
Common Causes
The different types of atrophy are:
- Atrophy of the muscles
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy
- Vaginal Atrophy
Related Conditions
You may have muscle atrophy if:
- One of your arms or legs is noticeably smaller than the other.
- You’re experiencing marked weakness in one limb.
- You’ve been physically inactive for a very long time.
What are the types of atrophy?
- Research health conditions
- Check your symptoms
- Prepare for a doctor's visit or test
- Find the best treatments and procedures for you
- Explore options for better nutrition and exercise
What are the signs of muscle atrophy?
What to know about brain atrophy
- Symptoms. Brain atrophy can affect one or multiple regions of the brain. ...
- Causes. Brain atrophy can occur as a result of injury, either from a traumatic brain injury (TBI) or a stroke.
- Diagnosis. When diagnosing brain atrophy, a doctor may begin by taking a full medical history and asking about a person’s symptoms.
- Treatment. ...
- Outlook. ...
- Summary. ...
How to reverse muscle weakness?
What causes moderate cerebral atrophy?
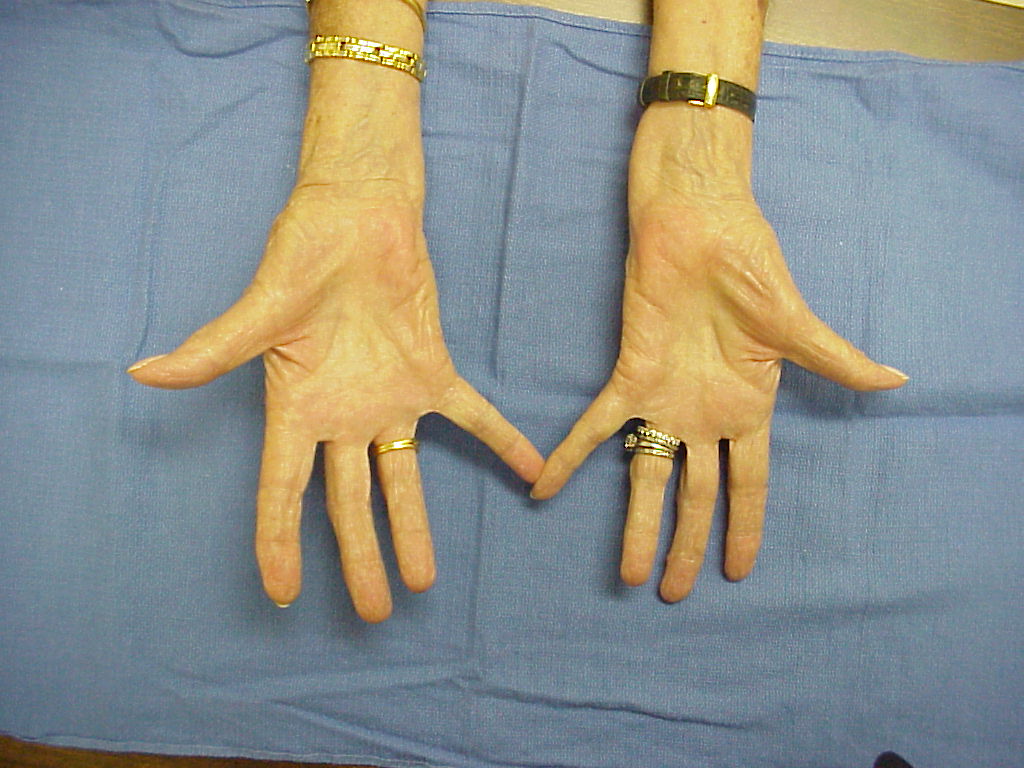
What happens during atrophy?
Atrophy is defined as a decrease in the size of a tissue or organ due to cellular shrinkage; the decrease in cell size is caused by the loss of organelles, cytoplasm and proteins.
