
Allele frequency, or gene frequency, is the relative frequency of an allele (variant of a gene) at a particular locus in a population, expressed as a fraction or percentage. Specifically, it is the fraction of all chromosomes in the population that carry that allele over the total population or sample size.
What processes affect allele frequencies in population?
Natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow are the mechanisms that cause changes in allele frequencies over time. When one or more of these forces are acting in a population, the population violates the Hardy-Weinberg assumptions, and evolution occurs.
Which would change the allele frequencies of population?
Allele frequencies in a population may change due to gene flow, genetic drift, natural selection and mutation. These are referred to as the four fundamental forces of evolution. …. The other three forces simply rearrange this variation within and among populations.
What can cause change in allele frequencies in a population?
Change in allele frequencies in a population over generations. What are the three main mechanisms that can cause changes in allele frequency? Natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow ... Chance events can cause allele frequencies to fluctuate unpredictably from 1 generation to the next.
How can genetic drift alter allele frequencies in a population?
Genetic drift stems from the chance occurrence that some individuals have more offspring than others and results in changes in allele frequencies that are random in direction. When individuals leave or join the population, allele frequencies can change as a result of gene flow.
What does allele frequency in a population mean?
Allele frequency refers to how common an allele is in a population. It is determined by counting how many times the allele appears in the population then dividing by the total number of copies of the gene.
How do you find allele frequency of a population?
The frequency of an allele is defined as the total number of copies of that allele in the population divided by the total number of copies of all alleles of the gene. We can calculate population allele frequencies from genotype numbers.
What is allele frequency example?
Example: assuming that in a human population, there are 100 individuals. Since each of them would have two alleles for a particular character (one allele inherited from the father, the other allele from the mother), the total number of genes in this population is 200 (=100 x 2).
What is gene frequency in a population?
Gene frequency is also called allele frequency. It is the ratio of an allele or gene variant present in the population to the total number of all the alleles present in a population for that particular gene, present at the same locus or position on the same chromosome.
Why is allele frequency important?
Relative genotype frequency and relative allele frequency are the most important measures of genetic variation. Relative genotype frequency is the percentage of individuals in a population that have a specific genotype. The relative genotype frequencies show the distribution of genetic variation in a population.
What is the difference between allele and genotype frequency?
Genotype frequency refers to the number of individuals with a given genotype divided by the total number of individuals in the population while allele frequency refers to the frequency of occurrence or proportions of different alleles of a particular gene in a given population.
What does high allele frequency mean?
High derived allele frequency means that a mutation likely occurred somewhere on the human lineage and is now found in about 95% of humans.
What affects allele frequency?
Natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow are the mechanisms that cause changes in allele frequencies over time. When one or more of these forces are acting in a population, the population violates the Hardy-Weinberg assumptions, and evolution occurs.
What is meant by allele frequency quizlet?
Allele frequency. Number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of alleles in that pool for the same gene.
What is gene frequency simple definition?
Definition of gene frequency : the ratio of the number of a specified allele in a population to the total of all alleles at its genetic locus.
How does population size affect allele frequency?
So, while allele frequencies are almost certain to change in each generation, the amount of change due to sampling error decreases as the population size increases. Perhaps the most important point is that the direction of the change is unpredictable; allele frequencies will randomly increase and decrease over time.
What is maximum allele frequency?
The maximum somatic allele frequency (MSAF) is an indicator of the proportion of tumor-derived plasma DNA, which could affect the concordance between bTMB and tissue-based TMB.
How do you calculate allele frequency after selection?
The initial frequency of allele A is (49 + 49 +42)/200 = 0.70. After selection, only 49 AA and 42 Aa individuals survive, for a total of 91 individuals surviving. The frequency of allele A, p, is now (49 + 49 + 42)/(91 + 91) = 140/182 = 0.769.
How do you find allele frequency and genotype frequency?
The frequency of genotype AA is determined by squaring the allele frequency A. The frequency of genotype Aa is determined by multiplying 2 times the frequency of A times the frequency of a. The frequency of aa is determined by squaring a. Try changing p and q to other values, ensuring only that p and q always equal 1.
