What is the prognosis of gingivitis?
With adequate treatment, the prognosis of Chronic Gingivitis is good and the symptoms can be resolved Strictly adhering to a good oral hygiene regimen after treatment can help prevent recurrence of gum disease In order to prevent periodontitis, gingivitis needs to be treated in the early stages
What is the treatment for ANUG?
- Antibiotics and Pain Relief Medications. Dentists often prescribe antibiotics in order to fight the bacterial growth and prevent infection from spreading. ...
- Professional dental cleaning. A gentle cleaning of teeth and gums by the dentist is usually the first step in the treatment of trench mouth. ...
- Oral hygiene. ...
- Impoved diet. ...
- Gum surgery. ...
What are the possible complications of gingivitis?
These complications can occur:
- Gingivitis returns
- Periodontitis
- Infection or abscess of the gums or the jaw bones
- Trench mouth
What are the bacterial causes of gingivitis?
The causative organisms are mostly anaerobic bacteria, particularly Fusobacteria and spirochete species. Predisposing factors include poor oral hygiene, smoking, poor nutrition, psychological stress, and a weakened immune system. When the attachments of the teeth to the bone are involved, the term NUP is used.
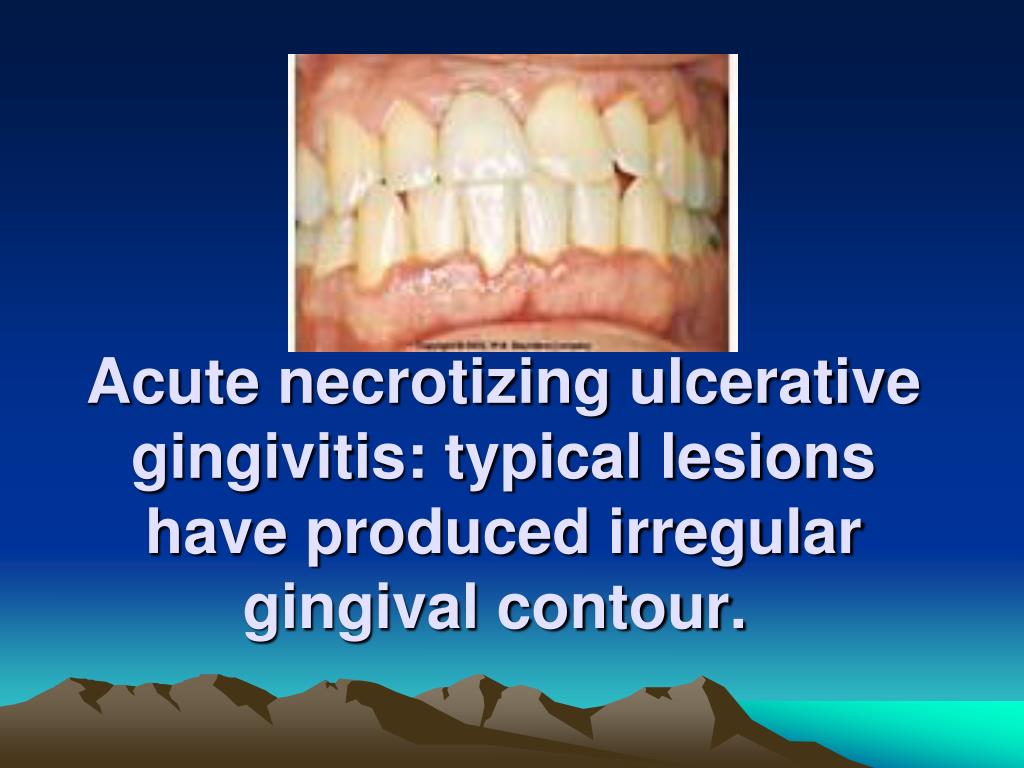
What causes acute gingivitis?
The most common cause of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene that encourages plaque to form on teeth, causing inflammation of the surrounding gum tissues. Here's how plaque can lead to gingivitis: Plaque forms on your teeth.
How is acute gingivitis treated?
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis is a painful infection of the gums. Symptoms are acute pain, bleeding, and foul breath. Diagnosis is based on clinical findings. Treatment is gentle debridement, improved oral hygiene, mouth rinses, supportive care, and, if debridement must be delayed, antibiotics.
How long does acute gingivitis last?
Treatment Time for Gingivitis But for those with gingivitis due to poor oral hygiene, the average time it takes for gingivitis to go away is about 10 to 14 days after your treatment, along with proper oral healthcare. Keep in mind that there are many, many factors that can change the timeline.
