
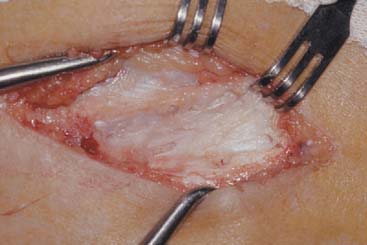
The term angiofibroblastic hyperplasia or angiofibroblastic tendinosis (hereafter referred to as tendinosis) describes the pathologic alterations seen in the tissue of clients diagnosed as having tendonitis. A visible change occurs in the gross appearance of the tissue. Microscopically, normal tendon fibers are arranged in an orderly fashion.
What does hyperplasia mean in medical terms?
Hyperplasia describes an increase in the number of cells in an area of the body. It causes the affected tissue or organ to enlarge. It can also cause pressure on the surrounding tissue, leading to further symptoms. Hyperplasia occurs when there is excessive or unnecessary growth of the cells in a body part.
What is benign prostate hyperplasia?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) — also called prostate gland enlargement — is a common condition as men get older. An enlarged prostate gland can cause uncomfortable urinary symptoms, such as blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder. It can also cause bladder, urinary tract or kidney problems.
What is atypical lobular hyperplasia?
In atypical hyperplasia (or hyperplasia with atypia), the cells are more distorted. This can be either atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) or atypical lobular hyperplasia (ALH). Hyperplasia doesn’t usually cause a lump that can be felt, but it can cause changes that can be seen on a mammogram. It’s diagnosed by doing a biopsy.
What are the symptoms of hyperplasia?
The symptoms you develop due to hyperplasia may depend on what type of hyperplasia you are experiencing. Symptoms that may be common across several different types of hyperplasia include: However, if the hyperplasia affects an area that is not close to the surface of the skin, you may not be able to see the overgrowth.
How does hyperplasia affect your risk for breast cancer?
What is the difference between lobular and ductal hyperplasia?
What is the term for the overgrowth of the ducts in the breast?
Is hyperplasia atypical or usual?
Is atypical hyperplasia a risk factor for breast cancer?
Can hyperplasia be felt?
Do you need to treat atypical hyperplasia?
See 4 more
About this website

What is Angiofibroblastic degeneration?
Thus, angiofibroblastic degeneration. refers to a weakening of the tendons due to decreased blood flow and damage to the. fibers that make up the tendons. The end result is the formation of an abnormal type of. tissue in the tendon, known as angiofibroblastic tissue.
What are the symptoms of elbow tendonitis?
Elbow Tendonitis Symptoms The main symptom of elbow tendonitis is pain (sometimes a burning pain) and tenderness on the outside of the elbow. Stiffness and pain in the elbow in the morning or at night are also common and are worse when trying to use the hand or arm.
How does tendinosis affect the body?
Tendinosis refers to hardening, thickening, and scarring of the tendons. This causes pain and a loss of flexibility in the joint. Common symptoms of tendinosis are: localized burning pain and swelling around the tendon.
How is elbow tendinopathy treated?
Strengthening exercises — A special type of strengthening exercise, known as "eccentric strengthening," is the most effective way to treat elbow tendinopathy. Patients can start these exercises once their flexibility has improved and they have little or no pain when performing a strengthening exercise.
What happens if elbow tendonitis goes untreated?
If tendonitis is left untreated, you could develop chronic tendonitis, a tendon rupture (a complete tear of the tendon), or tendonosis (which is degenerative). Chronic tendonitis can cause the tendon to degenerate and weaken over time.
Will elbow tendonitis ever go away?
Tennis elbow often gets better on its own. But if over-the-counter pain medications and other self-care measures aren't helping, your doctor may suggest physical therapy. Severe cases of tennis elbow may require surgery.
Is tendonosis serious?
Tendonosis can make your tendon more prone to injuries. The tendon may rupture (tear) and require surgery.
Does tendinosis require surgery?
Usually, tendinosis improves over time and surgery is not required, but in some severe cases surgery is considered as an option. Corticosteroids can be injected into the joint spaces to reduce inflammation. These injections can relieve pain but they can cause side effects such as thinning of the skin.
Do you need surgery for tendonosis?
Most cases of tendinitis can be successfully treated with rest, physical therapy and medications to reduce pain. If tendinitis is severe and leads to the rupture of a tendon, you may need surgery.
Should you massage elbow tendonitis?
Deep tissue massage to the forearm is a very effective method of easing tennis elbow and healing it much faster than rest alone. Deep tissue massage will enhance circulation and combining this with friction therapy to the tendons on the elbow joint, positive results are seen.
What are the stages of tendinopathy?
The pathogenesis of tendinopathy can be described as a three stage process: injury, failed healing and clinical presentation. It is likely that some of these "initial injuries" heal well and we speculate that predisposing intrinsic or extrinsic factors may be involved.
Is tendinopathy the same as tennis elbow?
Lateral elbow tendinopathy, commonly known as tennis elbow, is a condition that can cause significant functional impairment in working-age patients. The term tendinopathy is used to describe chronic overuse tendon disorders encompassing a group of pathologies, a spectrum of disease.
How do you test for tendonitis in the elbow?
How is tennis elbow diagnosed?An X-ray to look at the bones of your elbow to see if you have arthritis in your elbow.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can show your tendons and how severe the damage is. ... Electromyography (EMG) of your elbow may show if you have any nerve problems that may be causing your pain.
How can I check myself for tendonitis?
