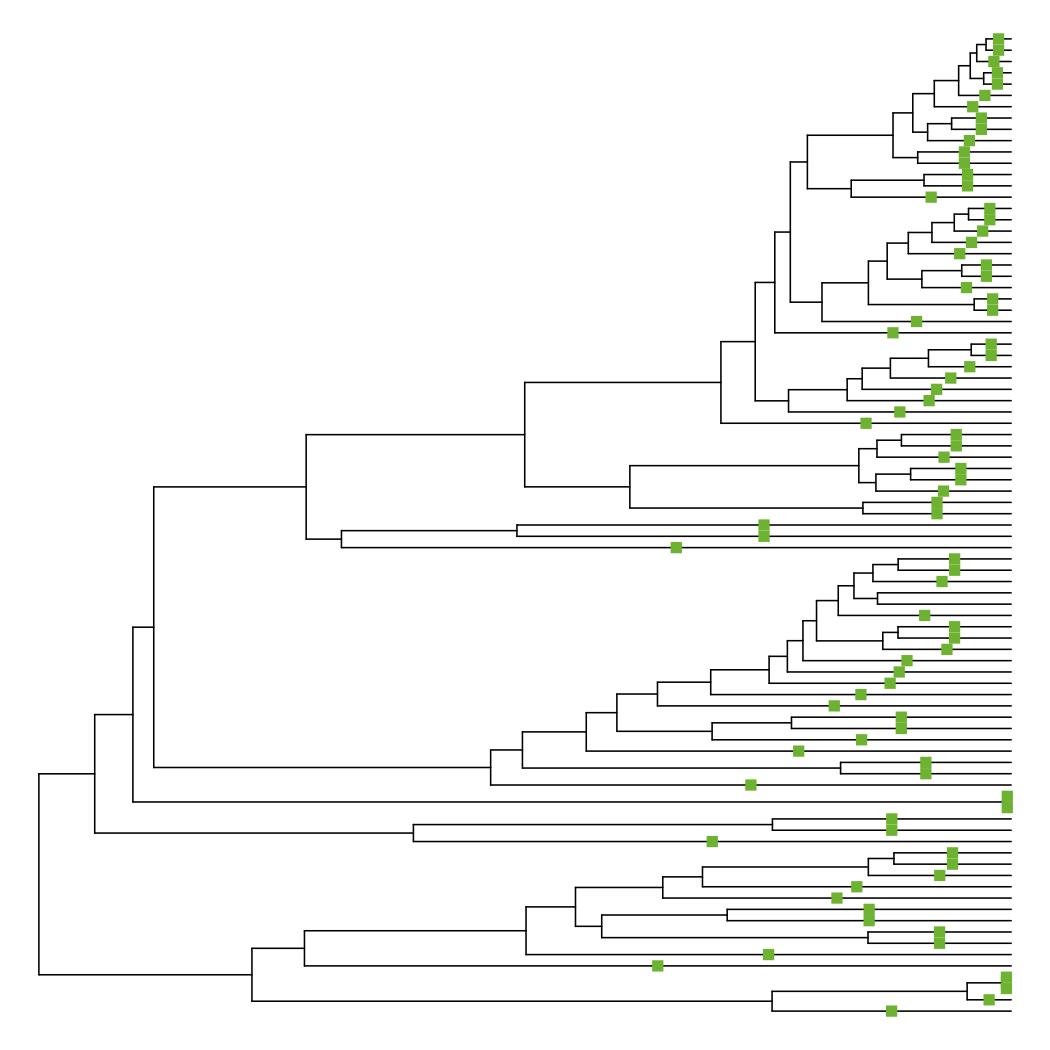
What is the ultrametricity of the tree?
Apr 06, 2022 · Ultrametric Tree An ultrametric tree is a rooted tree with edge lengths where all leaves are equidistant from the root. Often, ultrametric trees represent the molecular clock which states that the rate of mutation is the same across all lineages of the tree. A phylogram is a branching diagram (tree) that is assumed to be an estimate of a phylogeny. The branch lengths …
What are ultrametrics and why are they used?
Mar 11, 2020 · Ultrametric Tree An ultrametric tree is a rooted tree with edge lengths where all leaves are equidistant from the root. Often, ultrametric trees represent the molecular clock which states that the rate of mutation is the same across all lineages of the tree.
What is the difference between an ultrametric and binary tree?
Mar 09, 2022 · Ultrametric Tree An ultrametric tree is a rooted tree with edge lengths where all leaves are equidistant from the root. Often, ultrametric trees represent the molecular clock which states that the rate of mutation is the same across all lineages of the tree .
What is the difference between ultrametric and additive phylogenetic trees?