What is a atrophy mean?
decrease in size or wasting away1 : decrease in size or wasting away of a body part or tissue atrophy of muscles also : arrested development or loss of a part or organ incidental to the normal development or life of an animal or plant.
What are the signs of atrophy?
Other signs of muscle atrophy may include:One arm or one leg is smaller than the other.Weakness in one arm and or one leg.Numbness or tingling in your arms and legs.Trouble walking or balancing.Difficulty swallowing or speaking.Facial weakness.Gradual memory loss.
What can cause atrophy?
In most people, muscle atrophy is caused by not using the muscles enough. Those with sedentary jobs, medical conditions that limit their movement, or decreased activity levels can lose muscle tone and develop atrophy. Those who are bedridden can have significant muscle wasting.
How is atrophy treated?
Getting regular exercise and trying physical therapy may reverse this form of muscle atrophy. People can treat muscle atrophy by making certain lifestyle changes, trying physical therapy, or undergoing surgery. In this article, we look at some other causes, symptoms, and treatments of muscle atrophy.
How do you reverse atrophy?
1 Atrophy is a physical process that occurs gradually. The rebuilding of muscles takes time, as well. The most effective methods for reversing atrophy are the same as those used to prevent atrophy—staying active, physical therapy, passive movements, and maintaining adequate nutrition.
Does atrophy hurt?
Depending on the cause, atrophy may occur in one muscle, a group of muscles, or the entire body, and it may be accompanied by numbness, pain or swelling, as well as other types of neuromuscular or skin symptoms.
How long can you live with cerebral atrophy?
Life expectancy among patients with brain atrophy can be influenced by the condition that caused the brain shrinkage. People with Alzheimer's disease live an average of four to eight years after their diagnosis.
What is an example of atrophy?
An example of atrophy is the shrinking of the muscles of a person who is confined to bed during a long illness or due to an accident.
What are the different types of atrophy?
The different types of atrophy include Glandular Atrophy, Vaginal Atrophy, Skeletal Muscle Atrophy, Spinal Muscular Atrophy, and Multiple System Atrophy. Skeletal Muscle Atrophy is separated into either Disuse Atrophy or Neurogenic Atrophy. There are treatments that can address the different types of atrophy. These treatments can be noninvasive or invasive, depending on the type of atrophy. Only a series of testing and diagnosis of symptoms by a physician can determine if an individual is suffering from atrophy, and what course of action should be taken to mitigate its progression.
What is spinal muscular atrophy?
Spinal Muscular Atrophy – Spinal muscular atrophy is a genetic condition caused by the loss of nerve cells that control muscle movement throughout the body. With this form of atrophy, the muscles closer to the center of the body become weaker than other muscles. Adult-onset spinal muscular atrophy (also known as spinal muscle atrophy type 4, or SMA 4) is a disorder that affects control of muscle movement.
What is the term for the wasting away of a body part?
Atrophy is defined as a wasting away or progressive decline, typically of a body part, organ, or tissue. In other words, it is the arrested development or loss of a part or organ incidental to the normal development or life of an animal or plant.
What are the signs of aging?
Signs of aging; changes to the body, most notably the development of wrinkles and loss of muscle strength.
Is skeletal muscle atrophy a disease?
Skeletal Muscle Atrophy – Identified as either Disuse or Neurogenic Atrophy. Disuse Atrophy is normally due to physical issues involving poor nutrition or a lack of exercise. Neurogenic Atrophy is often quicker and more severe than disuse atrophy, and is caused by disease or injury. Symptoms of skeletal muscle atrophy might include one arm or leg being noticeably smaller than the other, experiencing marked weakness in one limb, or prolonged physical inactivity.
Can rheumatoid arthritis cause contracture deformity?
Rheumatoid arthritis can lead to contracture deformity.
What causes pathologic atrophy?
