An allogeneic stem cell transplant uses healthy blood stem cells from a donor to replace your diseased or damaged bone marrow. An allogeneic stem cell transplant is also called an allogeneic bone marrow transplant. A donor may be a family member, an acquaintance or someone you don't know.
Full Answer
Why are stem cell transplants used as cancer treatment?
Why are stem cell transplants carried out? Stem cell transplants are used to treat conditions in which the bone marrow is damaged and is no longer able to produce healthy blood cells. Transplants can also be carried out to replace blood cells that are damaged or destroyed as a result of intensive cancer treatment.
What is recovery from a stem cell transplant like?
Recovery is a slow process. Some 55 days after I underwent my stem cell transplant, I am still far from feeling like myself. I have friends who tell me it can take a year or more to regain strength and stamina. Of course, I also have a friend who is running marathons. Recovery is as personal as a fingerprint.
Can a patient be too old for stem cell transplant?
Once you get to 70, it should only be knee replacement according to that research. But as we have found, 70 is too young NOT to explore stem cell therapy. The determination of the effectiveness of stem cell therapy in the elderly needs to be made during a consultation.
Is there limit to the number of stem cell transplants?
There is a wide variation in the number of CD34+ cells infused for an autologous transplantation. While the minimum number of hematopoietic stem cells for a successful transplantation has been established, there is no definite information on the optimum number or the maximum number of stem cells.

What is allogeneic stem cell transplant used for?
An allogeneic stem cell transplant is most often used to treat blood cancers, such as leukemia and lymphoma, and certain types of blood or immune system disorders.
What is the difference between allogeneic and autologous?
Autologous: Auto means self. The stem cells in autologous transplants come from the same person who will get the transplant, so the patient is their own donor. Allogeneic: Allo means other. The stem cells in allogeneic transplants are from a person other than the patient, either a matched related or unrelated donor.
How long does it take to recover from an allogeneic stem cell transplant?
How long does it take to recover from an allogeneic stem cell transplantation? It may take a few months to recover from the transplantation process, including recovering from the pre-transplantation conditioning. It may take a year or two for your immune system to recover while your new stem cells make new blood cells.
How is allogeneic transplant done?
In an allogeneic transplant, a person's stem cells are replaced with new, healthy stem cells. The new cells come from a donor or from donated umbilical cord blood. Chemotherapy or a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy is given before the transplant.
What is the life expectancy after a stem cell transplant?
Compared with the general population, the relative mortality remained higher at 30 or more years after BMT (SMR, 5.4; 95% CI, 4.0-7.1). The cohort experienced a 20.8% reduction in life expectancy (8.7 years of life lost).
What is the age limit for a stem cell transplant?
To summarize, age should never be the sole factor in determining a patient's eligibility for a transplant. Patients as old as 80 could be considered for transplant if it is early in the course of treatment. Other indications include disease progression and overall health.
How painful is a stem cell transplant?
The stem cells will be passed slowly into your body through the central line. This process often takes around a couple of hours. The transplant won't be painful and you'll be awake throughout.
How do I prepare my home for stem cell transplant?
Get rid of dust, mold, mildew, and other tiny particles. Be sure to vacuum and dust all rooms, and shampoo all rugs. If you haven't done so in the past year, clean all of your drapes and blinds. Ask your care team whether it's okay to keep any house plants that you might have in your home.
How do you feel after a stem cell transplant?
It usually takes about 2 to 6 weeks to start seeing a steady return to normal blood cell counts. You will be in the hospital for some of this time. During this time, you may feel tired and generally unwell. You are at risk of fever, infection, bleeding, anemia, damage to the organs and dietary problems.
Is allogeneic stem cell transplant safe?
If you receive a transplant that uses stem cells from a donor (allogeneic transplant), you may be at risk of developing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). This condition occurs when the donor stem cells that make up your new immune system see your body's tissues and organs as something foreign and attack them.
How much does an allogeneic stem cell transplant cost?
The median inpatient costs for myeloablative allogeneic and autologous transplants were $406,195 and $194,125, respectively, for pediatric patients versus $212,332 and $111,419, respectively, for adults.
What is the best hospital for stem cell transplant?
Mayo Clinic is one of the largest providers of bone marrow transplants in the United States. It has performed nearly 10,000 stem cell transplants at its campuses in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota.
Why is autologous better than allogeneic?
Autologous transplants have a lower risk of life-threatening complications; there is no risk of GVHD and no need for immunosuppressive therapy to prevent GVHD and graft rejection. Immune reconstitution is more rapid than after an allogeneic transplant and there is a lower risk of opportunistic infections.
What are the major differences between allogeneic and autologous modes of gene therapy?
