What is an example of an equal interval?
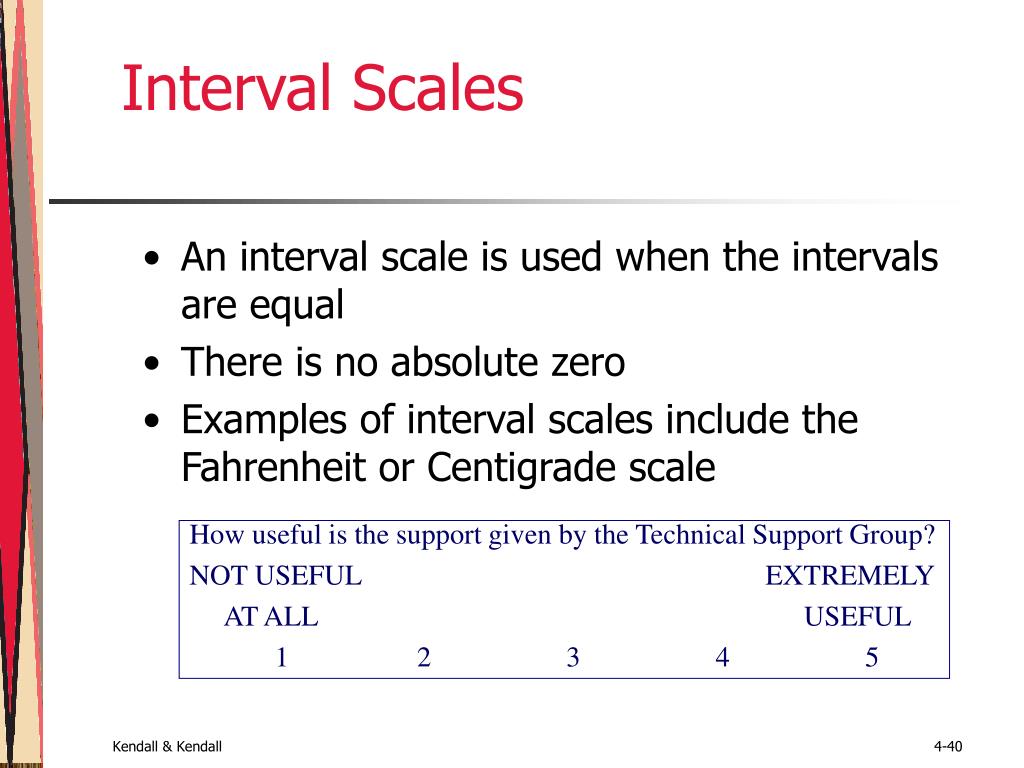
Equal interval means that the difference between two successive categories are the same. For example, temperature measured with Fahrenheit has equal intervals; that is, the difference between temperatures of 30 and 31 degrees is 1 degree, and the difference between 100 and 101 degrees is 1 degree.
What is equal interval scale in marketing research?
An interval scale can be defined as a quantitative measurement scale where variables have an order, the difference between two variables is equal, and the presence of zero is arbitrary. It can be used to measure variables that exist along a common scale in equal intervals. Market Research Toolkit.
What is interval scale explain with example?
The Interval scale is a numeric scale that represents not only the order but also the equal distances between the values of the objects. The most popular example is the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit.
What is an example of an interval scale variable?
An interval scale is one where there is order and the difference between two values is meaningful. Examples of interval variables include: temperature (Farenheit), temperature (Celcius), pH, SAT score (200-800), credit score (300-850).
What are the characteristics of interval scale?
Characteristics of Interval scale The interval scale is a numerical scale that not only contains data based on rank and order but also tells the difference between two variables and their value. The scale may show the value as zero but it does not mean true zero or absence.
What is the difference between interval scale and ratio scale?
Interval scale can measure size and magnitude as multiple factors of a defined unit. Ratio scale can measure size and magnitude as a factor of one defined unit in terms of another. A classic example of an interval scale is the temperature in Celsius.
How do you find the interval scale?
An interval scale is a scale (of measurement) created by units of equal size. When dealing with an interval scale, the difference between any two values can be calculated by using subtraction. Ratios of values have no meaning, because the value of zero is arbitrary.
How do you find the scale interval?
6:2311:09Scales of Measurement - Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, & Ratio Scale DataYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipData however ratios you can't measure the ratios for this form of data so what do we mean by that 60MoreData however ratios you can't measure the ratios for this form of data so what do we mean by that 60 degrees is not two times as hot as 30.. If you divide 60 by 30 you get 2.
Is age an interval or ratio?
Age is considered a ratio variable because it has a “true zero” value. It's possible for an individual to be zero years old (a newborn) and we can say that the difference between 0 years and 10 years is the same as the difference between 10 years and 20 years.