The common causes of pathologic atrophy are the following: Decreased workload (atrophy of disuse) When a broken limb is immobilized in a plaster cast or when a patient is restricted to complete bed rest, skeletal muscle atrophy rapidly ensues.
What is the term for the loss of trophic support due to other disease?
Atrophy resulting from disease of the tissue itself, or loss of trophic support due to other disease is termed pathological atrophy. Shrinkage in the size of the cell by loss of cell substance is known as atrophy. It represents a form of adaptive response and may culminate in cell death. When a sufficient number of cells are involved, ...
What is the term for the process of reabsorption and breakdown of tissues?
Hormonal and nerve inputs that maintain an organ or body part are referred to as trophic. Atrophy is a general physiological process of reabsorption and breakdown of tissues, involving apoptosis on a cellular level. It can be part of normal body development and homeostatic processes, or as a result of disease.
What is the term for the decrease in blood supply?
Diminished blood supply. A decrease in blood supply (Ischemia ) to a tissue as a result of arterial occlusive disease results in atrophy of tissue owing to progressive cell loss. In late adult life, the brain undergoes progressive atrophy, presumably as atherosclerosis narrows its blood supply. Inadequate nutrition.
What is the term for the loss of the size of cells, tissues, or organs?
atrophy. Definition: Decrease in the size of cells, tissues, or organs. Causes of atrophy include poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply to the target organ, disuse or lack of exercise, or disease intrinsic to the tissue it self. Hormonal and nerve inputs that maintain an organ or body part are referred ...
What is the term for the use of skeletal muscle as a source of energy after other reserves such as a?
Inadequate nutrition. Profound protein-calorie malnutrition (marasmus) is associated with the use of skeletal muscle as a source of energy after other reserves such as adipose stores have been depleted. This results in marked muscle wasting (cachexia).
Does atrophy increase autophagy?
In many situations, atrophy is also accompanied by marked increases in the number of autophagic vacuoles (autophagy).
What causes muscle atrophy?
Other causes for muscle atrophy include: lack of physical activity for an extended period of time. aging. alcohol-associated myopathy, a pain and weakness in muscles due to excessive drinking over long periods of time. burns. injuries, such as a torn rotator cuff or broken bones. malnutrition. spinal cord or peripheral nerve injuries.
How to treat muscle atrophy?
Common treatments for muscle atrophy include: exercise. physical therapy. ultrasound therapy. surgery. dietary changes. Recommended exercises might include water exercises to help make movement easier. Physical therapists can teach you the correct ways to exercise.
How can muscle atrophy be reversed?
Muscle atrophy can often be reversed through regular exercise and proper nutrition in addition to getting treatment for the condition that’s causing it.
What causes reduced motion in the joints?
osteoarthritis, causes reduced motion in the joints. polio, a viral disease affecting muscle tissue that can lead to paralysis. polymyositis, an inflammatory disease. rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic inflammatory autoimmune condition that affects the joints. spinal muscular atrophy, a hereditary condition causing arm and leg muscles to waste away.
How to reverse muscle wasting?
In some cases, muscle wasting can be reversed with a proper diet, exercise, or physical therapy.
What causes the arm and leg muscles to waste away?
spinal muscular atrophy, a hereditary condition causing arm and leg muscles to waste away
Can you waste muscle if you are not active?
Unused muscles can waste away if you’re not active. But even after it begins, this type of atrophy can often be reversed with exercise and improved nutrition. Muscle atrophy can also happen if you’re bedridden or unable to move certain body parts due to a medical condition.
What is disuse atrophy?
disuse atrophy atrophy of a tissue or organ as a result of inactivity or diminished function. gyrate atrophy of choroid and retina a rare hereditary, slowly progressive atrophy of the choroid and pigment epithelium of the retina; inherited as an autosomal recessive trait. juvenile spinal muscular atrophy Kugelberg-Welander syndrome.
What is the treatment for optic atrophy?
