Full Answer
How can I prevent an embolic stroke?
You can further prevent a stroke by following a healthy lifestyle:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Exercise regularly.
- Drink alcohol only in moderation.
- Refrain from illegal drug use.
What are the symptoms of an acute stroke?
What are the signs of stroke in men and women?
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body.
- Sudden confusion, trouble speaking, or difficulty understanding speech.
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes.
- Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance, or lack of coordination.
- Sudden severe headache with no known cause.
Which type of stroke is most common?
What is the most common type of stroke?
- Ischemic Stroke (Clots) Occurs when a blood vessel supplying blood to the brain is obstructed.
- Hemorrhagic Stroke (Bleeds) Occurs when a weakened blood vessel ruptures.
- TIA (Transient Ischemic Attack) Called a “mini stroke,” it's caused by a serious temporary clot.
- Cryptogenic Stroke.
What are the signs and symptoms of CVA?
- Unilateral (one-sided) weakness and/or numbness
- Unilateral facial drooping
- Unilateral vision changes
- Difficulty speaking
- Loss of ability to understand or express speech
What is the most common cause of an embolic stroke?
Embolic strokes are usually caused by a blood clot that forms elsewhere in the body (embolus) and travels through the bloodstream to the brain. Embolic strokes often result from heart disease or heart surgery and occur rapidly and without any warning signs.
How serious is an embolic stroke?
Embolic stroke is a life-threatening condition. Every second counts. Blood flow to the brain must be restored as quickly as possible. Your doctor may do this with oral or intravenous clot-busting medications.
What happens during an embolic stroke?
Embolic strokes occur when clots migrate from the source to block more distal cerebral arteries causing cessation of brain tissue perfusion and ischemia.
What is considered acute stroke?
An acute stroke starts suddenly and worsens quickly. It occurs when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, which can injure brain cells and tissues.
Can you recover from a embolic stroke?
If you're with someone you suspect is having a stroke, call 911 right away and observe the person closely while waiting for assistance. Remember, prompt embolic stroke treatment greatly improves a patient's chances of recovery.
What is the most serious type of stroke?
Hemorrhagic strokes are extremely dangerous because the blood in the brain can sometimes lead to further complications such as hydrocephalus, increased intracranial pressure, and blood vessel spasms. If not treated aggressively, these conditions can lead to severe brain damage and even death.
Is an embolic stroke a mini stroke?
A transient ischemic attack (TIA), or “mini stroke,” usually happens before a thrombotic stroke. Embolic stroke is caused by a clot that travels from somewhere else in the body, usually the heart. The clot then blocks an artery leading to or in the brain.
What is the difference between an embolism and stroke?
Thrombotic strokes are caused by a blood clot (thrombus) in an artery going to the brain. Embolic strokes occur when a clot that's formed elsewhere (usually in the heart or neck arteries) travels in the blood stream and clogs a blood vessel in or leading to the brain.
Is an embolism the same as a stroke?
embolic stroke. The other type of ischemic stroke is an embolic stroke. In this case, the blood clot, called an embolus, forms in another part of the body. It moves with your blood to an artery in your brain where it gets stuck and blocks off the artery.
What happens after an acute stroke?
Strokes can cause weakness or paralysis on one side of the body, and can result in problems with co-ordination and balance. Many people also experience extreme tiredness (fatigue) in the first few weeks after a stroke, and may also have difficulty sleeping, making them even more tired.
What can cause an acute stroke?
There are two main causes of stroke: a blocked artery (ischemic stroke) or leaking or bursting of a blood vessel (hemorrhagic stroke). Some people may have only a temporary disruption of blood flow to the brain, known as a transient ischemic attack (TIA), that doesn't cause lasting symptoms.
Is Acute Stroke curable?
Can stroke be cured? The short answer is yes, stroke can be cured — but it occurs in two stages. First, doctors administer specific treatment to restore normal blood flow in the brain. Then, the patient participates in rehabilitation to cure the secondary effects.
How long does it take to recover from an embolic stroke?
It may take six months or more to restore lost functions after a stroke. Many recover entirely and return to work and fulfilling lives.
Where do most embolic strokes occur?