Is height an interval or ratio?
Physical characteristics of persons and objects can be measured with ratio scales, and, thus, height and weight are examples of ratio measurement. A score of 0 means there is complete absence of height or weight.
Is time an interval scale?
Time and duration are two examples of interval and ratio scale respectively. Time is the value of the interval scale because there is no zero.
What are the 4 types of measurement scales?
Scales of measurement is how variables are defined and categorised. Psychologist Stanley Stevens developed the four common scales of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio. Each scale of measurement has properties that determine how to properly analyse the data.
What is interval measurement in research?
Interval data is measured along a numerical scale that has equal distances between adjacent values. These distances are called “intervals.” There is no true zero on an interval scale, which is what distinguishes it from a ratio scale.
What is an example of an interval question?
When you ask someone to select a meal from a menu, you're using a nominal scale. When you ask someone to rate their meal on a scale of one to ten, you're using an interval scale.
What is interval variable in research?
The interval variable is a measurement variable that is used to define values measured along a scale, with each point placed at an equal distance from one another. It is one of the 2 types of numerical variables and is an extension of the ordinal variable.
What is the purpose of interval scale?
The interval scale possesses all the characteristics of an ordinal scale, but it also allows the researcher to compare the difference between the objects.
Is time an interval?
Time is another most common example of an interval scale in which the values are known, constant and measurable. In the ordinal scales, there is no fixed beginning or a true zero point, which means these scales do not possess the origin characteristic.
What is the VSS scale?
The VSS is the first scale used to quantify the pliability, vascularity, pigmentation and height in the scar. By observing the scar at rest and amount of blood refilling after blanching, the vascularity is rated as ‘normal, pink, red or purple’ [33].
What is the Stanford Sleepiness Scale?
The Stanford Sleepiness Scale was constructed as a seven-point rating scale of equal-appearing intervals from wide awake to devastatingly sleepy, and subsequently validated against SD [ Box 1 ]. Studies have shown the Stanford Sleepiness Scale to be a reliable means of rating sleepiness in healthy, sleep-deprived individuals. Patients with chronic sleepiness seem to lose the ability to assess their internal level of sleepiness accurately [70].
What are the different vascularity measurement tools?
Based on the vascularity measurement tool that articles purposefully explored, they were classified into two types: (1) subjective vascularity measurement scales including the Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale (POSAS), the Vancouver Scar Scale (VSS) and the modified Vancouver Scar Scale (mVSS); (2) objective vascularity measurement devices including the color-measuring device, the blood flow measuring device and the morphological imaging device. Table 1 summarized the frequency of different vascularity measurement tools used in all the included studies. Tables 2 and 3 summarized the reliability and validity results of different vascularity measurement tools.
What is meaningful and valid comparisons of different groups?
Meaningful and valid comparisons of different groups assume that the generic measure is equivalent in the different groups. This means that the HRQOL scales should have the same level of acceptability, reliability, and validity in different segments of the population.
What is the gold standard for VPI evaluation?
Perceptual analysis , the gold standard of VPI evaluation, includes listening to the spontaneous or prompted production of specific pressure phonemes including plosives, fricatives, and affricatives while monitoring for misarticulations, hypernasal speech, nasal rustle, and facial grimacing. It may also use articulation measurement, equal-appearing interval scales, and global ratings to assess VPI. 12 Facial grimacing is a compensatory action used by the patient to narrow the external nares to decrease nasal air emission during non-nasal speech. Use of the dental mirror placed under the nares during vowel production, may also assist in determining the amount of visible nasal air emission as shown by fogging of the mirror.
How to analyze distance data?
Another common strategy, and one also used with interval or ordinal distance data, is to analyze the data using multidimensional scaling techniques (MDS). MDS techniques explore the latent structure of a set of distance estimates by assessing the dimensionality of the data. They do this by constructing a two-dimensional space from one-dimensional data using a series of algorithms. In essence, they construct a ‘map’ showing the relationship between a number of objects. This ‘map’ can then be compared to an actual map using techniques such as bidimensional regression.
What does equal interval mean?
Equal interval means that the size of a unit (or range of variables) is the same no matter where it occurs on the scale. For example, you are giving participants a 1-10 scale to measure their levels of distress. The scale would be assumed to have equal intervals- the distance between 1 and 2 is the same as the distance between 7 and 8 on the scale. ...
What is the difference between a ratio scale and an interval scale?
Measuring a variable using an interval scale includes the measurement properties of equal intervals and magnitude. A ratio scale of measurement uses a true absolute zero , magnitude , and equal intervals.
What is equal interval in psychology?
When using statistics in psychology variables (hyperlink) are used- simply speaking a variable is something that can have different values and can vary between individuals. Numbers are by far the most common way to record and organize variables and numerical variables have different measurement properties which influence ...
