
Examples of Positive Feedback
- Blood Clotting. When a part of the body is injured, it releases chemicals that activate blood platelets. ...
- The Menstrual Cycle. Before a woman ovulates, the hormone estrogen is released by the ovary. ...
- Labor and Childbirth. The process of labor and childbirth is perhaps the most-cited example of positive feedback. ...
- Digestion. ...
- Nerve Signaling. ...
What is the role of the endocrine's feedback system?
The endocrine system governs body temperature. Negative feedback in the endocrine system may be found in the regulation of thyroid hormones. Hormones are secreted into the blood by the endocrine organs, such as the thyroid gland. Hormones are secreted into the blood by the endocrine organs, such as the adrenal glands.
What is the negative feedback mechanism of the endocrine system?
What is feedback mechanism in endocrine system? A feedback mechanism is a loop in which a product feeds back to control its own production. Most hormone feedback mechanisms involve negative feedback loops. Negative feedback keeps the concentration of a hormone within a narrow range.
What are some examples of positive feedback mechanisms?
Positive Feedback Examples
- The Ferguson reflex is the start of contractions during delivery.
- In the case of childbirth, the uterine walls ultimately expand due to the baby’s development, which is represented by the stretch receptors.
- This stretching will promote the release of oxytocin hormones, which will engage the uterine muscles and reduce the uterine gap.
What is an example of negative feedback system?
Some systems that regulate through negative feedback to achieve homeostasis include:
- Blood pressure
- Body temperature
- Blood sugar
What is negative and positive feedback in endocrine system?
Summary. Most hormones are controlled by negative feedback, in which the hormone feeds back to decrease its own production. This type of feedback brings things back to normal whenever they start to become too extreme. Positive feedback is much less common because it causes conditions to become increasingly extreme.
Which of these is an example of positive feedback regulation in the endocrine system?
The increase in LH that causes an increase in estrogen, which causes an increase in LH that occurs before ovulation, is an example of positive-feedback regulation, since the original stimulus, increased LH, is amplified or increased.
What is an example of positive feedback involving hormones?
The release of oxytocin from the posterior pituitary gland during labor is an example of positive feedback mechanism. Oxytocin stimulates the muscle contractions that push the baby through the birth canal.
What is an example of a feedback loop in the endocrine system?
Most endocrine activities are regulated by a series of complex feedback loops. These feedback loops work like a thermostat that responds to temperature changes by telling a furnace to turn on and off. When it's cold, the thermostat signals the furnace to turn on and make heat.
Is the endocrine system positive feedback?
The major endocrine systems are regulated by negative feedback, a process believed to maintain hormonal levels within a relatively narrow range.
What are some examples of positive feedback?
Here are some positive feedback examples to help you get started:Your input to today's meeting was a game-changer for this project. ... I am truly impressed with how you have managed to meet every goal set before you. ... Consistency is one of your biggest strengths. ... You did a great job with your presentation today.More items...•
Is sweat positive or negative feedback?
negative feedbackAnother example of negative feedback occurs when your body's temperature begins to rise and a negative feedback response works to counteract and stop the rise in temperature. Sweating is a good example of negative feedback.
What are examples of positive and negative feedback?
Some examples of positive feedback are contractions in child birth and the ripening of fruit; negative feedback examples include the regulation of blood glucose levels and osmoregulation.
What is positive feedback in homeostasis example?
For example, a cold-blooded animal, like fish, maintains a lower body temperature according to the external environment whereas a warm-blooded animal like a whale preserves higher body temperature to maintain internal stability.
What is an example of negative feedback in the endocrine system?
An example of negative feedback is the regulation of the blood calcium level. The parathyroid glands secrete parathyroid hormone, which regulates the blood calcium amount. If calcium decreases, the parathyroid glands sense the decrease and secrete more parathyroid hormone.
What is the most common form of feedback in the endocrine system?
Because negative feedback mechanisms attempt to maintain a target level, these are the most common type of feedback mechanisms employed by your endocrine system.