Summary. Embolic strokes occur when blood clots or other blockages form outside the brain and travel to the brain, interrupting blood flow to part of the brain. Most of the time, this type of stroke is caused by a blood clot that forms in the heart.
What is the difference between ischemic and embolic stroke?
There are three types of Ischemic strokes: Thrombotic strokes are caused by a blood clot (thrombus) in an artery going to the brain. Embolic strokes occur when a clot that's formed elsewhere (usually in the heart or neck arteries) travels in the blood stream and clogs a blood vessel in or leading to the brain.
Can you survive a embolism?
Pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening. About one-third of people with undiagnosed and untreated pulmonary embolism don't survive. When the condition is diagnosed and treated promptly, however, that number drops dramatically.
Which type of stroke is the most severe?
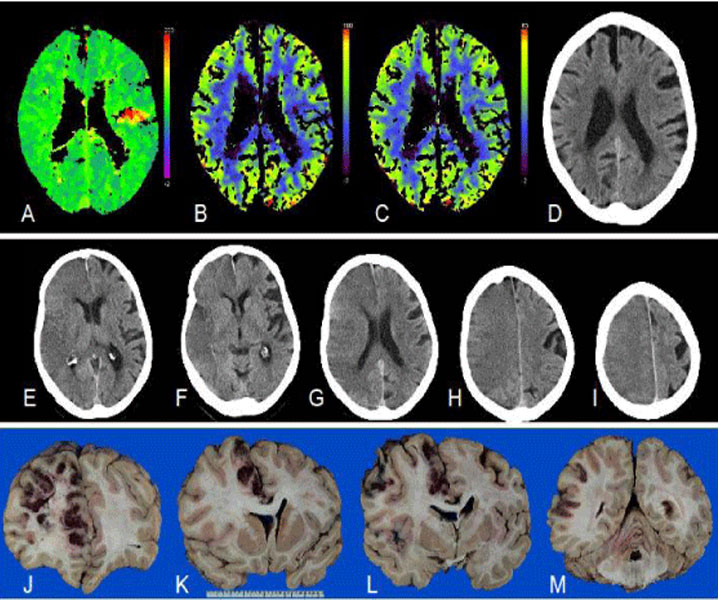
Ischemic strokes of cardioembolic source are generally the most severe ischemic stroke subtype. Although cardiac emboli can be variable in size, the emboli arising from blood stasis within the left cardiac chambers are usually large in size and may cause large vessel occlusions such as Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) and basilar artery occlusions, and hence severe strokes with higher rates of morbidity and mortality. They also carry a higher risk of stroke recurrence. [6][7]
What are the risks of embolism?
The embolism risk is variable. The most common potential high-risk cardiac conditions that can cause embolic ischemic stroke include atrial fibrillation (AF), recent myocardial infarction, mechanical prosthetic valve, dilated myocardiopathy, and mitral rheumatic stenosis respectively. However other identifiable high-risk cardioembolic sources include infective bacterial endocarditis, nonbacterial marantic endocarditis, and left atrial myxoma which is a rare condition but the most common tumor originating from the heart.
What causes AF in the heart?
AF is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia and cause of cardioembolic stroke. This is related to associated low cardiac output, blood stasis which is associated with increased concentration of prothrombotic fibrinogen, D-dimer, and von Willebrand factor, and results in thrombus formation within the atrial appendage and hence increased risk for cardioembolic strokes. Prevalence of AF increases with age particularly in people over 65 years reaching a peak of 5% in this group age. Hypertensive heart disease remains the most common underlying cause of AF in developed countries. Other associated causes of AF include heavy alcohol drinking, valvular heart disease, especially in developing countries, and thyrotoxicosis. [8]
How many strokes are cryptogenic?
In the United States, about 25 % of strokes are cryptogenic, and one-sixth are considered Embolic Strokes of Undetermined Source (ESUS). ESUS was first defined in 2014 as a stroke that appears non-lacunar in Neuroimaging with no evidence of underlying atrial fibrillation, carotid stenosis, or dissection. [10]
Why is neuroimaging important for stroke?