What are the characteristics of interval data?
So let’s sum the key characteristics of the interval data and scales: Interval scales not only show you the order and the direction, but also the exact differences between the values. The distances between each value on the interval scale are meaningful and equal. There is no true zero point or fixed beginning.
What are the disadvantages of interval data?
However, there is one major disadvantage – the lack of absolute zero.
What is the highest level of data measurement?
Interval and ratio data are the highest levels of data measurements. But still, there is important differences between them that define the way you can analyze your data.
Why is it important to know the measurement level of data?
Knowing the measurement level of your data helps you to interpret and manipulate data in the right way. Let’s define the interval data: Interval data refers not only to classification and ordering the measurements, but it also specifies that the distances between each value on the scale are equal .
Does the interval scale have a true zero?
They do not have a true zero even if one of the values carry the name “zero.”. For example, in the temperature, there is no point where the temperature can be zero. Zero degrees F does not mean the complete absence of temperature. Since the interval scale has no true zero point, you cannot calculate Ratios .
Can you do ratios with intervals?
So, with ratio data, you can do the same things as with interval data plus calculating ratios and correlations.
Is age a variable?
5. Age is also a variable that is measurable on an interval scale, like 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 years and etc.
What is equal interval?
The idea of Equal Interval is that an average of an A and an F should always yield a C (if they are equally set apart from one another). The average of an F and a C would always yield a D, and so on. When the interval between grade levels are the same, an F is no longer weighed so heavily (6 times more than any other grade level). And so you provide the student with an opportunity to dig themselves out of an F based on future effort.
What is a 50 - 60 score?
90 - 100 is an A, 80 - 90 is a B, 70 - 80 is a C, 60 - 70 is a D, and 50 - 60 is an F ). If someone scores below 50%, it’s simply regarded as 50%.
What is the average of an F and an A?
Compare this with the "Conventional Gradebook Averaging" above, in this case, the average of an F and an A is always a C. You can still see the raw score for the assignment, but when calculating the final grade, the Gradebook will use the scaled up marks instead.
What percentage of the grade is an A?
Traditionally, if a student receives an F and an A and you simply sought an average Final Grade, you’d average the marks. But an A typically covers the top 10%, while an F covers the bottom 60%. And so averaging a 100%-A and a 0%-F gets you an F at 50%. And the effort put in by the student who received an A is lost in the final grade.
Can you distinguish between a high performing F and a low performing F?
The main issue with this method is that you can’t distinguish between a high performing F and a low performing F. And again, it seems counter-intuitive that a student can never receive below 50% for any given assignment.
Is equal interval philosophy controversial?
The Equal Interval philosophy has been very controversial to say the least. When assessing a student's performance over time (presumably in your Gradebook), how would you weigh an F vs. an A? If a student received an F in one assignment, and an A in the next assignment, what should the average be?
What is the difference between interval and ratio scale?
The primary difference between interval and ratio scales is that, while interval scales are void of absolute or true zero, ratio scales have an absolute zero point. Understanding these differences is the key to getting the most appropriate research data. Another key difference in interval scale vs ratio scale is the levels of measurement that have been explained in this blog. Every statistician should thoroughly understand the difference between the two scales for data to be articulated accurately.
What is interval level?
The interval level of measurement classifies and orders a measurement. It specifies a distance between each interval on a scale is equivalent, from low interval to high interval. For example, the difference between 90 degrees Fahrenheit and 100 degrees Fahrenheit is the same as 110 degrees Fahrenheit and 120 degrees Fahrenheit.
What is interval variable?
Interval variables are commonly known as scaled variables. They’re often expressed as a unit, such as degrees. In statistics, mean, mode, and median can also define interval variables. A ratio scale displays the order and number of objects between the values of the scale. Zero is an option.
What is a ratio scale?
Ratio scale can measure size and magnitude as a factor of one defined unit in terms of another. Example. A classic example of an interval scale is the temperature in Celsius. The difference in temperature between 50 degrees and 60 degrees is 10 degrees; this is the same difference between 70 degrees and 80 degrees.
What are the variables of a ratio scale?
Age, money, and weight are common ratio scale variables. For example, if you are 50 years old and your child is 25 years old, you can accurately claim you are twice their age. Interval ratioscale measurements. Understanding the different scales of measurementallows you to see the different types of data you can gather.
Why is it important to understand the scales of measurement?
Understanding the different scales of measurementallows you to see the different types of data you can gather. These differences help you determine the kind of statistical analysis required for your research.
Can interval scales be ranked?
Any measurement of interval scale can be ranked, counted, subtracted, or added, and equal intervals separate each number on the scale. However, these measurements don’t provide any sense of ratio between one another. A ratio scale has the same properties as interval scales.