
Addition polymerization, or chain reaction polymerization, requires the monomers A monomer (mono-, "one" + -mer, "part") is a molecule that may bind chemically or supramolecularly to other molecules to form a (supramolecular) polymer. The process by which monomers combine end to end to form a polymer is called polymerization. Molecules made of a small number of monomer units (up to a few dozen) are called oligomers.Monomer
What is an example of an addition polymer?
What Are Some Examples of Polymers?
- Natural Polymers. Polymers are both found in nature and manufactured in laboratories. ...
- Synthetic Polymers. Polymers were first manufactured by people seeking substitutes for natural ones, in particular, rubber and silk.
- Non-Polymers. ...
What is the difference between addition and condensation?
this chain reaction can be of three types:
- Dedication
- Spreading
- Termination
How are addition polymers formed?
Optional Activity: Building polymers
- Join three of each type of monomer to form polyethene, polypropene and polyvinyl chloride.
- Identify the repeating unit in each polymer.
- List the differences and similarities between the monomers and the repeating unit.
What is polynomial addition?
What is Adding Polynomials? Adding polynomials is defined as summing up the like terms of two or more algebraic expressions by retaining their sign to get the result. It is very similar to a regular addition operation. For example: Let's add 3x + 8 and - 2x + 1. This will be (3x - 2x) + (8 + 1) = x + 9.
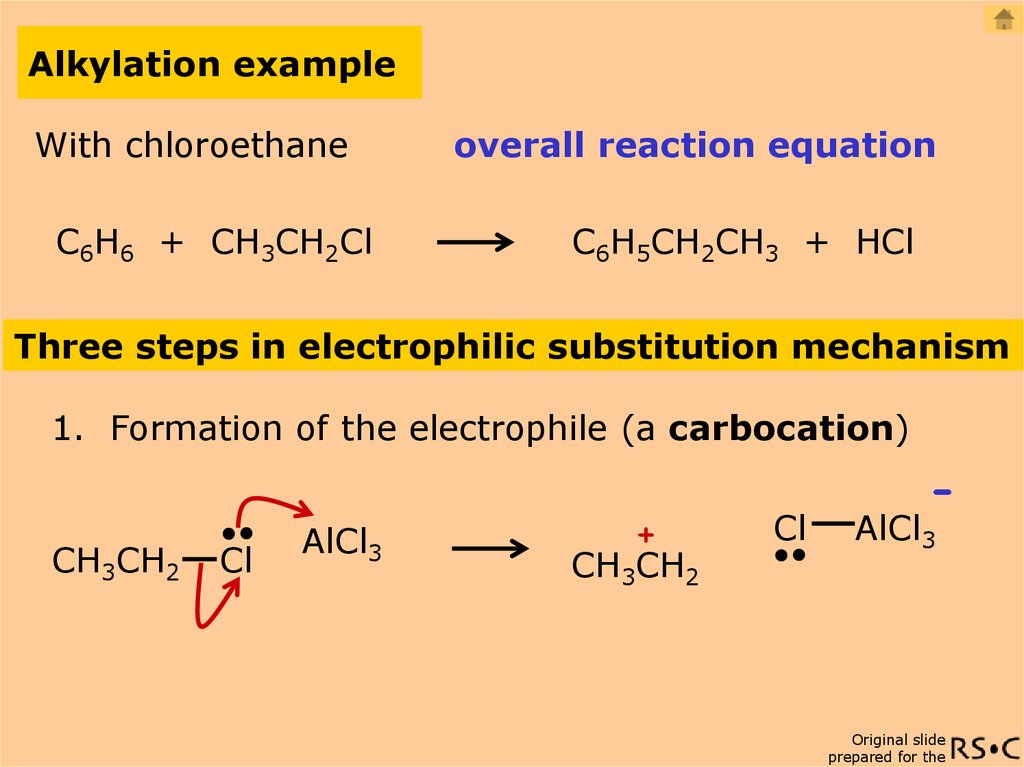
What is an addition polymerisation reaction?
Addition polymerisation involves addition reactions in which a large number of small molecules (monomers) join together to form very large molecules (polymers). In addition polymerisation the monomers have at least one double bond between carbon atoms.
What is addition polymerization with example?
Addition polymerization is when the monomer molecules bond to each other without the loss of any other atoms. Examples of addition polymers include polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, polyvinylchloride, polytetrafluoroethylene, etc.
What is addition polymerization and condensation polymerization?
Addition polymerization is the process of repeated addition of monomers that possess double or triple bonds to form polymers. Condensation polymerization is a process that involves repeated condensation reactions between two different bi-functional or tri-functional monomers.
What is meant by addition polymers?
In polymer chemistry, an addition polymer is a polymer that forms by simple linking of monomers without the co-generation of other products. Addition polymerization differs from condensation polymerization, which does co-generate a product, usually water.