In addition to history and physical examination, neuroimaging is crucial for stroke evaluation in order to confirm the stroke and understand the underlying etiology. Lacunar infarcts and particularly multiple lacunar infarcts of different ages make an underlying cardioembolic cause unlikely. Lacunar infarcts are small 0.2 to 15 mm in diameter noncortical infarcts caused by occlusion of a single penetrating branch of a large cerebral artery. It is mainly related to small vessel disease, and hypertension remains the most common vascular risk factor associated with this condition. [14]
What are the three main mechanisms that cause ischemic stroke?
There are three main mechanisms that can cause an ischemic stroke; thrombosis, hypoperfusion, or embolic phenomena. [4]
When should stroke mimics be considered?
Stroke mimics should be considered when evaluating patients with suspected embolic strokes in the Emergency department.
What is embolic stroke?
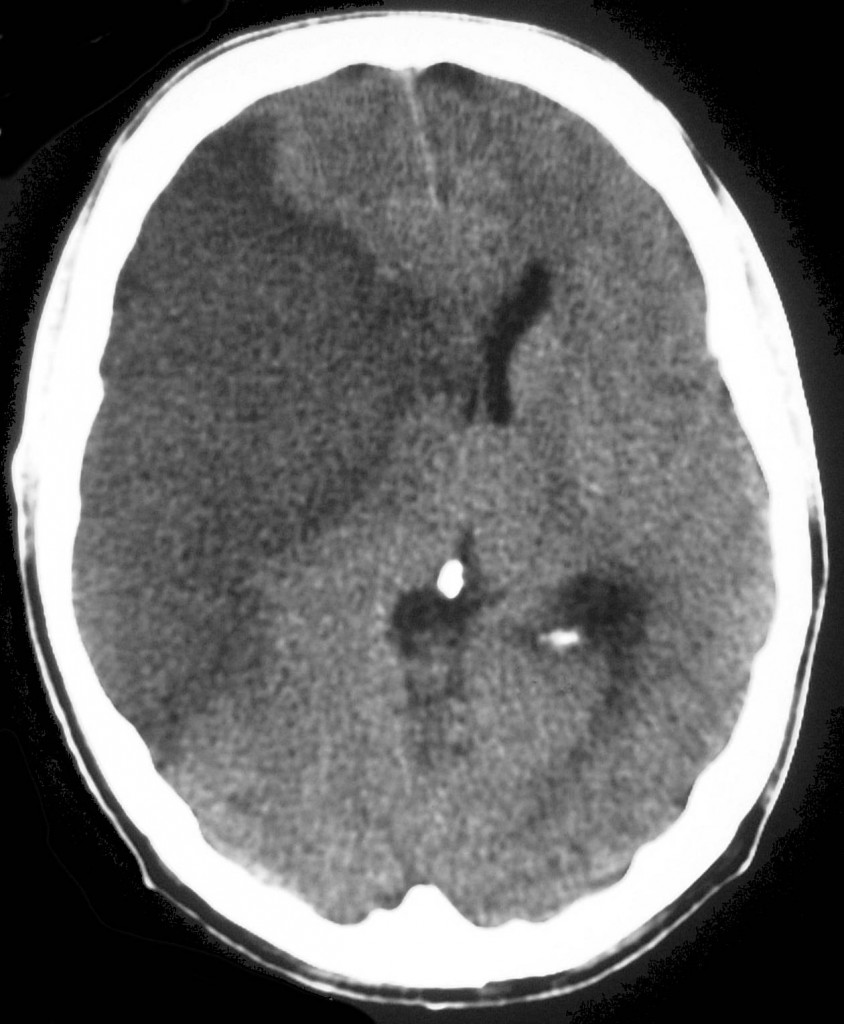
An embolic stroke is a type of ischemic stroke, which results from a blockage of blood flow to the brain. Embolic events begin when a clot forms somewhere other than the arteries that directly supply the brain with blood, such as the arteries of the heart. This clot can break off and travel through the arteries of the body before becoming lodged in the narrower vessel that provides the brain with blood, thereby stopping the flow of oxygen to the brain.
Should an embolic stroke be taken seriously?
