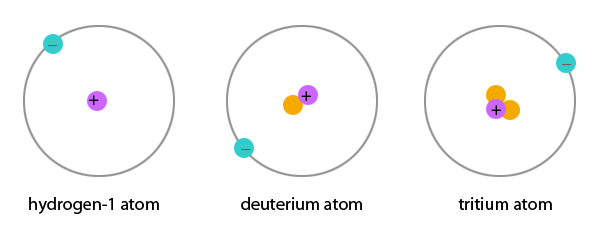
Which type of nucleus will most likely be unstable?
The end of the stable elements in the periodic table occurs after lead, largely due to the fact that nuclei with 128 neutrons are extraordinarily unstable and almost immediately shed alpha particles. This also contributes to the very short half-lives of astatine , radon , and francium relative to heavier elements.
What are very large nuclei tend to be unstable?
Very large nuclei tend to be unstable because of the: repulsive forces between protons. In nuclear reactions: small amounts of mass are converted to large amount of energy. For the most common types of radioactive decay, the order of least penetrating to human tissue, to most penetrating to human tissue is: ...
What does unstable nuclei mean?
Unstable Nuclei. In summary it is the balance of protons and neutrons in a nucleus which determines whether a nucleus will be stable or unstable. Too many neutrons or protons upset this balance disrupting the binding energy from the strong nuclear forces making the nucleus unstable.
What has an unstable nucleus?
It is unstable nuclei that are radioactive and are referred to as radioactive nuclei and in the case of their isotopes called radioisotopes. The unstable nuclei lie above and below the line of stability in the neutron – proton plot. This gives information of the type of radioactive decay they will undergo.
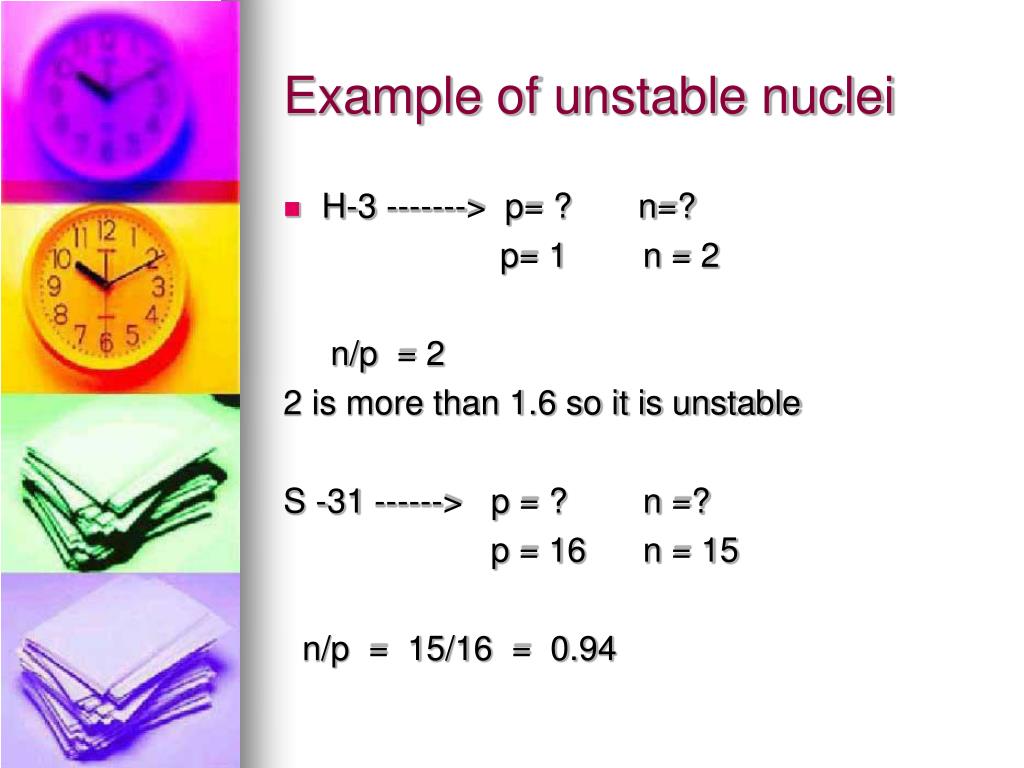
What is meant by unstable nucleus?
When the atoms of an element have extra neutrons or protons it creates extra energy in the nucleus and causes the atom to become unbalanced or unstable. Whether radioactive elements can become stable and if so, how. The unstable nucleus of radioactive atoms emit radiation.
What happens to unstable nuclei?
0:434:53Stable and Unstable Nuclei | Radioactivity | Physics | FuseSchoolYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd is what determines if a nucleus is stable in stable nuclei the force is strong enough and bringsMoreAnd is what determines if a nucleus is stable in stable nuclei the force is strong enough and brings sufficient energy to hold the nucleus together permanently. Most of the nuclei formed during the
What elements have unstable nuclei?