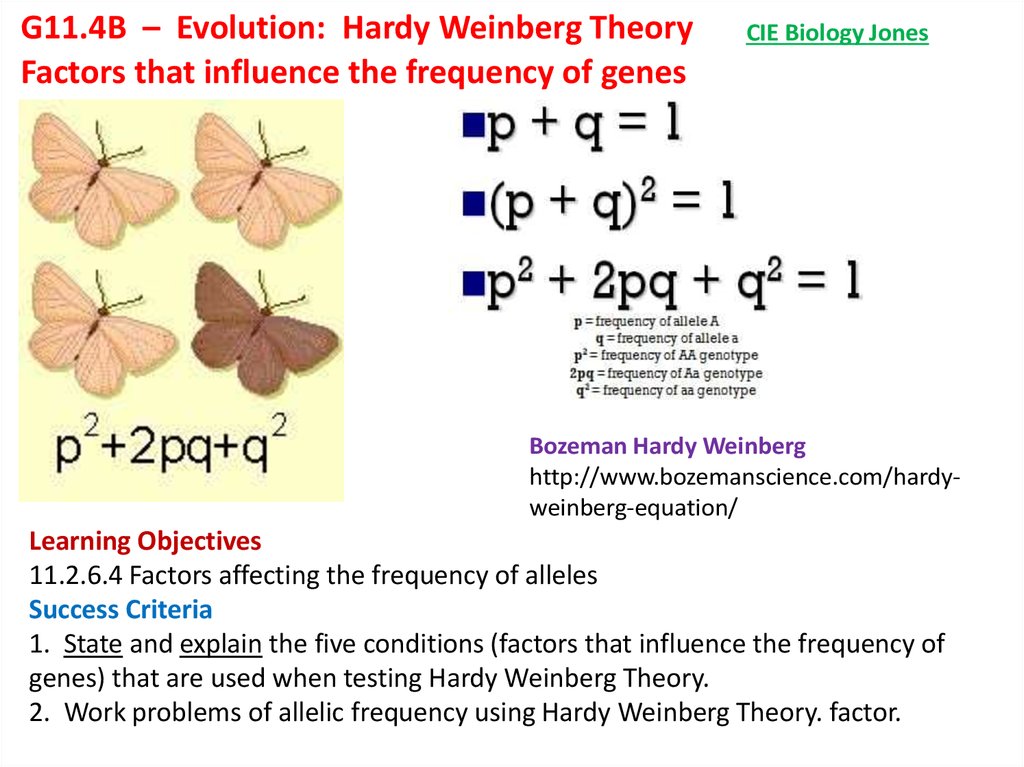
How does Hardy-Weinberg calculate allele frequency?
The Hardy-Weinberg equation used to determine genotype frequencies is: p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1. Where 'p2' represents the frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype (AA), '2pq' the frequency of the heterozygous genotype (Aa) and 'q2' the frequency of the homozygous recessive genotype (aa).
How do you find the allele frequency of two alleles?
Allele FrequencyAllele frequency is most commonly calculated using the Hardy-Weinberg equation, which describes the relationship between two alleles within a population. ... To find the number of alleles in a given population, you must look at all the phenotypes present. ... 1 = p2 + 2pq + q2More items...•
What is the frequency of alleles?
Allele frequency is a term applied to the relative frequency of an allele at a genetic locus in a population . The genotyping approach remains the gold standard of allele frequency determination; however, less expensive, much easier to perform DNA analytical methods for investigating pooled DNA samples have been recently introduced or are currently under investigation. Determining the allele frequency of candidate gene variants and single-nucleotide polymorphisms could have practical applications for, but not limited to, research design and data interpretation, identifying genetic associations with particular diseases or health-related traits, estimating the number of individuals with disease susceptibility or drug resistance in a population, and performing evolutionary and anthropological studies.
How do allele frequencies differ?
The allele frequencies of different populations may differentiate by genetic drift alone without any selection. When a population splits into many populations of effective size N in a generation, the extent of differentiation of allele frequencies in subsequent generations can be measured by Wright's FST Nei and Kumar, 2000. When there are only two populations but allele frequency data are available from many different loci, it is possible to develop a statistic whose expectation is equal to FST. One such statistic is given by
What is the sum of all allele frequencies for a specific locus?
The frequencies for the other alleles are calculated in a similar manner. The sum of all allele frequencies for a specific locus should equal 1.0.
What is the term for the fraction of alleles that are of a particular allele in a defined population?
Alle le frequency (also called gene frequency ) is the term used to describe the fraction of gene copies that are of a particular allele in a defined population.
What is the FST of population?
FST is a measure of genetic differentiation among groups relative to the total amount of genetic variation expected under no subdivision. FST can be difficult to interpret and compare across studies because it is affected by population size, rates of local and long-range gene flow, and time depth, among other influences.
What is differential survival?
The differential survival or reproductive success of individuals, associated with differences in phenotype or genotype.
What is the effect of mutations on fitness?
Mutations whose effects on fitness are either nonexistent or so small that their fate is controlled by genetic drift rather than by selection.
When codominant alleles are present in a two-allele system, each genotype has?
