
What are the two types of comparative anatomy?
Comparative anatomy is one among the type of evidence. The two major concepts of the comparative anatomy include Analogous Structures and Homologous Structures. Analogous structures are similar structures in different organisms. These structures are just opposite to that of homologous structures.
What is the difference between evolution and comparative anatomy?
Evolution is a change in the genetics of a population over time. Comparative anatomy is the study of the relatedness of species through examining anatomical structures. Some structures, like homologous structures, indicate two organisms shared a recent common ancestor, like the arm bones in humans, bats, whales, and birds.
What is the difference between comparative and homologous anatomy?
'Comparative' means to look at the similarities between two things, and 'anatomy' has to do with the structure of the body. Scientists can look at anatomical structures of seemingly unrelated animals to tell how related they are. Homologous structures are structures that are similar in two organisms because they have a common ancestor.
What is an example of comparative anatomy in whales?
Comparative Anatomy of Whales. This is evidence that whales, as mammals, share a common ancestor with other mammals. Another example of a homologous structure in whales is their inner ear bones. The inner ear bones of a whale are extremely similar to land mammals, but the one difference is that they are fused together.

What are some examples of comparative anatomy?
A common example of comparative anatomy is the similar bone structures in forelimbs of cats, whales, bats, and humans. All of these appendages consist of the same basic parts; yet, they serve completely different functions.
What is an example of comparative anatomy in evolution?
For example, the forelimbs of humans, birds, crocodiles, bats, dolphins, and rodents have been modified by evolution to perform different functions, but they are all evolutionarily traceable to the fins of crossopterygian fishes, in which that basic arrangement of bones was first established.
What is comparative anatomy simple?
Comparative anatomy is a study of the differences and similarities in the anatomy of two species. In general, it includes a comparison of body structures of two species. It is similar to phylogeny and evolutionary biology. Evolution is nothing but a genetic change that occurs in a population over time.
What are the 3 structures of comparative anatomy?
9.9 Evidence from Comparative Anatomy-Homologous, Analogous and Vestigial Structures.
Why is comparative anatomy important?
Comparative anatomy is important in evolutionary studies and provides evidence of evolution, such as homologous organs, analogous organs, etc. It is important in determining common ancestry and also in the classification of organisms based on their structural similarities and complexities.
What is the difference between anatomy and comparative anatomy?
Comparative anatomy involves comparing the body structures of two species. 'Comparative' means to look at the similarities between two things, and 'anatomy' has to do with the structure of the body. Scientists can look at anatomical structures of seemingly unrelated animals to tell how related they are.
What is an example of comparative embryology?
Comparative embryology is the study of the similarities and differences in the embryos of different species. Similarities in embryos are likely to be evidence of common ancestry. All vertebrate embryos, for example, have gill slits and tails.
How is comparative anatomy evidence for evolution?
One of the strongest forms of evidence is comparative anatomy; comparing structural similarities of organisms to determine their evolutionary relationships. Organisms with similar anatomical features are assumed to be relatively closely related evolutionarily, and they are assumed to share a common ancestor.
Who discovered comparative anatomy?
Many regard Aristotle as the founder of comparative anatomy because his overall approach is comparative and incorporates a wealth of anatomical and morphological description, his scope is comprehensive, and his methods are rigorous and systematic.
What are the 5 evidences of evolution?
Five types of evidence for evolution are discussed in this section: ancient organism remains, fossil layers, similarities among organisms alive today, similarities in DNA, and similarities of embryos.
What is comparative anatomy homologous structures?
Comparative Anatomy Homologous structures are structures that are similar in related organisms because they were inherited from a common ancestor. These structures may or may not hav e the same function in the descendants.
How is the whale flipper like a human arm?
A whale flipper and a bat wing are also homologous structures in the same sense as a human arm and cat arm with a humerus, radius and ulna, and so on. But the whale's “arm” is actually a flipper that it uses to swim while the bat uses its wing to fly.
How is comparative anatomy evidence for evolution?
One of the strongest forms of evidence is comparative anatomy; comparing structural similarities of organisms to determine their evolutionary relationships. Organisms with similar anatomical features are assumed to be relatively closely related evolutionarily, and they are assumed to share a common ancestor.
What is an example of comparative embryology?
Comparative embryology is the study of the similarities and differences in the embryos of different species. Similarities in embryos are likely to be evidence of common ancestry. All vertebrate embryos, for example, have gill slits and tails.
