What is the best example of angular motion?
The simplest angular motion is one in which the body moves along a curved path at a constant angular velocity, as when a runner travels along a circular path or an automobile rounds a curve.
What is an example of angular motion in sport?
During the performance of jumping jacks, both the arms and the legs rotate around imaginary anteroposterior axes passing through the shoulder and hip joints. The angular motion of sport implements such as golf clubs, baseball bats, and hockey sticks, as well as household and garden tools, is also often of interest.
What is an example of the conservation of angular motion?
An example of conservation of angular momentum is seen in an ice skater executing a spin, as shown in. The net torque on her is very close to zero, because 1) there is relatively little friction between her skates and the ice, and 2) the friction is exerted very close to the pivot point.
What type of motion is angular?
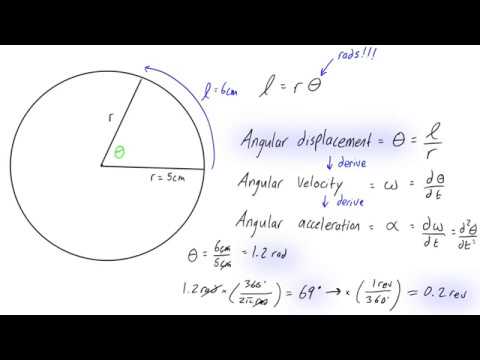
Angular motion is defined as, The motion of a body about a fixed point or fixed axis. It is equal to the angle passed over at the point or axis by a line drawn to the body....Relationship Between Linear And Angular Motion.FormulaLinearAngularAccelerationa = Δ v Δ ta = Δ ω Δ tDisplacements = v i t + 1 2 a t 2Θ = v i t + 1 2 α t 22 more rows
Which of the following is an example of angular motion anatomy?
Angular Movement Flexion, or bending, occurs when the angle between the bones decreases. Moving the forearm upward at the elbow or moving the wrist to move the hand toward the forearm are examples of flexion. Extension is the opposite of flexion in that the angle between the bones of a joint increases.
What is an example of rotary motion?
When an object rotates or spins about its axis, it is said to be exhibiting rotatory motion. Some examples of rotary or rotatory motion include the motion of a spinning top, rotation of the earth and other planets, movement of hands of a clock, etc.
What is law of conservation of angular momentum give example?
Statement: The angular momentum of a body remains constant if the resultant external torque acting on the body is zero. Example: A ballet dancer makes use of the law of conservation of angular momentum to vary her angular speed. The torque acting on her body is zero.
What is law of conservation of angular momentum explain with example?
The law of conservation of angular momentum states that when no external torque acts on an object, no change of angular momentum will occur. Some examples of momentum: The Earth continues to spin at the same rate it has for billions of years.
Why does a gyroscope not fall over?
This may seem counter-intuitive, but the lesson here is that the acceleration of an object can act in a direction that is very different from the direction of motion. This can result in some interesting physics, such as a gyroscope not falling over due to gravity as it precesses.
What is angular motion for kids?
In physics, the angular velocity specifies the angular speed at which an object is rotating along with the direction in which it is rotating. It is a vector quantity. The SI unit of angular velocity is radians per second.
What is angular motion class 11?
Class 11 Physics Rotational Motion. Angular velocity. Angular velocity & its relation with linear velocity. Every particle of a rotating body moves in a circle. Angular displacement of a given particle about its centre in unit time is defined as angular velocity.
Is circular motion and angular motion same?
In the case of rotation around a fixed axis of a rigid body that is not negligibly small compared to the radius of the path, each particle of the body describes a uniform circular motion with the same angular velocity, but with velocity and acceleration varying with the position with respect to the axis.