
What is an experimental hypothesis example? For example, a study designed to look at the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance might have a hypothesis that states, "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
What are some examples of a good hypothesis?
Some good hypothesis examples include, "When there is less oxygen in the water, rainbow trout suffer more lice" and, "Aphid-infested plants exposed to ladybugs have fewer aphids after a week than untreated plants." Effective hypotheses are simple enough to be testable, but not so simple that they are common knowledge.
Which describes the hypothesis of an experiment?
The Short Answer In its simplest form, an experiment is simply the test of a hypothesis. A hypothesis, in turn, is a proposed relationship or explanation of phenomena. The experiment is the foundation of the scientific method, which is a systematic means of exploring the world around you.
Can You Show Me an example of a hypothesis?
What Are Some Examples of a Good Hypothesis? Some good hypothesis examples include, “When there is less oxygen in the water, rainbow trout suffer more lice” and, “Aphid-infested plants exposed to ladybugs have fewer aphids after a week than untreated plants.”
What are the different types of hypothesis?
What are the 5 types of hypothesis?
- Simple hypothesis.
- Complex hypothesis.
- Directional hypothesis.
- Non-directional hypothesis.
- Null hypothesis.
- Associative and casual hypothesis.
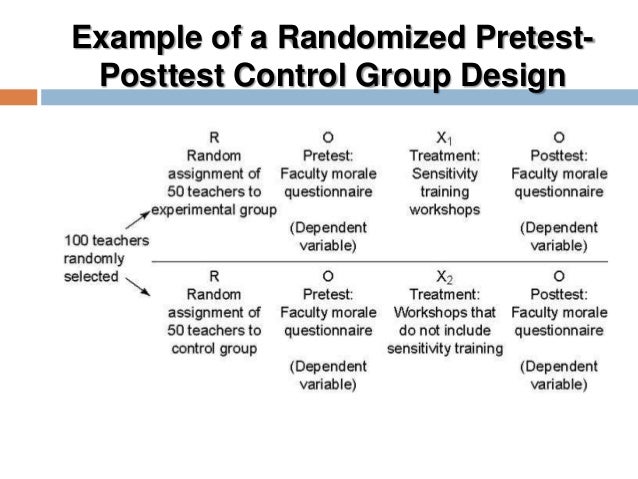
What are experimental hypotheses?
An experimental hypothesis predicts what changes will take place in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated. Also, it states that the results are not due to chance and that they are significant in terms of supporting the theory being investigated.
How do you write an experimental hypothesis?
How to Write Hypothesis in ResearchPredicts the relationship and outcome.Simple and concise – avoid wordiness.Clear with no ambiguity or assumptions about the readers' knowledge.Observable and testable results.Relevant and specific to the research question or problem.
What are examples of testable hypothesis?
Examples of a Testable HypothesisStudents who attend class have higher grades than students who skip class. ... People exposed to high levels of ultraviolet light have a higher incidence of cancer than the norm. ... If you put people in a dark room, then they will be unable to tell when an infrared light turns on.
What is experimental hypothesis and null hypothesis?
In a scientific experiment, the null hypothesis is the proposition that there is no effect or no relationship between phenomena or populations. If the null hypothesis is true, any observed difference in phenomena or populations would be due to sampling error (random chance) or experimental error.
What is the 3 types of hypothesis?
Types of hypothesis are: Simple hypothesis. Complex hypothesis. Directional hypothesis.
How do you start a hypothesis example?
How to write a hypothesis in 6 steps1 Ask a question. ... 2 Conduct preliminary research. ... 3 Define your variables. ... 4 Phrase it as an if-then statement. ... 5 Collect data to support your hypothesis. ... 6 Write with confidence.
Which of the following is the best example of hypothesis?
The best example of a hypothesis is If a plant receives water, then it will grow faster. Explanation: In the scientific method of research, a hypothesis can be described as a tentative statement that can be proved right or wrong. A hypothesis can be tested through experiments and the results can be deduced from it.
What is hypothesis and examples?
Professionals typically write hypotheses as if/then statements, such as if someone eats a lot of sugar, then they will develop cavities in their teeth. These statements identify specific variables and propose results. In this example, the variable is the amount of sugar and the result is developing cavities.
What does testable hypothesis mean?
In short, a hypothesis is testable if there is a possibility of deciding whether it is true or false based on experimentation by anyone. This allows to decide whether a theory can be supported or refuted by data. However, the interpretation of experimental data may be also inconclusive or uncertain.