How do you compare the structures in comparative anatomy as an evidence in evolution?
Comparing DNA Darwin could compare only the anatomy and embryos of living things. Today, scientists can compare their DNA. Similar DNA sequences are the strongest evidence for evolution from a common ancestor. More similarities in the DNA sequence is evidence for a closer evolutionary relationship.
What is comparative anatomy in biology?
Listen to pronunciation. (kum-PAYR-uh-tiv uh-NA-toh-mee) The comparison of the structure (anatomy) of one animal or plant with the structure of a different animal or plant.
What Is Comparative Anatomy?
Comparative anatomy involves comparing the body structures of two species. 'Comparative' means to look at the similarities between two things, and 'anatomy' has to do with the structure of the body. Scientists can look at anatomical structures of seemingly unrelated animals to tell how related they are.
What is the difference between homologous and analogous structures?
Some structures, like homologous structures, indicate two organisms shared a recent common ancestor, like the arm bones in humans, bats, whales, and birds. Analogous structures, however, are structures that have the same purpose in species, but the species are not closely related. Analogous structures arise from convergent evolution. Vestigial structures are anatomical features that are shared by different species but no longer have a purpose in one, like the appendix in humans, showing relatedness between the species.
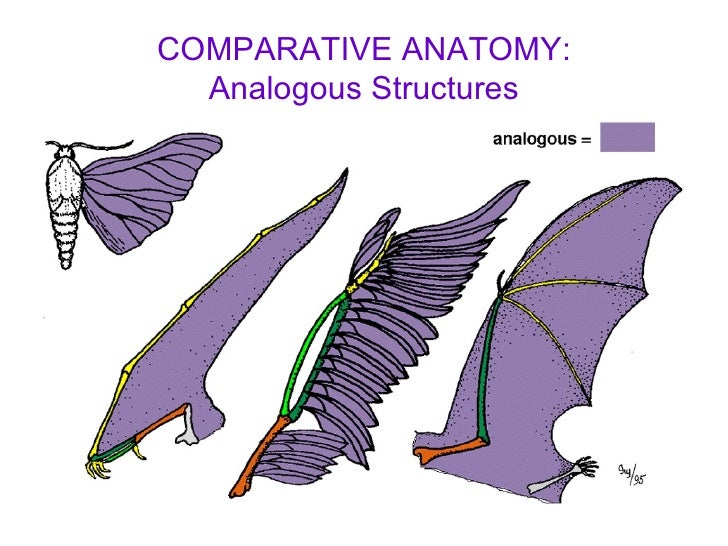
What are analogous structures?
Analogous structures are anatomical features of two species that look similar, or serve the same purpose, but the species are not closely related. An example of an analogous structure is bird wings and insect wings.
Why are bird wings more similar to human wings than insect wings?
Analogous structures are caused by convergent evolution.
How are analogous structures caused?
Analogous structures are caused by convergent evolution. In convergent evolution, two species evolve the same traits to adapt to an environment side by side, but they didn't come from the same ancestor. Think of analogous structures like a choice in jewelry. You and your best friend might choose the same pink necklace because you have similar taste, or because you are both going to the same party, but that doesn't make you related. On the other hand, imagine if you and your sister both inherited the same style of necklace from your great grandmother. In both cases you and another person are wearing the same jewelry, but you and your sister inherited them together, whereas you and your friend just happened to purchase the same item.
Do humans have cecums?
Humans have a cecum, but it is just a dead-end structure with no function. Animals that still need to eat plenty of grass maintain their full cecum, like rabbits. Thus, although we might not look or act very similar, somewhere along the evolutionary timeline humans and rabbits shared a common ancestor. Lesson Summary.
Do whales and humans have the same arm bone?
For example, birds, humans, bats, and even whales all have a similar arm bone structure. At first glance, you wouldn't think whales and humans are very closely related, but millions of years ago, there was one ancestor whom we are both related to.
What is comparative anatomy?
Comparative anatomy is a study of the differences and similarities in the anatomy of two species. In general, it includes a comparison of body structures of two species. It is similar to phylogeny and evolutionary biology. Evolution is nothing but a genetic change that occurs in a population over time. As a result, the offsprings look much different from their parents. It is caused due to the shuffling of genes resulting in a new trait thus helping the organism to survive.
What are the two major concepts of comparative anatomy?
Comparative anatomy is one among the type of evidence. The two major concepts of the comparative anatomy include Analogous Structures and Homologous Structures.