Which of the following describes an example of how hormones are regulated quizlet?
Which of the following describes an example of how hormones are regulated? One hormone stimulates the release of another hormone.
Which of the following describes an endocrine gland?
An organ that makes hormones that are released directly into the blood and travel to tissues and organs all over the body. Endocrine glands help control many body functions, including growth and development, metabolism, and fertility.
Where are the hormones oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone ADH stored?
the pituitary glandThe hypothalamus produces hormones that are stored in the pituitary gland. For example, oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) are made by nerve cells in the hypothalamus and are stored in the pituitary prior to their release into the blood.
Which of the following structures regulates the activities of both the nervous and endocrine systems?
Hypothalamus: The hypothalamus (hi-po-THAL-uh-mus) is in the lower central part of the brain. It links the endocrine system and nervous system. Nerve cells in the hypothalamus make chemicals that control the release of hormones secreted from the pituitary gland.
What is the function of feedback in the body?
Feedback also regulates your internal body temperature, which is critical to cel lular processes. Your hypothalamus, another important component of the endocrine system, sits above the roof of your mouth and tells your brain when you get too hot or too cold.
Why are negative feedback mechanisms the most common?
Negative feedback mechanisms are the most common because they attempt to maintain a target level. In contrast, positive feedback mechanisms are amplifications away from a target level. Don't let these names fool you though - negative feedback is a very good thing when it comes to homeostasis.
How does negative feedback work?
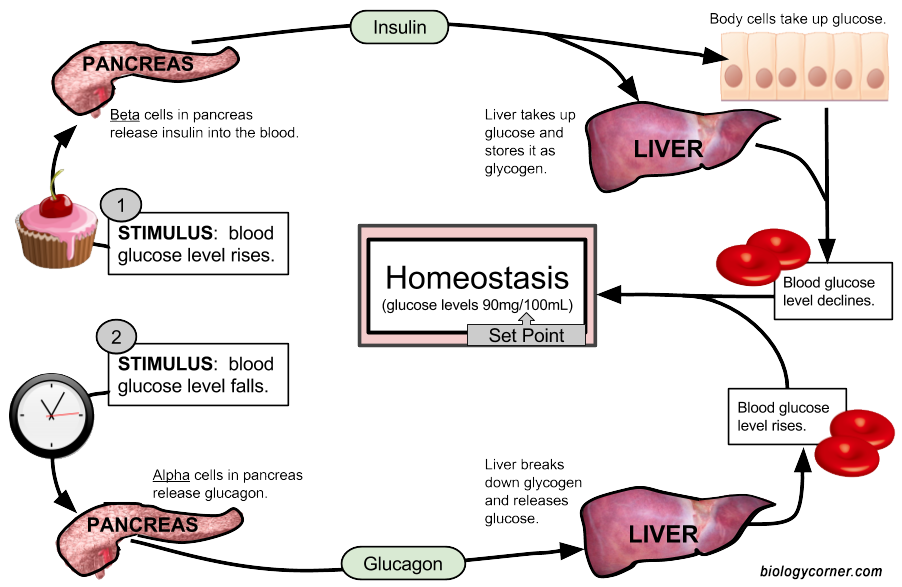
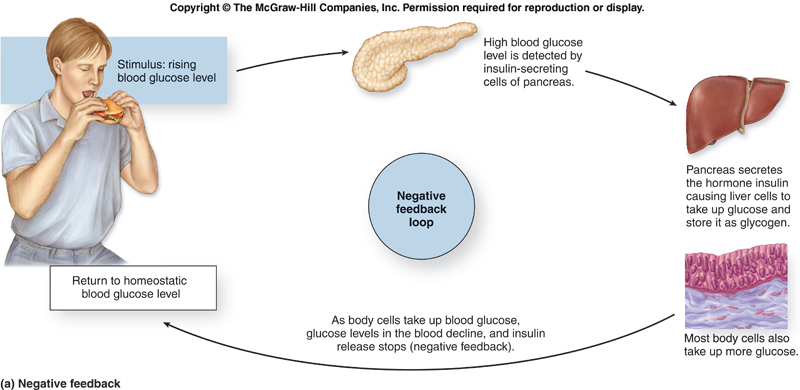
For example, your pancreas (an important gland in your endocrine system) relies on negative feedback to regulate blood glucose levels. An influx of glucose, say from a carbohydrate-heavy dinner, triggers your pancreas to produce a hormone called insulin. Insulin's message to your body is to take up that extra sugar into cells in order to bring your blood sugar back to the target level. Once enough glucose has been taken up by your cells, your pancreas stops secreting insulin. It's negative feedback!