As a life-threatening condition, embolic stroke should be taken seriously and promptly addressed. A patient experiencing an embolic stroke should immediately call 911 or go to the hospital, where doctors can perform various diagnostic tests, such as:
What is an embolic stroke?
Updated on July 24, 2021. Embolic stroke is a type of ischemic stroke, which occur when blood flow to the brain is interrupted because an artery is blocked. More than 85 percent of strokes are ischemic .
How to diagnose stroke?
Stroke diagnosis begins with a physical and neurological exam. In addition to checking your vital signs (such as blood pressure), a first responder or your doctor will also test your reflexes, look for limb weakness or numbness and perform an exam to see how well your nervous system is working.
What happens when a blood clot forms in the brain?
Unlike a thrombotic stroke (which happens when a blood clot forms in an artery in the brain) an embolic stroke occurs when an embolus —a blood clot or other blockage–travels to the brain from another part of the body. A stroke is a medical emergency. When the brain cannot get the blood it needs to function, brain cells start to die.
What are the symptoms of an ischemic stroke?
These include: 2. Numbness or weakness (especially on one side of the body) Difficulty walking, or trouble with coordination and balance. Dizziness or vertigo.
How to tell if you have a stroke?
Whether the blockage forms in the brain or elsewhere, ischemic strokes share the same symptoms. These include: 2 1 Numbness or weakness (especially on one side of the body) 2 Difficulty walking, or trouble with coordination and balance 3 Dizziness or vertigo 4 Speech problems, such as slurring 5 Nausea or vomiting 6 Sudden headache with no specific cause
What are the risk factors for stroke?
High blood pressure. High cholesterol. Coronary artery disease or heart valve disease. Other risk factors for stroke can include: Age: The chance of having a stroke approximately doubles for each decade of life after age 55. While stroke is common among the elderly, a lot of people under 65 also have strokes.
Why do African Americans have a higher risk of stroke than Caucasians?
This is partly because blacks have higher risks of high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity. Gender: Each year, women have more strokes than men, and stroke kills more women than men.
How to diagnose embolic stroke?
How to diagnose and treat embolic stroke. Any kind of stroke is a life-threatening medical emergency and should be treated immediately. Diagnosis can take several different routes, but most often includes blood tests and brain imaging. Blood tests can determine how quickly the patient’s blood normally clots, whether there is a critical chemical ...
Where does embolic stroke come from?
The blood clot that causes the embolic stroke can originate from anywhere in the body, but it most often comes from the heart or somewhere in the upper chest or neck. The blockage created when it enters a blood vessel too small to pass through is called an embolus. Emboli are created from air bubbles, fat, and plaque found in the vessel wall.
What happens when blood clots in the brain are blocked?
Once in the brain, the blood clot gets lodged in an artery, resulting in an embolic stroke. Embolic strokes are a type of ischemic stroke, which occur when arteries in the brain become blocked and account for 80 percent of all strokes. The brain relies on arteries to bring in blood, which carries the oxygen and nutrients it needs ...
How to treat a stroke in the brain?
As the stroke is caused by a blood clot that moves into the brain, one common treatment is clot-dissolving medication. These can be administered orally or through an intravenous and are sometimes injected through a catheter. In some cases, surgery may be required to prevent additional strokes. This involves widening the arteries where there is a build-up of fatty deposits or plaque and is called a carotid endarterectomy. The surgeon may even install stents to keep the blood vessel from collapsing. Long-term treatment is often focused on regaining any motor or cognitive functions that were impaired by the stroke. Therapies include physiotherapy and speech therapy.
What are the complications of embolic stroke?
Common complications derived from a stroke include brain edema or the swelling of the brain, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, seizures, depression, bedsores, limb contractures or muscle shortening due to infrequent movement in the affected area, ...
What causes emboli in the heart?
Emboli are created from air bubbles, fat, and plaque found in the vessel wall. They can also be caused by an irregular heartbeat, which is called atrial fibrillation. Conditions that increase the risk of stroke include high blood pressure, heart disease, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, and an unhealthy lifestyle.
What happens if you have a stroke?
A stroke could also induce difficulty speaking and understanding speech (aphasia), difficulty moving one side of the body (hemiparesis), and lack of sensation on one side of the body (hemisensory deficit).