While donor's and patient's body during an autologous cell therapy correspond, patients undergoing an allogeneic treatment receive cells from a donor other than themselves.
What is the allogeneic mean?
Listen to pronunciation. (A-loh-jeh-NAY-ik) Taken from different individuals of the same species. Also called allogenic.
What is the difference between allogeneic and Xenogeneic?
A graft transplanted between two genetically different individuals of the same species is called an allogeneic graft (allograft) while a graft transplanted between members of 2 different species is called a xenogeneic graft.
What is an allogeneic stem cell transplant?
When you have an allogeneic stem cell transplant, stem cells are harvested (collected) from a donor. “Allogeneic” means that the stem cells come from someone else. The 3 general sources of stem cells that can be used in an allogeneic stem cell transplant are: Peripheral blood stem cells.
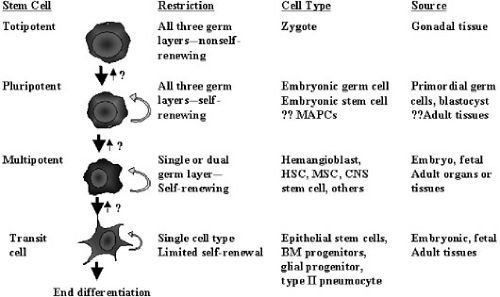
What is the stem cell?
Hematopoietic (hee-MA-toh-poy-EH-tik) stem cells (usually just called stem cells) are immature cells that grow into all the blood cells in your body: the white blood cells that fight infection, red blood cells that carry oxygen, and platelets that help control bleeding. Your stem cells are constantly dividing and changing into these different types of blood cells to replace older blood cells. Stem cells also divide to make newer stem cells.
How long does it take to get T cells from a donor?
If you’re going to have a T cell-depleted stem cell transplant, you’ll get it after the T cells are removed in the laboratory. This takes 12 to 24 hours, so you’ll get it the day after your donor has given the stem cells. The stem cells will be injected directly into your tunneled catheter from a large syringe. There usually aren’t any side effects from the infusion of T cell-depleted stem cells.
How do stem cells travel?
Almost right away after the stem cells are infused into your body, they’ll travel through your bloodstream to your bone marrow. They’ll start to divide and create healthy new blood cells. Engraftment is when your body accepts the transplant and your blood cell counts start to recover.
How long does it take to get discharged from a stem cell transplant?
Once your blood counts have recovered and any side effects or complications you had have resolved, your inpatient team will start working with you and your caregiver to get you ready for discharge. On average, people can be discharged about 3 weeks from their day of transplant. It may be a few days before that or it may be longer than 3 weeks, depending on your stem cell source and your exact treatment plan.
Where do stem cells come from in bone marrow transplant?
With a stem cell transplant, the stem cells are taken from either the bone marrow or the bloodstream.
How long does it take for your immune system to recover from a transplant?
It usually takes 12 to 18 months for your immune system to recover from your transplant. We often tell people that the first year after transplant is like your first year of life as a newborn baby. During that time, you’re at risk for infection. Your transplant team will check your blood cell counts to see how well your immune system is working. This will help them advise you about any changes to the guidelines you must follow.
What is an allogeneic stem cell transplant?
In an allogeneic transplant, stem cells are collected from a matching donor and transplanted into the patient to suppress the disease and restore the patient’s immune system. An allogeneic stem cell transplant is different from an autologous stem cell transplant, which uses stem cells from the patient's own body.
How to find a match for a stem cell transplant?
A donor is often a brother, sister or other relative. In many cases, donor registries are used to find the appropriate match, through tissue typing. Tissue typing uses proteins called human leukocyte antigens (HLA), which are found on white blood cells and tissues, to determine whether a donor’s stem cells are the right match. Through an HLA test, pathologists compare the patient’s blood and tissue type against a donor’s blood samples.
What is a mini transplant?
A mini-transplant is an allogeneic transplant that uses lower, less toxic doses of chemotherapy and/or total body irradiation (TBI) before the transplant procedure.
What is a donor lymphocyte infusion?
This is called a donor lymphocyte infusion. After the transplant, your hematology oncology team will collaborate to reduce the risk of complications and address your needs throughout the stem cell transplant process. Because it takes time to rebuild the immune system following a transplant, doctors will monitor you closely in ...
How long does it take for a stem cell transplant to take place?
Much like a blood transfusion, the donated stem cells are delivered intravenously. The procedure takes about an hour. After entering the bloodstream, the stem cells travel to the bone marrow and begin to produce new blood cells in a process known as engraftment. The transplant restores the supply of normal cells that have been destroyed by ...
Why are stem cells frozen at birth?
And since the cells are frozen at birth, they have avoided environmental damage and aging.
Do cord blood transplants require a compatible tissue type?
