assets. This cash can then be taken for short term liquidity of the company, hence improving the quick ratio of the company.
What Does the Acid-Test Ratio Tell You?from investopedia.com
The acid-test, or quick ratio, shows if a company has, or can get, enough cash to pay its immediate liabilities, such as short-term debt. For most industries, the acid-test ratio should exceed 1. If it's less than 1 then companies do not have enough liquid assets to pay their current liabilities and should be treated with caution. If the acid-test ratio is much lower than the current ratio, it means that a company's current assets are highly dependent on inventory. On the other hand, a very high ratio could indicate that accumulated cash is sitting idle, rather than being reinvested, returned to shareholders, or otherwise put to productive use.
How to Calculate the Acid-Test Ratio?from investopedia.com
To calculate the acid-test ratio of a company, divide a company’s current cash, marketable securities, and total accounts receivable by its current liabilities. This information can be found on the company’s balance sheet.
What are the items on a balance sheet?from corporatefinanceinstitute.com
The following items can all be found on a company’s balance sheet#N#Balance Sheet The balance sheet is one of the three fundamental financial statements. The financial statements are key to both financial modeling and accounting.#N#: 1 Cash and cash equivalents are the most liquid current assets on a company’s balance sheet, such as savings accounts, a term deposit with a maturity of fewer than 3 months, and T-bills#N#Treasury Bills (T-Bills) Treasury Bills (or T-Bills for short) are a short-term financial instrument issued by the US Treasury with maturity periods from a few days up to 52 weeks.#N#. 2 Marketable securities are liquid financial instruments that can be readily converted into cash. 3 Accounts receivables are the money owed to the company from providing customers with goods and/or services. 4 Current liabilities are debts or obligations due within one year.
Why is cash flow ratio used in conjunction with acid test?from corporatefinanceinstitute.com
or cash flow ratio are commonly used in conjunction with the acid-test ratio to provide a more complete and accurate estimation of a company’s liquidity position. The ratio excludes inventory from the calculation because inventory is not generally considered a liquid asset.
What is the numerator of the acid test ratio?from investopedia.com
The numerator of the acid-test ratio can be defined in various ways, but the main consideration should be gaining a realistic view of the company's liquid assets. Cash and cash equivalents should definitely be included, as should short-term investments, such as marketable securities.
What does it mean when a company has an acid test ratio of less than 1?from investopedia.com
If the acid-test ratio is much lower than the current ratio, it means that a company's current assets are highly dependent on inventory.
What is the acid test?from investopedia.com
The acid-test, or quick ratio, compares a company's most short-term assets to its most short-term liabilities to see if a company has enough cash to pay its immediate liabilities, such as short-term debt.

The Acid-Test Ratio Formula
- The formula for calculating the ratio is as follows: The following items can all be found on a company’s balance sheet: 1. Cash and cash equivalents are the most liquid current assets on a company’s balance sheet, such as savings accounts, a term deposit with a maturity of fewer than 3 months, and T-bills. 2. Marketable securitiesare liquid financi...
Example of The Acid-Test Ratio
- Consider three hypothetical companies: Here are the calculations of the acid-test ratio for each company: 1. Company A: ($95,125 – $5,412) / ($75,231 – $45,232) = 2.99 2. Company B: ($102,343 – $6,454) / ($85,010 – $34,142) = 1.89 3. Company C: ($152,342 – $10,343) / ($95,010 – $53,434) = 3.42 Note: To determine the current liabilities for each company, total liabilities are …
Interpretation of The Acid-Test Ratio
- The acid-test ratio is used to indicate a company’s ability to pay off its current liabilitieswithout relying on the sale of inventory or on obtaining additional financing. Inventory is not included in calculating the ratio, as it is not ordinarily an asset that can be easily and quickly converted into cash. Compared to the current ratio – a liquidity or debt ratio which does include inventory valu…
Drawbacks of The Acid-Test Ratio
- As with virtually any financial metric, there are a number of limitations and potential drawbacks to using the quick ratio: 1. The acid-test ratio alone is not sufficient to determine the liquidity position of the company. Other liquidity ratios such as the current ratioor cash flow ratio are commonly used in conjunction with the acid-test ratio to provide a more complete and accurate estimation …
Other Resources
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Acid-Test Ratio. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources listed below will be useful: 1. Debt to Assets Ratio 2. Debt Capacity 3. Analysis of Financial Statements 4. Valuation Methods
What Is The Acid-Test Ratio?
Understanding The Acid-Test Ratio
- In certain situations, analysts prefer to use the acid-test ratio rather than the current ratio (also known as the working capital ratio) because the acid-test method ignores assets such as inventory, which may be difficult to quickly liquidate. The acid test ratio is thus a more conservative metric. Companies with an acid-test ratio of less than 1 do not have enough liquid …
Calculating The Acid-Test Ratio
- The numerator of the acid-test ratio can be defined in various ways, but the main consideration should be gaining a realistic view of the company's liquid assets. Cash and cash equivalents should definitely be included, as should short-term investments, such as marketable securities. Accounts receivable are generally included, but this is not appropriate for every industry. In the c…
Acid-Test Ratio Example
- A company's acid-test ratio can be calculated using its balance sheet. Below is an abbreviated version of Apple Inc.'s (AAPL) balance sheet as of Jan. 27, 2022, showing the components of the company's current assets and current liabilities (all figures in millions of dollars):1 To obtain the company's liquid current assets, add cash and cash equiva...
Explanation
Significance and Uses of Acid-Test Ratio Formula
- There are many advantages and uses of Acid-test ratio formula and they are as follows- 1. The acid-test formula provides an appropriate picture of liquidity of the company. 2. It is most useful when the proportion of illiquid current assets to total current assets is high. 3. It helps to find the financial condition of the company. 4. This formula helps the investor to choose the right compa…
Disadvantages of Acid-Test Ratio Formula
- There are some issues with acid-test ratio they are as follows- 1. Acid-test ratio alone is not sufficient to find liquidity of the company. 2. As acid-test ratio does not include inventory it will not provide a clear picture as it may possible company have high inventories. 3. In this formula, cash receivable is considered as a current asset but it may possible company will not able to collect t…
Acid-Test Ratio Formula in Excel
- Here we will do the same example of the Acid-Test Ratio formula in Excel. It is very easy and simple. You need to provide the three inputs of i.e Current Assets, Inventory, and Current Liability You can easily calculate the Acid-Test Ratio using Formula in the template provided. Acid-test for HML Pvt. Ltd is calculated as: Acid-test for all three Companies is calculated as: Acid-test fo…
Recommended Articles
- This has been a guide to an Acid-Test Ratio formula. Here we discuss its uses along with practical examples. We also provide you with Acid-Test Ratio Calculator with downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more – 1. Calculator for Bid-Ask Spread Formula 2. Formula for Payback Period 3. Bond Equivalent Yield Formula 4. Examples of Debt …