What is addition polymerization example class 12?
Give example . Solution : Addition polymer: The polymer which is formed by the addition of molecules of monomers of same type (or) different type containing double bonds is called addition polymers .
E.g. polythene ,poly acrylonitrile.
What is addition polymerization with Example Class 12?
Addition polymerization The formation of addition polymers occurs by the repeated addition of monomer molecules which possess triple or double bonds. For example, the formation of ((C3H6)n) polypropene from (C3H6) propene, and ((C2H4)n) polythene from (C2H4) ethene.
What is the difference between addition polymerization and polymerization?
The addition polymerization definition is that this is the process of repeated addition of monomers. These monomers possess double or triple bonds to form polymers. On the other hand, condensation polymerization is a process that involves repeated condensation reactions between tri-functional or bi-functional monomers.
What are addition and condensation polymers with examples?
Addition polymers include polystyrene, polyethylene, polyacrylates, and methacrylates. Condensation polymers are formed by the reaction of bi- or polyfunctional molecules, with the elimination of some small molecule (such as water) as a by-product. Examples include polyester, polyamide, polyurethane, and polysiloxane.
What are the characteristics of addition polymerization?
Characteristics of AdditionPolymerizationnMany monomers bond together via rearrangement ofbondsnThere is no loss of atoms or molecules when monomersbindnMost of the common addition polymers are formed fromunsaturated monomers (usually having a double bond)nAddition polymers are generally chemically inert.
Why is it called addition polymerisation?
The small molecules which make up polymers are called monomers. Polymers generally form either from an addition reaction or a condensation reaction. An addition polymer is a polymer formed by chain addition reactions between monomers that contain a double bond.
How addition polymerization is formed?
3.12. In addition polymerization, a polymer is formed from monomers via a very reactive intermediate (such as a free radical: an ion or a transition metal alkyl complex). Addition polymerization is categorized as coordination, ionic, and radical polymerization.
What is addition polymerization Igcse?
Addition polymers are formed by the joining up of many monomers and only occurs in monomers that contain C=C bonds. One of the bonds in each C=C bond breaks and forms a bond with the adjacent monomer with the polymer being formed containing single bonds only. Many polymers can be made by the addition of alkene monomers.
What is addition polymerization Igcse?
Addition polymers are formed by the joining up of many monomers and only occurs in monomers that contain C=C bonds. One of the bonds in each C=C bond breaks and forms a bond with the adjacent monomer with the polymer being formed containing single bonds only. Many polymers can be made by the addition of alkene monomers.
What are addition polymers Class 12?
An addition polymer is a polymer formed by simply linking the monomers with no co-generation of other products. These polymers are generally made from molecules having carbon-carbon double bonds which means addition polymers are prepared from alkenes. They are also called chain growth polymers.
Is nylon 66 an addition polymer?
Nylon-6,6 is not an example of addition polymer. It is a condensation polymer. This polymer is prepared by the condensation copolymerisation of hexamethylene-diamine and adipic acid under high pressure and at high temperature.
How addition polymerization is formed?
3.12. In addition polymerization, a polymer is formed from monomers via a very reactive intermediate (such as a free radical: an ion or a transition metal alkyl complex). Addition polymerization is categorized as coordination, ionic, and radical polymerization.
What is the process of adding polymerization?
The initiator, usually BPO, dissociates upon the provision of thermal, chemical, or light energy and generates free radicals in a process called activation. These free radicals react with the C C of the methyl methacrylate monomer, resulting in the formation of a single C–C bond and another free radical at the advancing end of the chain is created. This stage is physically characterized by the mixing of PMMA beads with the MMA monomer, and the mixed polymer appears as a grainy or sandy mass.
Why is addition polymerization exothermic?
The polymerization reaction has exothermic nature because the process involves the formation of new bonds. The negative ∆ S arises from the decreased degree of freedom of the polymer compared to the monomer. Gibbs free energy (∆ G) depends on both parameters and is given by
How does the function of a monomer affect the structure of a polymer?
The functionality of the monomer greatly affects the architecture of the resulting polymer. Difunctional monomers result in linear polymers because they can only grow from either end, but trifunctional monomers allow the chain to branch, e.g., the reaction between a triol and dibasic acid. Tetrafunctional monomers can also be used to create a very high degree of branching or a network polymer.
What is coordination polymerization?
Coordination polymerization is another variant of addition polymerization which is neither free radical nor simply ionic. In coordination polymerization the monomers with side groups are attached to the growing chain in a highly defined spatial arrangement (stereoregular). The significant feature of this mechanism is the ability to orient each monomer and join it to the growing polymer chain in a very specific configuration. There is a high interest of these materials in the field of molecule-based magnetic materials and in creating molecules that can self-assemble in predetermined fashion into a larger architecture. Some of the uses of these polymers are in creating nonlinear properties such as porosity, selective optical activity, reactive networks, luminescence, and multifunctional materials [7].