When codominant alleles are present in a two-allele system, each genotype has a characteristic phenotype. The numbers of each allele in both homozygous and heterozygous conditions may be counted in a sample of individuals from the population and expressed as a percentage of total number of alleles in a sample.
What is the function of gene frequency?
Gene frequencies expressed as decimals may be used directly to state probabilities (a probability is a function that represents the likelihood of occurrence of any particular form of an event).
What is the ratio of codominant alleles in Mendelian genetics?
Thus, the frequencies of the two codominant alleles in this sample are almost equal, and this is reflected in the close approximation to a 1: 2: 1 ratio, which is a simple monohybrid ratio for codominant alleles in Mendelian genetics.
Which phenotype is known for certain?
The only phenotype whose genotype is known for certain is the recessive (aa). If the population is in equilibrium then we can obtain an estimate of q (the frequency of the recessive allele) from q^ (the frequency of the recessive genotype or phenotype).
What percentage of population would have recessive phenotype?
If 75% of a population was of the dominant phenotype (A-), then 25% would have recessive phenotype (aa). If the population is in equilibrium with respect to this gene locus, we expect q 2 = frequency of aa.
How many genes are in a L M and L N?
To calculate frequencies of the two codominant alleles, L M and L N, it should be kept in mind that these 6,129 persons possess a total of 6,129 x 2 = 12,258 genes. The number of L M alleles, for example, is 1,787 + 1,787 + 3,039. Thus, calculation of the frequency of L M and L N alleles is worked out in this way.
How much of the American white population can taste?
About 70 per cent of an American white population can taste the substance, generally as very bitter, rarely as sweetish. Although the physiological basis is unknown, tasting ability does depend on a completely dominant gene, which we will designate as T. Thus tasters are T- (TT or Tt) and nontasters are tt.
What is an allele frequency?
An allele frequency is simply how common that particular version of the gene in question is present in this gene pool. So if you have 40 individuals in a population with the following genotypes:
How many alleles are there in the ABO blood type?
The next chart shows how to extend it to situations where there are three or more alleles. It uses the ABO blood types which have three alleles. [ 2]
Why should frequencies stay constant?
To directly answer your question, then, the reason that frequencies should stay constant is that you are grabbing from a mixed bucket of alleles and then creating a new bucket from that grabbing. As long as you are grabbing ‘fairly’ (blindly) and throw all the alleles grabbed into the new bucket (i.e. nobody dies, nobody leaves) then the proportions will remain the same.
What is the allele of a pea?
An allele is one of the form a gene can take , coding for yellow peas is one allele and for green peas another. Basic Mendelian genetics as taught in highschool shows how the alleles of both parents are shuffled when the next generation is produced.
What is the frequency of 40/80?
then you have a total of 40A and 40a alleles, or the frequency of A is 40/80 or 50% = 0.5; and a frequency of 40/80 = 0.5 a as well.
Does the frequency of alleles in a population change?
It states that the frequency of alleles in a population doesn’t change , provided, among other things, that the population is infinite and that there is no selective force acting on it.
Is there migration in or out of the population?
7. There is no migration in or out of the population. Human populations are by definition constantly migrating, this seems to be a fact of human biology, our wanderlust. Globalization may remove reproductive barriers to some extent, but different human populations have different influxes of people from different parts of the world.

Allele Frequency Overview
- The allele frequency is different from the phenotypic ratioin that it accounts for all alleles, even if they are recessive and are “hidden” within carrier organisms. The phenotypic ratio only describes the phenotypes, or actual physical features that are present within a population. To find the allel…
How to Calculate Allele Frequency
- To find the number of alleles in a given population, you must look at all the phenotypes present. The phenotypes that represent the allele are often masked by dominant and recessive alleles working in conjunction. To analyze the allele frequency in a population, scientists use the Hardy-Weinberg (HW) equation.The Hardy-Weinberg equation is written as follows: 1 = p2 + 2pq + q2 …
Allele Frequency Example
- In a simplified scenario, p and q are the only alleles in the population, and the population is not developing any mutations.If this is the case, the sum of the allele frequencies of p and q must equal 1 because with only two alleles the combined frequency must equal 100%.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Trying to Find p First
One mistake that students commonly make is trying to calculate p by observing the population, then taking the square root. This does not work in typical recessive/dominant allele relationships, simply because a dominant allele can hide a recessive allele. For instance, if we were to calculat… - Relating Allele Frequency to Fitness
A common misconception of allele frequency is that it is directly related to the evolutionary fitness of a particular allele. Just because an allele is frequent or infrequent has no bearing on the fitness of that allele.For example, many recessive traits that are deleterious “hide” in a populatio…