Which is an example of a null hypothesis?
The null hypothesis assumes that any kind of difference between the chosen characteristics that you see in a set of data is due to chance. For example, if the expected earnings for the gambling game are truly equal to zero, then any difference between the average earnings in the data and zero is due to chance.
What is an example of a null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis?
Null Hypothesis: On the average, the dosage sold under this brand is 50 mg (population mean dosage = 50 mg). Alternative Hypothesis: On the average, the dosage sold under this brand is not 50 mg (population mean dosage ≠ 50 mg). This is a two-sided alternative hypothesis.
What is null hypothesis in simple words?
The null hypothesis is a typical statistical theory which suggests that no statistical relationship and significance exists in a set of given single observed variable, between two sets of observed data and measured phenomena.
What are the types of hypothesis with examples?
Different Types of HypothesesNull hypothesis. A null hypothesis proposes no relationship between two variables. ... Alternative hypothesis. ... Simple hypothesis. ... Complex hypothesis. ... Associative and casual hypothesis. ... Empirical hypothesis. ... Statistical hypothesis.
What is an example of a hypothesis in biology?
Hypothesis: If plants are watered with a 10% detergent solution, their growth will be negatively affected. Some people prefer to state a hypothesis in an "If, then" format. An alternate hypothesis might be: Plant growth will be unaffected by water with a 10% detergent solution.
What is an example of a hypothesis in psychology?
Simple Hypothesis Examples The hypothesis that includes only one independent variable (predictor variable) and one dependent variable (outcome variable) is termed the simple hypothesis. For example, the children are more likely to get clinical depression if their parents had also suffered from the clinical depression.
What is hypothesis in research?
The hypothesis is at the core of an experimental research design. Researchers propose a tentative answer after defining the problem and then test the hypothesis to either confirm or disregard it. Here are a few characteristics of experimental research:
What Is Experimental Research?
Experimental research is a scientific method of conducting research using two variables: independent and dependent. Independent variables can be manipulated to apply to dependent variables and the effect is measured. This measurement usually happens over a significant period of time to establish conditions and conclusions about the relationship between these two variables.
What is the difference between dependent and extraneous variables?
Dependent variables are manipulated or treated while independent variables are exerted on dependent variables as an experimental treatment. Extraneous variables are variables generated from other factors that can affect the experiment and contribute to change. Researchers have to exercise control to reduce the influence of these variables by randomization, making homogeneous groups and applying statistical analysis techniques.
How to evaluate teaching methods?
To evaluate the teaching methods of two teachers, they can be assigned two student groups. After teaching their respective groups on the same topic, a posttest can determine which group scored better and who is better at teaching. This method can have its drawbacks as certain human factors, such as attitudes of students and effectiveness to grasp a subject, may negatively influence results.
What is a one shot case study?
A one-shot case study research design is a study where one dependent variable is considered. It’s a posttest study as it’s carried out after treating what presumably caused the change.
What is it called when researchers deliberately operate independent variables on the subject of the experiment?
Researchers deliberately operate independent variables on the subject of the experiment. This is known as manipulation.
What determines the types of experimental research design?
The way a researcher assigns subjects to different groups determines the types of experimental research design.
What does an experimental hypothesis predict?
An experimental hypothesis predicts what change (s) will take place in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
What is a hypothesis in a research study?
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a precise, testable statement of what the researcher (s) predict will be the outcome of the study. This usually involves proposing a possible relationship between two variables: the independent variable (what the researcher changes) and the dependent variable (what the research measures).
What is a non-directional hypothesis?
A non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis predicts that the independent variable will have an effect on the dependent variable, but the direction of the effect is not specified. It just states that there will be a difference.
How to write alternative and null hypotheses?
1. To write the alternative and null hypotheses for an investigation, you need to identify the key variables in the study. The independent variable is manipulated by the researcher and the dependent variable is the outcome which is measured. 2.
What happens if you reject the null hypothesis?
If we reject the null hypothesis, this doesn’t really mean that our alternative hypothesis is correct – but it does provide support for the alternative / experimental hypothesis.
What is the opposite of the alternative hypothesis?
Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors. The null hypothesis is, therefore, the opposite of the alternative hypothesis in that it states that there will be no change in behavior. At this point, you might be asking why we seem so interested in the null hypothesis.
What is the difference between the independent and dependent variables?
The independent variable is manipulated by the researcher and the dependent variable is the outcome which is measured.