Is gingivitis acute or chronic?
There are two forms of gingivitis: chronic and acute. Chronic gingivitis comes from the biofilm (plaque) that covers the teeth and causes inflammation. Acute gingivitis usually comes from specific infections or trauma to the gums.
Which toothpaste is best for gingivitis?
parodontax Extra Fresh – a daily toothpaste that works to remove the plaque bacteria that can cause bleeding gums – a sign of gingivitis. parodontax Clean Mint – a daily toothpaste for removing plaque bacteria that can cause bleeding gums, with a cool, refreshing mint flavor.
What is the fastest way to cure gingivitis?
How to Cure GingivitisBrush Your Teeth Twice a Day. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to gently brush around each tooth. ... Floss Your Teeth Once a Day. Plaque loves to hide in between teeth where toothbrush bristles can't reach. ... Use a Fluoride Mouth Rinse. ... Don't Skip Dental Appointments. ... Avoid Sugary Foods and Beverages.
Will gingivitis go away with brushing?
Steps you can take at home to prevent and reverse gingivitis include: Brush your teeth twice a day or, better yet, after every meal or snack. Use a soft toothbrush and replace it at least every three to four months. Consider using an electric toothbrush, which may be more effective at removing plaque and tartar.
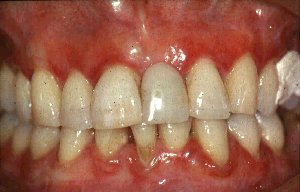
What do gingivitis gums look like?
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease, an infection of the tissues around your teeth caused by plaque. If you have gingivitis, your gums may become red, swollen and bleed easily. You may also experience bad breath.
How long before gingivitis turns into periodontitis?
Slight Periodontal Disease Within two to three weeks, the signs of generalized gingivitis become more noticeable. If you still leave this untreated, it would progress to slight periodontal disease. At this stage, your gums will start to pull away or "recede" from your teeth.
What is the best antibiotic for gingivitis?
What is the best antibiotic for a gum infection? The most common antibiotics used for gum infections are tetracyclines (like minocycline or doxycycline), amoxicillin, clindamycin, metronidazole, ciprofloxacin, and azithromycin.
Do I need antibiotics for gingivitis?
Gum disease like periodontitis or gingivitis can be treated with antibiotics, although they are not recommended as the sole treatment.
Can gingivitis make you sick?
In the early stage of gum disease—called gingivitis—signs such as bleeding gums and slight gum recession are ignored. However, if not addressed in the early stages, it is possible to experience swollen gums that are constantly tender, chills, fever, and a runny nose.
How do dentists treat gingivitis?
Your dentist or periodontist will thoroughly clean your teeth to remove harmful bacteria, plaque and tartar. Additional treatments include: Perform scaling and root planing: Scaling removes tartar and bacteria from teeth and from underneath your gums. Planing smooths the surfaces of the roots of the teeth.
What is the best antibiotic for gingivitis?
What is the best antibiotic for a gum infection? The most common antibiotics used for gum infections are tetracyclines (like minocycline or doxycycline), amoxicillin, clindamycin, metronidazole, ciprofloxacin, and azithromycin.
Do you need antibiotics for gingivitis?
Gum disease like periodontitis or gingivitis can be treated with antibiotics, although they are not recommended as the sole treatment.
How long does it take for gingivitis to turn into periodontitis?
Slight Periodontal Disease Within two to three weeks, the signs of generalized gingivitis become more noticeable. If you still leave this untreated, it would progress to slight periodontal disease. At this stage, your gums will start to pull away or "recede" from your teeth.
What is gingivitis in the body?
Gingivitis refers to a group of periodontal diseases . The gingiva enters the periodontal complex of the tissues.
What are the forms of gingivitis?
By forms: gingivitis is divided into catarrhal, hypertrophic and ulcerative.
What is the spread of atrophic gingivitis?
Atrophic gingivitis spreads to the interdental papillae, they resemble cutting, the marginal gums are also flattened. Atrophic gingivitis is the storehouse of infection, it can provoke the development of exacerbation of internal disease.
What to do if you have gingivitis on your eighth tooth?
If the cause of gingivitis is the eruption of the eighth tooth, rinse with solutions of weak anesthetics (chamomile, sage), a soda solution. In case of difficulty, the eruption of the gums is surgically opened to facilitate the eruption.
What is the characteristic of chronic catarrhal gingivitis?
Its characteristic is a long, dull current. Patient complaints are not voiced.
How long does it take for gingivitis to form?