What is the process of adding monomers to a growing polymer?
In addition polymerization (sometimes called chain-growth polymerization), a chain reaction adds new monomer units to the growing polymer molecule one at a time through double or triple bonds in the monomer. The polymerization process takes place in three distinct steps:
How is a monomer converted into a polymer?
The monomer is converted into the polymer by the opening of the double bond. Step-growth polymerization is often characterized by the loss (or elimination) of a small molecule such as H 2 O or HCl and a wide range of ‘high-performance’ polymers can be produced using this type of polymerization.
What are the two most common methods of polymer synthesis?
Condensation and addition polymerization are the two most common methods for polymer synthesis. In organic chemistry, reactions are described that occur between different functional groups. For instance, a carboxylic acid group can react with an amine group to form an amide bond and liberate a water molecule.
What is polymerization in polymerization?
polymers. In polymerization. In addition polymerization, monomers react to form a polymer without the formation of by-products. Addition polymerizations usually are carried out in the presence of catalysts, which in certain cases exert control over structural details that have important effects on the properties of the polymer. Read More.
What is chain growth polymerization?
Chain-growth polymerization is most commonly applied to vinyl monomers (that is, monomers containing carbon-carbon double bonds) and to certain types of cyclic monomers (that is, monomers in which the double bond is contained in ring-shaped molecules). The other process, called step-growth polymerization, involves…. Read More.
Is polymerization exothermic or exothermic?
In chemistry of industrial polymers: Industrial polymerization methods. The addition polymerization reactions described above are usually exothermic —that is, they generate heat. Heat generation is seldom a problem in small-scale laboratory reactions, but on a large industrial scale it can be dangerous, since heat causes an increase in ...
Why does polymerization occur in chemical reactions?
The polymerization reaction in many chemical compounds may occur through a variety of reaction mechanisms that differ in complexity because of the presence of the functional groups in the reactants as well as due to their inherent steric effects.
How is the Polymerization Reaction Classified?
Polymers are formed from repeating units of a monomer, which are linked to each other by covalent bonds. The reaction which leads to the formation of polymers from their respective monomers is called Polymerization Reaction. We are talking about polymers but have you thought, ‘what is a monomer?’, a monomer is a reactive molecule which has a simple structure and when these molecules combine and form chains with the help of covalent bonds, a polymer is formed. We can broadly classify the polymerization reaction under the following category:
What happens when you polymerize ethene?
When we polymerize ethene to polythene, we first heat the mixture of ethane with a small amount of benzoyl peroxide initiator. There is an addition of phenyl free radical that is formed by peroxide to the double bond of ethane, which results in generating a new and large free radical.
What type of reaction involves the repetitive condensation between two bi-functional monomers?
Condensation polymerization : This type of reaction involves the repetitive condensation between two bi-functional monomers. There is a loss of some simple molecules such as water and alcohol due to the condensation mechanism. Condensation mechanism refers to combining of smaller molecules to obtain larger molecules.
How many types of polymerization reactions are there?
So far we have seen that there are two types of the polymerization reaction, how the polymerization of monomers take place and the addition and condensation mechanism. The concepts here are explained in brief, for further details and clarification on the topic of polymerization reaction download BYJU’S the learning app.
What is the process of adding monomers to obtain a large chain called?
When we keep adding monomers to obtain a large chain, such a process is also called as the chain growth polymerization. The monomers that are used here are unsaturated ...
What is condensation mechanism?
Condensation mechanism refers to combining of smaller molecules to obtain larger molecules. In these types of the polymerization reaction, the product that is formed after every step is again a bi-functional species, and so these species undergo a sequence of the condensation process.
What is a polymer made of?
A polymer is a substance of high relative formula mass, made up of small repeating units.
Is it difficult to model a polymer molecule?
It is too difficult to model a complete addition polymer molecule, as it contains many atoms. Instead, we show the structure of its repeating unit, the part that is repeated many times. To deduce the structure of a polymer from the monomer:
Is ethene a monomer or polymer?
ethene is the monomer . poly (ethene) is the polymer. The C=C double bond in ethene is involved in the polymerisation reaction. It allows ethene molecules to join together to form a single product, so it is an example of an addition reaction. Poly (ethene) is an addition polymer.
What is addition polymer?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. An addition polymer is a polymer that forms by simple linking of monomers without the co-generation of other products. Addition polymerization differs from condensation polymerization, which does co-generate a product, usually water. Addition polymers can be formed by chain ...
How are addition polymers formed?
Addition polymers can be formed by chain polymerization, when the polymer is formed by the sequential addition of monomer units to an active site in a chain reaction, or by polyaddition, when the polymer is formed by addition reactions between species of all degrees of polymerization. Addition polymers are formed by the addition ...