Therefore, cord blood transplants generally don’t require an extremely compatible tissue type and may help to reduce the risk of complications. Before an allogeneic stem cell transplant, the patient undergoes a conditioning regimen, which typically involves intensive treatment—high doses of chemotherapy and radiation therapy, ...
What is the concern with allogeneic stem cells?
Another key concern related to allogeneic stem cells transplant is GVHD. More specifically, it is graft-versus-host-disease. The name offers some insight into what this condition is. When it happens, the donor’s stem cells attack the patient’s body. This can create devastating results. There are medications available to reduce some of this risk.
What are the benefits of umbilical cord blood transplant?
First, the stem cells here are younger. They are not as mature as others. This means the cells are able to mature more effectively into various types of new cells . Another benefit is their preservation.
Can stem cells cause complications?
The actual process of transplanting stem cells does not cause many complications. However, the use of intense drugs and radiation beforehand can. Most patients are very weak and struggle as a result. Individuals also need constant monitoring for infection. If an infection occurs, it can be difficult for the body to overcome it. Remember, there is no immune system present.
What is the difference between autologous and allogeneic stem cells?
Transplants can be: Autologous, which means the stem cells come from you, the patient. Allogeneic, which means the stem cells come from someone else. The donor may be a blood relative but can also be someone who is not related. Syngeneic, which means the stem cells come from your identical twin, if you have one.
Where do you go to get an allogeneic stem cell transplant?
When you need an allogeneic stem cell transplant, you will need to go to a hospital that has a specialized transplant center. The National Marrow Donor Program® maintains a list of transplant centers in the United States. that can help you find a transplant center.
What is stem cell transplant?
Stem cell transplants help restore blood-forming stem cells in people who have had theirs destroyed by certain cancer treatments. Stem cell transplants are procedures that restore blood-forming stem cells in people who have had theirs destroyed by the very high doses of chemotherapy or radiation therapy that are used to treat certain cancers.
Why does graft versus tumor occur?
Graft-versus-tumor occurs when white blood cells from your donor (the graft) attack any cancer cells that remain in your body (the tumor) after high-dose treatments. This effect improves the success of the treatments.
What happens if you have an allogeneic transplant?
If you have an allogeneic transplant, you might develop a serious problem called graft-versus-host disease. Graft-versus-host disease can occur when white blood cells from your donor (the graft) recognize cells in your body (the host) as foreign and attack them. This problem can cause damage to your skin, liver, intestines, and many other organs. It can occur a few weeks after the transplant or much later. Graft-versus-host disease can be treated with steroids or other drugs that suppress your immune system.
Why are stem cells important?
Blood-forming stem cells are important because they grow into different types of blood cells. The main types of blood cells are: White blood cells, which are part of your immune system and help your body fight infection. Red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout your body. Platelets, which help the blood clot.
What type of cancer is stem cell transplant?
Who Receives Stem Cell Transplants. Stem cell transplants are most often used to help people with leukemia and lymphoma. They may also be used for neuroblastoma and multiple myeloma. Stem cell transplants for other types of cancer are being studied in clinical trials, which are research studies involving people.
Why are allogeneic stem cells beneficial?
Benefits of Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplants. Because donor stem cells come from another person, the cells can create a new immune system in the recipient. Ideally, the stem cells will begin making new WBCs and immune cells that recognize and kill lingering leukemia cells in the body.
What is the purpose of stem cell transplant?
There are two types of stem cell transplants used to treat leukemia, allo geneic and autologous. In an allogeneic stem cell transplant, stem cells come from a donor. In an autologous transplant, the stem cells come from ...
What Are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are an important part of the body because they can develop into any type of cell. Blood stem cells live in the bone marrow, where they divide and mature into many different types of blood cells. These types of cells include:
Why do autologous stem cells not have a graft versus tumor effect?
However, unlike allogeneic transplants, autologous stem cell transplants do not offer the benefit of a graft-versus-tumor effect, because the recipient’s cells cannot make a new immune system.
What is the best treatment for leukemia?
One option for treating leukemia is an allogeneic stem cell transplant. The term “allogeneic” refers to the fact that the stem cells come from a healthy donor who may not necessarily be a genetic match to the person receiving them.
How do autologous stem cells work?
In the first step of an autologous stem cell transplant, the recipient is treated with medications that cause the body to make more stem cells and move them into the bloodstream. This makes it much easier to collect the stem cells through a needle inserted into a vein in the arm . The blood is then processed through a specialized machine that removes the stem cells and returns the rest of the blood to the recipient. The collected stem cells are then frozen for later use.
Why is HLA important in stem cell transplants?
This protein is especially important in transplants because a person’s immune system recognizes HLA proteins that are different from their own.