Treatment includes pyridoxine (vitamin B6) supplement and arginine-restricted diet. optic atrophy Degeneration of the optic nerve fibres characterized by a pallor of the optic disc which may appear greyish, yellowish or white. This condition leads to a loss of visual acuity or changes in the visual fields or both.
What does "a wasting or decrease in size of a body organ, tissue, or part owing to disease?
1. A wasting or decrease in size of a body organ, tissue, or part owing to disease, injury, or lack of use: muscular atrophy of a person affected with paralysis.
What is progressive neuromuscular atrophy?
progressive neuromuscular atrophy hereditary muscular atrophy beginning in the muscles supplied by the fibular (peroneal) nerves, progressing slowly to involve the muscles of the hands and arms. Called also peroneal or peroneal muscular atrophy and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
What is myelopathic muscular atrophy?
myelopathic muscular atrophy muscular atrophy due to lesion of the spinal cord, as in spinal muscular atrophy.
What is a wasting, shrinking, or degeneration of an organ or tissue due to malnutrition,?
atrophy. A wasting, shrinking or degeneration of an organ or tissue due to malnutrition, poor blood circulation, loss of nerve supply, disuse, disease or hormonal changes. choroidal atrophy A group of ocular degenerations of the choroid. These lesions have been grouped according to the area involved and the topographical pattern noted.
What is the term for a reduction in tissue mass and cell substance, which can be physiological (normal) or path?
atrophy. A reduction in tissue mass and cell substance, which can be physiological (normal) or pathological (abnormal). Mechanism. Atrophy is not completely understood, but largely attributed to decreased protein production and increased protein degradation (e.g., via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway).
What is gelatinous atrophy?
Gelatinous atrophy of fat: associated with the atrophic changes in fatty tissues, particularly around the heart, in the renal pelvis and bone marrow which accompanies starvation.
What happens when the trophic influence of nerves is lost?
The loss of the trophic influence of nerves plus the immobilization of the organ when its nerve supply is lost may lead to atrophy.
What is brain atrophy?
Outlook. Summary. Brain atrophy refers to a loss of brain cells or a loss in the number of connections between brain cells. People who experience brain atrophy typically develop poorer cognitive functioning as a result of this type of brain damage. There are two main types of brain atrophy: focal atrophy, which occurs in specific brain regions, ...
What are the two types of brain atrophy?
There are two main types of brain atrophy: focal atrophy, which occurs in specific brain regions, and generalized atrophy, which occurs across the brain.
What is the term for a loss of neurons in the brain?
Brain atrophy refers to a loss of neurons within the brain or a loss in the number of connections between the neurons. This loss may be the result of an injury, infection, or underlying health condition.
How many regions of the brain are affected by brain atrophy?
Brain atrophy can affect one or multiple regions of the brain.
How to diagnose brain atrophy?
Diagnosis. When diagnosing brain atrophy, a doctor may begin by taking a full medical history and asking about a person’s symptoms. This may include asking questions about when the symptoms began and if there was an event that triggered them.
What tests are done to determine if you have brain atrophy?
The doctor may also carry out language or memory tests , or other specific tests of brain function. If they suspect that a person has brain atrophy, they will need to locate the brain damage and assess its severity. This will require an MRI or CT scan.
Does donepezil cause brain atrophy?
However, it was not clear if donepezil would have similar effects on brain atrophy resulting from causes other than alcohol-induced damage.
Which organs are most affected by atrophy?
Cells in the brain and the kidneys are especially affected for this type of atrophy.
What is the term for the development of an organ or tissue beyond an early embryonic stage?
Aplasia refers to defective development of an organ or tissue beyond an early embryonic stage. As a result, the embryonic remnants of the organ are often present.
Why do muscles become weaker and smaller?
Your muscles become weaker and smaller because you didn’t use them. These situations are reversible since the cells decreases in size. However, if this immobility is prolonged, the cells will undergo apoptosis and there will be a decrease in both cell number and size.