Why do adrenal glands release glucose?
The hormones from your adrenal glands that trigger these involuntary reactions also stimulate liver cells to release glucose. This influx of energy into your bloodstream gives your cells an extra boost for any suddenly needed cellular work, like answering pop quiz questions, or maybe just running away as fast as you can to avoid the exam altogether!
What is the endocrine system?
By now, you should have a good understanding of your endocrine system, which is made of hormone-producing glands that help regulate your energy levels, growth, emotions, ability to reproduce, and more. There are over a dozen glands that make up your endocrine system, including your pancreas, adrenal glands, thyroid, ...
Why are hormones important?
Hormones are important because they are substances that act as chemical signals in your body. They are like microscopic messengers, carrying important information with them as they travel through your bloodstream.
What hormones are involved in reproduction?
These hormones, such as estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone, are involved not only in reproduction, but also in growth and development.
What is positive feedback?
Positive feedback is a process in which the end products of an action cause more of that action to occur in a feedback loop . This amplifies the original action. It is contrasted with negative feedback, which is when the end results of an action inhibit that action from continuing to occur. These mechanisms are found in many biological systems. An important example of positive feedback is the process of labor and childbirth.
What is the effector of a positive feedback loop?
Effector. An effector is any organ or cell that ultimately responds to the stimulus. For example, in labor, the end result of the positive feedback loop is that the uterus contracts. In this case, the uterus is the effector organ. These four parts are also found in negative feedback loops, but the end result is different because in negative ...
Why are negative feedback loops different from positive feedback loops?
These four parts are also found in negative feedback loops, but the end result is different because in negative feedback the effector organs work to hinder the process that caused them to activate. Positive feedback loops do not go on forever; they are ultimately stopped by negative feedback loops once the process they were used for is complete.
What is the target of the feedback loop?
The control center responds to the sensor and takes action, such as producing a hormone. The effector organs are the target of the feedback loop and respond to the stimulus.
What is feedback mechanism?
Related Biology Terms. Feedback mechanism – A process that uses one component to regulate another, either through positive or negative feedback. Negative feedback – The result of a process inhibits the process from continuing to occur; it is the opposite of positive feedback.
What causes action potentials in the brain?
Action potentials are caused by an influx of sodium ions in the nerve cell. If a small amount of sodium enters the nerve, it causes more channels to open which cause more sodium to rush in, creating a positive feedback loop that causes a large amount of sodium to enter the nerve and create an action potential.
Which part of the body responds to changes in the body?
A control center is the part of the body that responds to the change and takes action. The pituitary gland, located near the brain, is the control center in many feedback loops; it produces many different hormones, such as oxytocin, growth hormone, and anti-diuretic hormone (ADH), in response to stimuli.
What is the positive feedback mechanism?
The release of oxytocin from the posterior pituitary gland during labor is an example of positive feedback mechanism. Oxytocin stimulates the muscle contractions that push the baby through the birth canal. The release of oxytocin result in stronger or augmented contractions during labor.
What happens when you have negative feedback?
Due to positive and negative feedback, our body will be in homeostasis. <_o3a_p>. In negative feedback, the response will reverse or cause the opposite effect of the original stimulus. Negative feedback can be explained with the process of insulin production and release. After a meal the blood sugar level will be elevated due to the absorption ...