In elements with more than 83 protons, all of the isotopes are radioactive. In the Figure above, these are the elements with a yellow background. The force of repulsion among all those protons makes the nuclei unstable. Elements with more than 92 protons have such unstable nuclei that they don't even exist in nature.
What is an unstable nuclei BBC Bitesize?
Nuclei with too many, or too few, neutrons do exist naturally but are unstable and will disintegrate (or decay) by emitting radiation. This is called radioactive decay. It is important to realise that radioactive nuclei disintegrate: spontaneously; and randomly.
What is stable and unstable nuclei?
An atom is stable if the forces among the particles that makeup the nucleus are balanced. An atom is unstable (radioactive) if these forces are unbalanced; if the nucleus has an excess of internal energy. Instability of an atom's nucleus may result from an excess of either neutrons or protons.
What unstable nuclei lose energy?
Radioactive decay Unstable nuclei lose energy by emitting radiation in a spontaneous process called radioactive decay.
What are nuclei?
A nucleus, as related to genomics, is the membrane-enclosed organelle within a cell that contains the chromosomes. An array of holes, or pores, in the nuclear membrane allows for the selective passage of certain molecules (such as proteins and nucleic acids) into and out of the nucleus.
What is the difference between a stable and unstable isotope?
Stable isotopes are naturally occurring forms of elements that are non-radioactive. Unstable isotopes are atoms having unstable nuclei. Therefore, these elements undergo radioactivity. This is the main difference between stable and unstable isotopes.
What is stable nucleus?
Stable nuclei generally have even numbers of both protons and neutrons and a neutron-to-proton ratio of at least 1. Nuclei that contain magic numbers of protons and neutrons are often especially stable. Superheavy elements, with atomic numbers near 126, may even be stable enough to exist in nature.
Why are atoms unstable?
An atom can be considered unstable in one of two ways. If it picks up or loses an electron, it becomes electrically charged and highly reactive. Such electrically charged atoms are known as ions. Instability can also occur in the nucleus when the number of protons and neutrons is unbalanced.
How do you know if a nucleus is stable?
The principal factor for determining whether a nucleus is stable is the neutron to proton ratio. Elements with (Z<20) are lighter and these elements' nuclei and have a ratio of 1:1 and prefer to have the same amount of protons and neutrons.
Why are large nuclei unstable?
Bigger nuclei are unstable because of presence of large number of like charge particles. Bigger nuclei have very less number of protons which makes them unstable. Bigger nuclei have less number of neutron which makes them unstable.
Have unstable nuclei and emit rays and particles to become more stable?
Radioactive atoms have unstable nuclei, and when the nuclei emit radiation, they become more stable. Radioactive decay is a nuclear—rather than chemical—reaction because it involves only the nuclei of atoms.
What must happen for a nucleus to be stable?
A stable nucleus must have the right combination of protons and neutrons. Occurs if there are too many neutrons. A neutron to proton conversion occurs. This releases an electron or beta particle.
What happens to the nucleus during alpha decay?
Alpha decay is a nuclear decay process where an unstable nucleus changes to another element by shooting out a particle composed of two protons and two neutrons. This ejected particle is known as an alpha particle and is simply a helium nucleus.
How does an unstable nucleus release energy quizlet?
An unstable nucleus releases energy by emitting radiation during the process of radioactive decay.
What is the decay of unstable nuclei?
B. Decay of Unstable Nuclei. The unstable nuclei, in order to become stable nuclei, emit particles and/or electromagnetic radiation. These types of nuclei are said to be radioactive, and the emission is called radioactivity. The three type of emission that originate from the nucleus are: Gamma particles (γ).
What is stable nucleus?
A stable nucleus is a nucleus that has enough binding energy to hold the elements of the nucleus together permanently. In unstable nuclei, the strong nuclear forces do not generate enough binding energy to hold the elements of the nucleus together permanently. Hadrons (Mesons & Baryons) experience the strong nuclear force but Leptons do not.
What are the three types of nuclei?
The unstable nuclei, in order to become stable nuclei, emit particles and/or electromagnetic radiation. These types of nuclei are said to be radioactive, and the emission is called radioactivity. The three type of emission that originate from the nucleus are: 1 Alpha particles (α) 2 Beta particles (β) 3 Gamma particles (γ).
How does the nucleus return to its unexcited state?
The nucleus may return to its unexcited or stable state by emitting energy in the form of γ particles. γ−radiation is part of the electromagnetic spectrum with wavelengths between. For example, when uranium-238 decays by emitting an α particle, the resulting nucleus of thorium-234 contains excess energy and emits a photon ...
How many protons does the nucleus lose?
The nucleus loses two protons and two neutrons in this emission. Each element has a particular number of protons, and therefore α decay causes one element to change into another. This process is also called transmutation. The original nuclide is called the parent nuclide, and the new one is the daughter nuclide.