What is embolic stroke?
An embolic stroke occurs when some brain artery is occluded by an embolus. An embolus is some object or mass traveling with a blood flow. Emboli may have gas, liquid or solid composition. Embolic strokes caused by fat (in bone fractures), gas, or liquid (amniotic fluid during labor) are relatively rare. The majority of embolic strokes are caused by blood clot fragments.
What are the risk factors for stroke?
Presence of other risk factors, such as congestive heart failure, diabetes, hypertension, heart valve disease, or previous strokes, increase the chance of stroke.
What is the best treatment for atrial fibrillation?
The mainstay of stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation is a pharmacological delay of blood clot formation. It is called an anticoagulation therapy. Warfarin (Coumadin) reduces the chance of stroke 68%.
What is it called when a blood clot is formed in the brain?
Eventually, this embolus reaches some smaller artery and plugs it. Occlusion of some brain or spinal cord artery by embolus is called embolic stroke.
What is the most vulnerable part of the heart?
Especially vulnerable portion is called an atrium appendage. It is a pouch attached to the left atrium. Slow blood flow within this pouch promotes clot formation inside of this structure. Pieces of the clot may get into the bloodstream and cause a stroke.
Do cardioembolic strokes recur?
Cardioembolic strokes tend to recur if nothing is done about stroke prevention.
Is ischemic stroke the same as thrombolytic therapy?
Acute ischemic stroke management is the same irrelevantly of the cause – thrombolytic therapy. In emergency setting it is not practical to differentiate the exact mechanism of ischemic stroke.
What is the most important concept in understanding acute stroke and its treatment?
This is the most important "time is brain" concept in understanding acute stroke and its treatment. There are numerous causes of stroke, such as prolonged hypertension, arteriosclerosis, and emboli that have formed in the heart as a result of atrial fibrillation or rheumatic heart disease.
What is a stroke in continuing education?
Continuing Education Activity. Acute strokes, also known as cerebrovascular accidents, are broadly classified as either ischemic or hemorrhagic. Acute strokes result in loss of blood flow, nutrients and oxygen to a region of the brain, resulting in neuronal damage and subsequent neurological deficits.
What is the commoner type of stroke?
The commoner type is an ischemic stroke, caused by interruption of blood flow to a certain area of the brain. Ischemic stroke accounts for 85% of all acute strokes. 15% of acute strokes are hemorrhagic strokes which are caused by bursting of a blood vessel i.e. acute hemorrhage.
What are the two types of strokes?
There are two main types of strokes. The commoner type is an ischemic stroke, caused by interruption of blood flow to a certain area of the brain. Ischemic stroke accounts for 85% of all acute strokes. 15% of acute strokes are hemorrhagic strokes which are caused by bursting of a blood vessel i.e. acute hemorrhage.
What are the risk factors for stroke?
Some of the most common risk factors include hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, physical inactivity, obesity, genetics, and smoking. Cerebral emboli commonly originate from the heart, especially in patients with preexisting heart arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation), valvular disease, structural defects (atrial and ventricular septal defects) and chronic rheumatic heart disease. Emboli may lodge in areas of preexisting stenosis.[3] Alcohol intake has a J-shaped relationship with ischemic stroke. Mild to moderate drinking carries a slightly lower risk of ischemic stroke yet heavier drinking increases the risk drastically. Alcohol intake increases the risk of hemorrhagic stroke in a near linear relationship.
How many types of strokes are there?
According to the TOAST[1]classification, there are four main types of ischemic strokes. These are large vessel atherosclerosis, small vessel diseases (lacunar infarcts), cardioembolic strokes and cryptogenic strokes. Each of these has different causes and pathophysiology. Regardless o the type of stroke, it is important to know that with each minute of large vessel ischemic stroke untreated, close to two million neurons die. This is the most important "time is brain" concept in understanding acute stroke and its treatment.
How long after stroke should blood pressure be elevated?