What hormones are released when calcium levels decrease?
If calcium decreases, the parathyroid glands sense the decrease and secrete more parathyroid hormone. The parathyroid hormone stimulates calcium release from the bones and increases the calcium uptake into the bloodstream from the collecting tubules in the kidneys.
What is the endocrine system?
Negative and Positive Feedback Mechanisms. <_o3a_p>. The endocrine system helps regulate and maintain various body functions by synthesizing and releasing hormones. It is composed of glands located through out the body that secrete chemicals called hormones directly into the blood.
Why is there negative feedback after eating?
Negative feedback can be explained with the process of insulin production and release. After a meal the blood sugar level will be elevated due to the absorption of sugars from the digestive tract. This triggers the release of insulin from pancreas.
How do hormones stimulate the body?
Hormones stimulate various body tissues. <_o3a_p>. The hormone levels in the blood are regulated by a highly specialized homeostatic mechanism called feedback. Information regarding the hormone level or its effect is fed back to the gland that the hormone secreted from.
What happens when oxytocin is released?
The release of oxytocin result in stronger or augmented contractions during labor. The contractions intensify and increase until the baby is outside the birth canal. When the stimulus to the pressure receptors ends, oxytocin production stops and labor contractions cease.
Why is positive feedback important?
Instead of reversing it, positive feedback encourages and intensifies a change in the body’s physiological condition, actually driving it farther out of the normal range. This type of feedback is normal for the body, provided there is a definite endpoint.
What are some examples of negative feedback loops?
Other examples of negative feedback loops include the regulation of blood sugar, blood pressure, blood gases, blood pH, fluid balance, and erythropoiesis.
What are the components of a feedback loop?
Feedback loops have three components—the sensors, the control, and the effector. Sensors are also called receptors and they monitor conditions inside and outside the body. Some examples are thermoreceptors and mechanoreceptors. The control center, often in the brain, compares the value the sensor receives to the values in the range.
Why is thermoregulation the primary reaction?
This type of thermoregulation is the primary reaction because the effects will occur faster than the physiological mechanisms. It is important to realize that this feedback mechanism is based on controlling heat loss or heat gain in the body.
How does the body regulate temperature?
Core body temperature in mammals is regulated by thermoreceptors in the hypothalamus in the brain, spinal cord, large veins, and internal organs. When the core temperature gets too high, the animals first reaction is usually behavioral thermoregulation, also called allostasis. The animal may seek shade to get out of the sun or move into the water to cool its skin. This type of thermoregulation is the primary reaction because the effects will occur faster than the physiological mechanisms. It is important to realize that this feedback mechanism is based on controlling heat loss or heat gain in the body. The body does not “cool itself” in the literal sense, meaning it does not turn on an internal air conditioning system or synthesize chemicals that cool the body.
Positive Feedback Definition
Parts of A Positive Feedback Loop
- What is a positive feedback mechanism?
A positive feedback loop in the endocrine system is more rare, happening for only some hormones. A positive feedback loop in the endocrine system is when release of a hormone initiates actions that lead to an additional release of that hormone. Unlike a negative feedback lo… - Example of a positive feedback loop in the endocrine system
Oxytocin is one of the few hormones regulated by a positive feedback mechanism. In both childbirth and breastfeeding, oxytocin is released and causes additional release of oxytocin. During childbirth, release of oxytocin results in uterine contractions, and uterine contractions cau…
Examples of Positive Feedback
Related Biology Terms
Quiz
- Stimulus
A stimulus is something that disrupts the body’s homeostasis, which is the tendency toward equilibrium in all body systems. A bodily injury or an infection are examples of stimuli. They disrupt normal processes in the body. - Sensor
A sensor detects the change in homeostasis. For example, nerve cells in the cervix detect pressure placed on it from the head of the fetusduring labor. Nerve impulses from a sensor will travel to the control center.