What are gamma particles?
E. Gamma Particles (γ) Alpha and beta particles are emitted by unstable nuclei, which have excess energy. The emission of these particles results in changes in the ratio of protons to neutrons, but the nuclei may still have excess energy.
What type of nucleus is a negative electron?
A radioactive nucleus that undergoes alpha decay emits alpha particles. It contains two protons and two neutrons. A radioactive nucleus that undergoes beta decay may emit a negative or positive electron. The nucleus may return to its unexcited or stable state by emitting energy in the form of γ particles.
What is it called when a nucleus has too many neutrons?
This is called radioactive decay. and randomly. This means that the process of radioactive decay can not be speeded up or slowed down by artificial means (spontaneous decay).
Why are elements with fewer protons stable?
Elements with fewer protons, such as the ones near the top of the periodic table, are stable if they have the same number of neutrons and protons. For example carbon, carbon-12 is stable and has six protons and six neutrons.
How many neutrons are in carbon?
For example carbon, carbon-12 is stable and has six protons and six neutrons. However as the number of protons increases, more neutrons are needed to keep the nucleus stable. For example lead, lead-206 has 82 protons and has 124 neutrons.
Can radioactive decay be slowed down?
This means that the process of radioactive decay can not be speeded up or slowed down by artificial means (spontaneous decay). It also means that we cannot tell when a particular unstable nucleus will decay (random decay). Some nuclei are unstable. They disintegrate, emitting radiation randomly, and spontaneously.
What is unstable nucleus?
Unstable Nuclei. In unstable nuclei the strong nuclear forces do not generate enough binding energy to hold the nucleus together permanently. It is unstable nuclei that are radioactive and are referred to as radioactive nuclei and in the case of their isotopes called radioisotopes.
Which nuclei are on the stability line?
Nuclei which lie on the stability line are stable nuclei. From the plot it can be seen that many of the stable nuclei have equal number of protons and neutrons. These are usually the elements in the lighter section of the periodic table. For the heavier stable nuclei the there are approximately 50% more neutrons to protons.
What is the force between protons and neutrons called?
Strong Nuclear Force. A strong force must exist between the protons and neutrons in a nucleus to overcome the electrostatic repulsion between the protons. This additional force is called the strong nuclear force. This force is attractive over short distances, but this is not all.
Why is the combined gravitational force from the protons and neutrons in a nucleus insignificant
The combined gravitational force from the protons and neutrons in a nucleus is insignificant as an attractive force because their masses are so tiny. This implies there must be an additional attractive force similar in size to the electrostatic repulsion which holds the nucleus together.
What is neutron rich?
They are referred to as “neutron rich”. Those that lie below the line of stability contain too many protons to be stable and are called “proton rich”. In summary it is the balance of protons and neutrons in a nucleus which determines whether a nucleus will be stable or unstable.
What is the force that holds the nucleus together called?
This is the force that holds the nucleus together and the energy associated with this force is called the binding energy. It is the amount of strong nuclear force and the associated binding energy in ...
Is the nucleus stable?
Many nucle i in nature are very stable, most of the nuclei formed at the creation of the universe or after supernovae explosions many millions of years ago are still in existence now. The graph below is a plot of neutron number against proton number. It is used as rule to determine which nuclei are stable or unstable.
Which nucleus is more stable?
It is found that nuclei with even numbers of protons and neutrons are more stable than those with odd numbers. Nuclei which have both neutron number and proton number equal to one of the magic numberscan be called “doubly magic“, and are found to be particularly stable. There are further special propertis of nu clei, ...
How is nuclear stability determined?
A nuclear stabilityis determined by the competition between two fundamental interactions. Atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons, which attract each other through the nuclear force, while protons repel each other via the electromagnetic force due to their positive charge. These two forces compete, leading to various stability of nuclei. ...
What is the role of neutrons in nuclear reactors?
This type of radiation plays key role in nuclear reactor control, because these neutrons are delayed neutrons.
Why do neutrons stabilize the nucleus?
Neutrons stabilize the nucleus, because they attract each other and protons , which helps offset the electrical repulsion between protons. As a result, as the number of protons increases, an increasing ratio of neutrons to protons is needed to form ...
What is the closing of shells?
These correspond to the closing of shells (or sub-shells). Nuclei with closed shells are more tightly bound than the next higher number. The closing of shells occurs at Z or N = 2, 8, 20, 28, (40), 50, 82, 126. It is found that nuclei with even numbers of protons and neutrons are more stable than those with odd numbers.
Which nuclei have a magic number?
The stable elements at the end of the decay series all have a “magic number” of neutrons or protons. The nuclei He-4, O-16, and Pb-208 (82 protons and ...
What is nuclear decay?
Nuclear decay(Radioactive decay)occurs when an unstable atom loses energy by emitting ionizing radiation. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms, in that, according to quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay.