Blood pressure should be maintained slightly elevated for the first few days after a stroke to improve perfusion to the peri-infarction zones. Blood pressure should also be lowered by no more than 15% if diastolic blood pressure is over 220 mm Hg or if systolic blood pressure is over 120 mm Hg. BP does need to be lower than 180/110 for IV Alteplase therapy. Comorbidities also need to be addressed and managed during the patient’s hospital stay. [28]
What is a thrombus stroke?
Thrombotic strokes are strokes caused by a thrombus (blood clot) that develops in the arteries supplying blood to the brain. This type of stroke is usually seen in older persons, especially those with high cholesterol and atherosclerosis (a buildup of fat and lipids inside the walls of blood vessels) or diabetes.
What is a hemorrhagic stroke?
Hemorrhagic strokes occur when a blood vessel that supplies the brain ruptures and bleeds. When an artery bleeds into the brain, brain cells and tissues do not get oxygen and nutrients. In addition, pressure builds up in surrounding tissues and irritation and swelling occur, which can lead to further brain damage. Hemorrhagic strokes are divided into 2 main categories, including the following:
What are recurrent strokes?
Recurrent strokes occur in about 1 in 4 people who have had a stroke within 5 years after a first stroke. The risk is greatest right after a stroke and decreases over time. The likelihood of severe disability and death increases with each recurrent stroke. About 3% of people who have had a stroke have a second stroke within 30 days of their first stroke, and about one-third have a second stroke within 2 years.
How long does a stroke last?
Thrombotic strokes may be preceded by one or more "mini-strokes," called transient ischemic attacks, or TIAs. TIAs may last for a few minutes or up to 24 hours, and are often a warning sign that a stroke may occur.
What happens when a blood vessel bleeds into the brain?
Hemorrhagic strokes occur when a blood vessel that supplies the brain ruptures and bleeds. When an artery bleeds into the brain, brain cells and tissues do not get oxygen and nutrients. In addition, pressure builds up in surrounding tissues and irritation and swelling occur, which can lead to further brain damage.
What is a stroke caused by?
Thrombotic strokes. These are caused by a blood clot that develops in the blood vessels inside the brain. Embolic strokes. These are caused by a blood clot or plaque debris that develops elsewhere in the body and then travels to one of the blood vessels in the brain through the bloodstream.
What causes a stroke to occur?
Embolic strokes are usually caused by a blood clot that forms elsewhere in the body ( embolus) and travels through the bloodstream to the brain. Embolic strokes often result from heart disease or heart surgery and occur rapidly and without any warning signs.
What is the thrombus in a stroke?
In a thrombotic stroke, the artery is blocked by a thrombus (blood clot) that forms there. The thrombus is made up of a hardened buildup of cholesterol and other substances, which is called plaque.
What is the other type of ischemic stroke?
Vs. embolic stroke. The other type of ischemic stroke is an embolic stroke. In this case, the blood clot, called an embolus, forms in another part of the body. It moves with your blood to an artery in your brain where it gets stuck and blocks off the artery.
What are the risk factors for a thrombotic stroke?
The risk factors for a thrombotic stroke are the same as for atherosclerosis. They include: high cholesterol. high blood pressure.
What is the best treatment for ischemic stroke?
The current standard treatment for an ischemic stroke is a “clot buster” drug called alteplase. This tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) must be given via a vein within 4.5 hours of stroke onset. It breaks up the clot and opens the artery, so blood can flow to the brain tissue again.
How long after a stroke can you have a mechanical thrombectomy?
It must be done within six hours of the stroke.
How long does it take to recover from a stroke?
A thrombotic stroke can be difficult. It can leave a person unable to walk, talk, or think clearly. But when diagnosed and successfully treated within a few hours, complete recovery is possible.
How high is the risk of a stroke in a smoker?
Stop smoking. According to the National Stroke Association, the risk of a stroke in a smoker is twice as high as that of a nonsmoker.

Embolic Stroke Symptoms
Causes
Diagnosis
Treatment
Risk Factors For Stroke
Prognosis
Summary
- Embolic strokes occur when blood clots or other blockages form outside the brain and travel to the brain, interrupting blood flow to part of the brain. Most of the time, this type of stroke is caused by a blood clot that forms in the heart. This is often caused by Afib, an irregular heart rhythm that allows blood to pool and clot in the heart. Like...
A Word from Verywell