Under the null hypothesis, the phylogeny is ultrametric (i.e., rooted and the branch lengths are constrained such that all of the tips can be drawn at a single time plane). Under the alternative hypothesis, each branch is allowed to vary independently.

What is an ultrametric phylogenetic tree?
Ultrametric tree An ultrametric tree or chronogram is a phylogenetic tree where edge lengths represent time (so current taxa are equidistant from the root).
How can you tell if tree is ultrametric?
1:266:32Ultrametric Trees - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSimply by taking the difference between edge between the ages. So for example the age of this noteMoreSimply by taking the difference between edge between the ages. So for example the age of this note is 33 the age of that note is 23 we get the edge weight 10 for free just by subtracting the two h's.
Are ultrametric trees always additive?
– All ultrametric matrices are additive – But, an additive matrix is not necessarily ultrametric.
What does it mean if a tree shows Polytomy?
However, you may see trees with a polytomy (poly, many; tomy, cuts), meaning a branch point that has three or more different species coming off of it 2. In general, a polytomy shows where we don't have enough information to determine branching order.
What is an additive tree?
An additive tree is a general way to represent clusters of data in a graph. It is used when your data table is composed of rows and columns that represent the same units; the measure must be a distance or a similarity. A “tree” is a finite, connected graph where any two nodes are connected by one path.Jun 14, 2015
What is neighbor joining method?
The neighbor-joining method is a special case of the star decomposition method. In contrast to cluster analysis neighbor-joining keeps track of nodes on a tree rather than taxa or clusters of taxa. The raw data are provided as a distance matrix and the initial tree is a star tree.Aug 8, 1997
What is ultrametric Matrix?
1. A matrix D is an ultrametric matrix if there exists a rooted tree T with function height(v) = 0 defined for each node v ? V (T) (height(v) = Di,j, where v is the most recent common ancestor of i and j) such that whenever v > w (i.e., v is on the path from w to the root of T), we have height(v) > height(w).
What is an ultrametric assumption?
When DNA, RNA and protein data are analyzed, the ultrametricity assumption is called the molecular clock. Models of intermittency in three dimensional turbulence of fluids make use of so-called cascades, and in discrete models of dyadic cascades, which have an ultrametric structure.
How many internal branches are there in a fully resolved unrooted tree for 5 taxa?
8. Furthermore, we connect the fifth taxon to each branch (5 branches per tree) on each of these 3 trees to yield all 15 possible unrooted trees for the five taxa as shown in Fig. 9.
What is a branching tree?
Definition. A branching identification key where the structure of the decision tree is displayed graphically as a branching structure, involving lines between items. Supplement. Depending on the number of branches at a single point, a branching key may be dichotomous or polytomous.Jun 28, 2021
Why do polytomy exist?
Polytomies are multifurcating (as opposed to bifurcating) relationships in phylogenetic hypotheses and occur for two reasons: First, polytomies can result from poor resolution of true bifurcating relationships (due to lack of sufficient data or inappropriate analysis of characters), and these are "soft" polytomies; ...Dec 23, 2011
What is an example of polytomy?
If the lineages in the phylogenetic tree stand for species, a polytomy shows the simultaneous speciation of three or more species. In particular situations they may be common, for example when a species that has rapidly expanded its range or is highly panmictic undergoes peripatric speciation in different regions.
What is an ultrametric tree?
Ultrametric Tree An ultrametric tree is a rooted tree with edge lengths where all leaves are equidistant from the root. Often, ultrametric trees represent the molecular clock which states that the rate of mutation is the same across all lineages of the tree. Click to see full answer. Just so, what is a Phylogram?
What is the difference between a phylogram and an ultrametric tree?
A phylogram is a phylogenetic tree where edge lengths signify time or genetic distance while an ultrametric tree or “chronogram” is a phylogenetic tree where edge lengths represent time. Also in an ultrametric tree, all tips of the tree are equidistant from the root of the tree. Similarly one may ask, what is an additive tree?
What is an upgma tree?
A “tree” is a finite, connected graph where any two nodes are connected by one path. What is Upgma tree? UPGMA (unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean) is a simple agglomerative (bottom-up) hierarchical clustering method. The method is generally attributed to Sokal and Michener.
What is additive tree?
Similarly one may ask, what is an additive tree? An additive tree is a general way to represent clusters of data in a graph. It is used when your data table is composed of rows and columns that represent the same units; the measure must be a distance or a similarity.
Description
This function tests whether a tree is ultrametric using the distances from each tip to the root.
Details
The test is based on the distances from each tip to the root and a criterion: if option = 1, the criterion is the scaled range ( (max - min/max)), if option = 2, the variance is used (this was the method used until ape 3.5). The default criterion is invariant to linear changes of the branch lengths.