The risk of acute gingivitis in children is much higher, since up to 6-7 years of immunity has not yet fully formed, it is finally formed by 14-15 years.
How do you know if you have gingivitis?
The symptoms of gingivitis of the gums are swelling of the gums, pain, which patients especially complain about bleeding when cleaning the teeth or eating solid food, redness and possibly heavy breathing from the mouth.
What are the symptoms of gingivitis?
Signs and symptoms of gingivitis might include: bright red or purple gums. tender gums that may be painful to the touch. bleeding from the gums when brushing or flossing. halitosis, or bad breath.
How to treat gingivitis?
Gingivitis often resolves with good oral hygiene, such as longer and more frequent brushing, and flossing. In addition, an antiseptic mouthwash may help.
What are the two types of gingival diseases?
Types. There are two main categories of gingival diseases: Dental plaque-induced gingival disease: This can be caused by plaque, systemic factors, medications, or malnutrition. Non-plaque induced gingival lesions: This can be caused by a specific bacterium, virus, or fungus.
What causes gingivitis in the mouth?
Causes. The most common cause of gingivitis is the accumulation of bacterial plaque between and around the teeth. The plaque triggers an immune response, which, in turn, can eventually lead to the destruction of gingival, or gum, tissue. It may also, eventually, lead to further complications, including the loss of teeth.
What is the term for the inflammation of the gums?
Gingivitis means inflammation of the gums, or gingiva. It commonly occurs because a film of plaque, or bacteria, accumulates on the teeth. Gingivitis is a non-destructive type of periodontal disease, but untreated gingivitis can progress to periodontitis. This is more serious and can eventually lead to loss of teeth.
How can gingivitis be reversed?
Treatment. If diagnosis happens early, and if treatment is prompt and proper, gingivitis can be successfully reversed. Treatment involves care by a dental professional, and follow-up procedures carried out by the patient at home.
Why do people with gingivitis have a higher risk of developing it?
This is thought to be due to the type of bacteria we acquire during our early life.
How to treat acute necrotizing gingivitis?
Oral hygiene. Following a proper daily oral hygiene routine is essential for the treatment of Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis. Teeth should be brushed gently with a soft toothbrush at least twice a day after very meal and flossed at least once a day. If the gums feel very painful for brushing, an antiseptic mouthwash may be used for a few days for the home treatment of ANUG, until the pain subsides enough to allow brushing and flossing. Salt water rinses and hydrogen peroxide mouthwashes can also help soothe the pain of sore gums.
What Causes Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis?
The main cause of Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis is the excessive growth of certain harmful bacteria in the mouth, resulting in severe infection of the gums.
How to treat acute necrotizing ulcerative gum disease?
The main goals of the treatment of Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis are to stop the infection, relieve the symptoms and restore the damaged gum tissue using: Antibiotics and Pain Relief Medications. Dentists often prescribe antibiotics in order to fight the bacterial growth and prevent infection from spreading.
What is the name of the disease that is caused by a soldier's teeth?
Another common name for Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis is ‘trench mouth’ which comes from World War I, when many soldiers suffered from the disease as they were fighting in the trenches under extremely stressful conditions and without the means to take proper care of their teeth and gums.
What is the condition of the gums that causes ulcers?
Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis is a severe and painful inflammation of the gums, which causes deep ulcerations of the gingival tissues. The condition is caused by poor oral hygiene combined with poor nutrition and weak immune system. If left untreated, the infection can lead to the necrosis of gum tissues and may spread to other areas ...
What causes trench mouth?
Several factors can increase the risk of developing trench mouth by disrupting the normal balance of bacteria in the mouth : Lack of dental care and overall poor dental hygiene allows the build-up of dental plaque on the gums and contributes to the development of ANUG.
What is the grayish film on the gums?
Grayish film on the gums, created by decomposed gum tissue, is one of the most characteristic symptoms of trench mouth.
What causes acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis?
Other risk factors are poor oral hygiene, nutritional deficiencies, immunodeficiency (eg, HIV/AIDS, use of immunosuppressive drugs), and sleep deprivation. Some patients also have oral candidiasis.
What is anug necrosis?
The hallmark sign of ANUG is necrosis and cratering of the interproximal papillae, referred to as “pun ched-out papillae.". Image courtesy of Craig Fowler, DDS. Often, ANUG can manifest without a significant odor, and it also may manifest as a localized condition.
How to treat anug?
Treatment of ANUG consists of gentle debridement with a hand scaler or ultrasonic device. Debridement is done over several days. The patient uses a soft toothbrush or washcloth to wipe the teeth.