What is ring-opening polymerization?
Ring-opening polymerization is an additive process but tends to give condensation-like polymers but follows the stoichiometry of addition polymerization. For example, polyethylene glycol is formed by opening ethylene oxide rings:
What is the name of the process in which the growth of a polymer chain proceeds exclusively by reaction (s)?
Chain polymerization: Chain reaction in which the growth of a polymer chain proceeds exclusively by reaction (s) between monomer (s) and active site (s) on the polymer chain with regeneration of the active site (s) at the end of each growth step.
Why are addition polymers more biodegradable than condensation polymers?
In contrast, condensation polymers tend to be more readily bio-degradable because their backbones contain weaker bonds.
What is the most prevalent addition polymer?
The most prevalent addition polymers are polyolefins, i.e. polymers derived by the conversion of olefins (alkenes) to long-chain alkanes. The stoichiometry is simple: n RCH=CH 2 → [RCH-CH 2] n. This conversion can be induced by a variety of catalysts including free radicals, acids, carbanions and metal complexes .
When was the addition polymer invented?
The first useful addition polymer was made by accident in 1933 by ICI chemists Reginald Gibson and Eric Fawcett. They were carrying out a series of experiments that involved reacting organic compounds under high temperatures and high pressures.
What are the chemicals formed by polymerization?
Some of the more common chemicals formed by polymerization include plastics, polyurethane, nylon, proteins, DNA, and RNA. Without this chemical reaction occurring, life as we know it would not exist.
What is polymerization of monomers?
Polymerization that occurs through the coupling of monomers using their multiple bonds is called addition polymerization. The simplest example involves the formation of polyethylene from ethylene molecules. In this reaction, the double bond in each ethylene molecule opens up, and two of the electrons originally in this bond are used to form new carbon-carbon single bonds with two other ethylene molecules.
How do cells break polymers?
Monomers are connected by a reaction in which two molecules are covalently bonded to each other through loss of a water molecule; this is called a condensation polymerization because the lost molecule is water. When a bond forms between two monomers, each monomer contributes part of the water molecule that is lost; one molecule provides a hydroxyl group, while the other provides a hydrogen. To make a polymer, this reaction is repeated as monomers are added to the chain one by one.
What is the process of connecting monomers together and creating large macromolecules of different sizes and shapes?
Polymerization is the process of connecting these monomers together and creating large macromolecules of different sizes and shapes. Polymerization is similar to constructing a large building out of the same type of Lego blocks.
How are bonds between monomers broken?
Bonds between monomers are broken by the addition of water molecules, a hydrogen from the water attaching to one monomer and a hydroxyl attaching to the adjacent monomer. The process of digestion in our bodies is an example of hydrolysis.
What is the process of forming larger macromolecules from simpler sub-units known as monomers?
Polymerization is the process of forming larger macromolecules from simpler sub-units known as monomers. The two major types of polymerization are addition polymerization and condensation polymerization.
How are polymers disassembled?
To make a polymer, this reaction is repeated as monomers are added to the chain one by one. Polymers are disassembled to monomers by hydrolysis, a process that is essentially the reverse of the dehydration reaction. 'Hydrolysis,' from Greek, means to 'break with water.'.
How do addition polymers form?
As the name suggests addition polymers form when an addition reaction occurs. The repeating monomers form a linear or branch structure depending on the type of monomer. During addition polymerization, the monomers rearrange themselves to form a new structure. But there is no loss of an atom or a molecule. Again there are four types of addition ...
What are the four types of addition polymerizations?
Again there are four types of addition polymerizations which are. Free Radical Polymerization: Here the addition polymer forms by addition of atoms with a free electron in its valence shells. These are known as free radicals. They join in a successive chain during free radical polymerization. Cationic polymerization: A polymerization ...
What type of polymers are formed when a monomer is condensation polymerized?
The type of polymers that result from a condensation polymerization depends on the monomers. If the monomer has only one reactive group, the polymers that form have low molecular weight. When monomers have two reactive end groups we get linear polymers.
What is the term for a polymerization where a cation is formed causing a chain reaction?
They join in a successive chain during free radical polymerization. Cationic polymerization : A polymerization where a cation is formed causing a chain reaction. It results in forming a long chain of repeating monomers.
What is the difference between condensation and addition polymers?
The most significant difference is that in addition polymers there is no loss of atom. But in condensation reaction, there is a loss of a molecule of water, ammonia etc as a by-product.
What is the basic unit of polymer?
By now you are familiar with the concept of polymers. They are huge chains or sometimes even 3D structures of repeating units known as monomers. The monomer is the basic unit of a polymer. These monomers can bond to each other on each side, potentially forever.
Which polymer is a result of condensation polymerization?
Polyester and nylon are two common condensation polymers. Even Proteins and Carbohydrates are a result of condensation polymerization.
