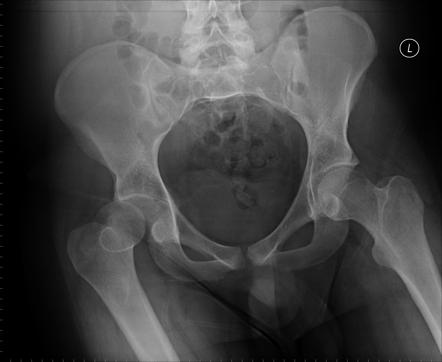
How is an anterior hip dislocation treated?
Anterior hip dislocation is commonly reduced by inline traction and external rotation, with an assistant pushing on the femoral head or pulling the femur laterally to assist reduction. Posterior hip dislocations are the most common type and are reduced by placing longitudinal traction with internal rotation on the hip.
What are the symptoms of anterior hip dislocation?
What are the symptoms of hip dislocation?Acute pain.Muscle spasms.Swelling or discoloration at your hip joint.Leg is rotated inward or outward.Inability to move your leg.Inability to bear weight on your leg.Loss of feeling in your hip or foot.Hip is visibly out of place.
Can hip dislocation be fixed without surgery?
Nonsurgical reduction by manipulation: Usually, an orthopedist can simply push the ball back in by hand while the patient is under anesthesia. If, however, the imaging reveals fractures or significant damage to soft tissues, blood vessels or nerves, orthopedic surgery may be required.
Are anterior or posterior hip dislocations more common?
Posterior hip dislocations (90%) are much more common than anterior hip dislocations; additionally, there is significant morbidity and mortality associated with posterior hip dislocations if there are any associated fractures.
What causes anterior hip dislocation?
Anterior hip dislocations are usually caused by forceful abduction with external rotation of the thigh and most commonly following a motor vehicle accident or fall. Enormous force is required to dislocate a hip as it is quite stable due to its bony construction and the associated muscular and ligamentous attachments.
Can you move your leg if your hip is dislocated?
A hip dislocation is very painful. Patients are unable to move the leg, and, if there is nerve damage, they may not have any feeling in the foot or ankle area.
Is hip dislocation life threatening?
Hip dislocation is a marker for a high-force mechanism. Most mortality is the result of associated injuries. Life-threatening injuries to the pelvis, abdomen, chest, and head should be specifically sought out. Long-term disability after hip dislocation is a significant risk.
Can you sit with dislocated hip?
Your doctor will give you safety precautions to keep your hip centred in its socket during the healing period. Be sure to follow these precautions. Keep your knees and toes pointed forward when you sit in a chair, walk, or stand. Do not sit with your legs crossed.
What does it feel like when your hip pops out of place?
Sometimes the hip joint can feel like it is wobbly or out of place. You might feel like something isn't quite right around the hip area or feel hesitant to take a step or put your full weight on that side of the body. Sometimes when your hip feels out of place it is also accompanied by pain and stiffness in the area.
How much force does it take to dislocate a hip?
About 400 newtons of force are required to cause hip joint separation. 3 Due to the large force required to cause a native hip dislocation, there is a 95% incidence of injury to other areas of the body in these patients, especially injuries to the knee.
In what position is the hip most vulnerable to dislocation?
Hip dislocations are classified by fracture association and by the positioning of the dislocated femoral head. A posteriorly positioned head is the most common dislocation type. Hip dislocations are a medical emergency, requiring prompt placement of the femoral head back into the acetabulum (reduction).
How long does a dislocated hip take to heal?
It can take a minimum of six weeks for any soft–tissue damage around the hip joint to heal.
What are the first signs of hip problems?
What Are the First Signs of Hip Problems?Hip Pain or Groin Pain. This pain is usually located between the hip and the knee. ... Stiffness. A common symptom of stiffness in the hip is difficulty putting on your shoes or socks. ... Limping. ... Swelling and Tenderness of the Hip.
How do you know if your hip is out of alignment?
5 Signs Your Hip Has Poor Alignmentpinching at the front of your hip.weak glutes.weak or tight pelvic floor.pain when lying on your side.anterior pelvic tilt a.k.a “duck bottom” posture.
What is an Anterior Hip Dislocation?
The head of the femur inserts into a portion of the pelvis called the acetabulum, also known as the hip socket. Sometimes, due to trauma, the head of the femur can get dislocated and pop out of the hip socket. This is termed a hip dislocation.
Mechanism of Injury
An anterior hip dislocation is one of numerous traumatic injuries that can be seen when someone is involved in an auto accident or a bicycle accident. If the head of the femur has been popped out of place in an anterior hip dislocation, the force typically comes from behind the patient.
Treatment of an Anterior Hip Dislocation
Treatment of the injury must first start with a reduction of the hip dislocation. This is typically done in a closed manner; however, the patient must be assessed for other associated injuries prior to this reduction to ensure that ancillary structures aren’t damaged in the process.
Complications are Possible
Because the hips and pelvis are home to important structures, a couple of comorbidities must be kept in mind. If there are fractures involved, it is possible for nerves that run through the pelvis to be damaged. This could lead to a loss of motor and sensory function.
Structures at Risk
One of the major complications to keep in mind is avascular necrosis of the femoral head. This happens when the blood flow to the head of the femur has been severed. This could lead to death of bone cells in the vicinity. The organs inside the pelvis, such as the uterus, are also at risk.
Differential Diagnosis
There are multiple diagnoses that must be considered with an anterior hip dislocation, including:
Injury Prognosis
The prognosis of an anterior hip dislocation will hinge on whether or not ancillary structures have been damaged. If they have been spared, the prognosis is typically a fast recovery; however, patients should remember a subsequent dislocation is more likely once a bone has been dislocated the first time.
What is the most common type of hip dislocation?
Posterior hip dislocations are the most common type, with anterior occurring only about 10% of the time. These injuries are true orthopedic emergencies and should be reduced expediently. The majority will resolve with a closed reduction in the emergency department. Anatomy.
Why is it important to dislocate a hip?
A significant force is generally required to dislocate a hip as this ball and socket joint is quite stable due to its bony structure and the associated muscular and ligamentous attachments. Due to the required force, hip dislocations often are associated with other significant injuries; for example, fractures are found in over 50% of these patients.
What is the hip joint?
The hip joint is a synovial ball-and-socket structure with stability related to both its bony and ligamentous arrangement. The acetabulum covers approximately 40% of the femoral head during all maneuvers, and the labrum serves to deepen this joint and adds additional stability.
Where does the sciatic nerve exit the pelvis?
The sciatic nerve exits the pelvis at the greater sciatic notch and lays just infero-posterior to the hip joint.
What is the hip capsule made of?
Furthermore, the hip joint capsule is composed of dense fibers that preclude extreme hip extension. The main blood supply to the femoral head arises from the medial and lateral femoral circumflex arteries, which are branches of the profunda femoral artery.