What are homologous structures?
Homologous structures are similar in two organisms which have the same ancestors but the functions performed may or may not be the same. For instance whales, birds and humans all possess the same arm bone structure.
What is Comparative Anatomy?
Comparative anatomy can be defined as the study of the anatomy of different animal species in order to understand the history of evolution from their common ancestors by studying the adaptive changes that have occurred. It's like phylogeny and evolutionary biology together.
History of Comparative Anatomy
The work of French naturalist Pierre Belon, who demonstrated in 1555, that the bones of humans and birds are made up of comparable materials arranged in the same way, is the foundation of modern comparative anatomy.
Analogous Structures
Analogous structures are structures that are similar in different animals. Although the equivalent organs perform similar duties, their origins and arrangement are vastly different. The wings of birds and insects, for example, perform the same function, i.e., both creatures use their wings to fly, yet their origins are different.
Homologous Structures
Homologous structures are organs or structures seen in vertebrates that have a similar structural arrangement but differing functionalities. The forelimbs of bats, horses, birds, and whales, for example, have similar anatomy and origin, but they serve diverse purposes.
Comparative Anatomy Representative Samples
The anatomy of the brain in different vertebrates has undergone evolutionary alterations.
Things to Remember
Comparative anatomy is the study of the body architecture of distinct species of animals in order to comprehend the adaptive changes that over time have occurred as the species evolved from common ancestors.
Sample Questions
Ans: Comparative anatomy elucidates the evolutionary links between certain anatomical structures, allowing biologists and scientists to classify those structures and animals. There are two sorts of relationships between structures in comparative anatomy: homologous structures and similar structures.
What is comparative anatomy?
Comparative Anatomy is the study of the similarities and differences in the anatomy of difference species. It has long served as one of the main evidences for evolution, due to the fact that it is very concrete, and does not require extensive technology.
What is an example of an appendix?
One example in humans is the appendix. The appendix was once an enlarged part of the digestive system, used to digest leaves in primates who were herbivores. As evolution occured and the appendix was no longer needed, it shrank in size and function over a very long time.
What is the second type of structure?
The second type of structure is a Vestigial Structure. These are structures that, over time, have lost much of their ancestral function.
Do whales have homologous bones?
We can first look at the homologous structures in whales. One major homolgous structure is the fin of a whale. If you look at the skeleton of a whale's fin, notice that all of the bones match up to comparative bones in other mammals. This is evidence that whales, as mammals, share a common ancestor with other mammals.
What is comparative anatomy?
Comparative anatomy is the study of the similarities and differences in the structures of different species. Similar body parts may be homologies or analogies. Both provide evidence for evolution.
Which part of the body has the same bone structure?
The forelimbs of all mammals have the same basic bone structure.
What is the cladogram of humans and apes?
Cladogram of Humans and Apes. This cladogram is based on DNA comparisons. It shows how humans are related to apes by descent from common ancestors.
What is an analogous structure?
Analogous structures are structures that are similar in unrelated organisms.
Which evidence provides the strongest evidence of evolutionary relationships?
Comparing DNA sequen ces provided some of the strongest evidence of evolutionary relationships.
Can Darwin compare DNA?
Darwin could compare only the anatomy and embryos of living things. Today, scientists can compare their DNA. Similar DNA sequences are the strongest evidence for evolution from a common ancestor. More similarities in the DNA sequence is evidence for a closer evolutionary relationship. Look at the cladogram in the Figure below. It shows how humans and apes are related based on their DNA sequences.
What Is Comparative Anatomy?
History of Comparative Anatomy
Analogous Structures
Homologous Structures
Comparative Anatomy Representative Samples
- The anatomy of the brain in different vertebrates has undergone evolutionary alterations. The Olfactory lobes, Optic lobes, Cerebral lobes, Cerebellum, and Medulla oblongata are the five lobes of t...
- The cerebral hemisphere of mammals is substantially larger than that of fishes, owing to structural variations in the brain of different vertebrates. Fishes, on the other hand, have a sig…
- The anatomy of the brain in different vertebrates has undergone evolutionary alterations. The Olfactory lobes, Optic lobes, Cerebral lobes, Cerebellum, and Medulla oblongata are the five lobes of t...
- The cerebral hemisphere of mammals is substantially larger than that of fishes, owing to structural variations in the brain of different vertebrates. Fishes, on the other hand, have a significantly...
Things to Remember