This test includes making a fist with the fingers covering the thumb and then bending the wrist toward the little finger. Pain on the thumb side of the wrist is a positive indication of tendonitis in the wrist area.
How do u know if u have tendonitis?
Signs and symptoms of tendinitis tend to occur at the point where a tendon attaches to a bone and typically include: Pain often described as a dull ache, especially when moving the affected limb or joint. Tenderness. Mild swelling.
What triggers tendonitis?
They may be caused by strain, overuse, injury, or too much exercise. Tendonitis may also be related to a disease such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or infection.
Benign breast conditions: Hyperplasia and atypical hyperplasia
6. What this means for you . Having usual ductal hyperplasia doesn’t increase your risk of developing breast cancer. However, it’s still important to be breast aware and go back to your GP if you notice any changes in your breasts regardless of how soon these occur after your diagnosis of hyperplasia.. If you have atypical hyperplasia, you may be worried or anxious that your risk of breast ...
Hyperplasia of the breast: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment - I Live! OK
Hyperplasia of the breast is a disease of the breast caused by the overgrowth of its tissues. It occurs very often, according to statistics, 8 women out of 10 are susceptible to this disease.
Florid hyperplasia causing a breast nodule - Moose and Doc
Florid Hyperplasia. Hyperplasia is a term used to describe rapid and unexpected new cell growth in various tissues, but in the context of breast cancer screening it usually refers to the lining of the breast ducts. ‘Florid‘ hyperplasia is a term which describes the degree or amount of hyperplasia, on an informal continuum from mild, to moderate, to florid.
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia - breast cancer
If you have a core needle biopsy that discovers atypical cells, your doctor likely will go on to remove more of the tissue in that area. Since ADH is not a true cancer, though, there can be some variation in how doctors approach them.
How does hyperplasia affect your risk for breast cancer?
Hyperplasia can affect your risk for breast cancer, but how much depends on what type it is:
What is the difference between lobular and ductal hyperplasia?
Ductal hyperplasia (also called duct epithelial hyperplasia) is an overgrowth of the cells that line the small tubes (ducts) inside the breast, while lobular hyperplasia is an overgrowth of cell lining the milk glands (lobules). Ductal and lobular hyperplasia occur at about the same rate, and have about the same effect on breast cancer risk.
What is the term for the overgrowth of the ducts in the breast?
Hyperplasia of the Breast (Ductal or Lobular) Hyperplasia is also known as epithelial hyperplasia or proliferative breast disease. It’s an overgrowth of the cells that line the ducts or the milk glands (lobules) inside the breast. Ductal hyperplasia (also called duct epithelial hyperplasia) is an overgrowth of the cells that line the small tubes ...
Is hyperplasia atypical or usual?
Hyperplasia is often described as either usual or atypical based on how the cells look under a microscope.
Is atypical hyperplasia a risk factor for breast cancer?
Atypical hyperplasia (ADH or ALH) is linked to a higher risk of breast cancer. Even though most women with atypical hyperplasia will not develop breast cancer, it's still important to talk with a health care provider about your risk and what, if any, options are best for you.
Can hyperplasia be felt?
Hyperplasia doesn’t usually cause a lump that can be felt, but it can cause changes that can be seen on a mammogram. It’s diagnosed by doing a biopsy. (A hollow needle may be used to remove a small piece of tissue that’s checked in the lab. Or, surgery may be done to take out the abnormal breast tissue.)
Do you need to treat atypical hyperplasia?
Most types of usual hyperplasia do not need to be treated. But if atypical hyperplasia (ADH or ALH) is found on a needle biopsy, more breast tissue around it might be removed with surgery to be sure that there is nothing more serious nearby, such as cancer. (This is more likely to be recommended for ADH than for ALH.)
What causes endometrial hyperplasia?
Endometrial hyperplasia is caused by too much estrogen or not enough progesterone . Both of these hormones play roles in the menstrual cycle. Estrogen makes the cells grow, while progesterone signals the shedding of the cells. A hormonal imbalance can produce too many cells or abnormal cells.
Is endometrial hyperplasia a treatable condition?
In most cases, endometrial hyperplasia is very treatable. Work with your doctor to create a treatment plan. If you have a severe type or if the condition is ongoing, you might need to see your doctor more often to monitor any changes.
Can endometrial hyperplasia cause cancer?
Atypical types of endometrial hyperplasia, especially complex, increase your risk of getting cancer. If you have these types, you might consider a hysterectomy. This is a surgery to remove your uterus. Doctors recommend this if you no longer want to become pregnant.
Can endometrial hyperplasia be prevented or avoided?
You are more likely to have endometrial hyperplasia if you have gone through menopause. This is because your body’s hormones and menstrual cycles change. Other risk factors for this condition are:
What is the rarest form of adrenal hyperplasia?
There are two major types of congenital adrenal hyperplasia: Classic CAH. This form is rarer and is usually detected in infancy. Approximately two-thirds of people who have classic CAH have what's known as the salt-losing form, while one-third have what's referred to as the simple-virilizing form. Nonclassic CAH.
What is the name of the disorder that affects the adrenal glands?
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) refers to a group of genetic disorders that affect the adrenal glands, a pair of walnut-sized organs above the kidneys. The adrenal glands produce important hormones, including: Cortisol, which regulates the body's response to illness or stress. Mineralocorticoids, such as aldosterone, ...
Why is CAH dangerous?
People who have classic CAH are at risk of adrenal crisis because they have very low levels of cortisol in the blood. This can cause diarrhea, vomiting, dehydration, low blood sugar levels and shock. Adrenal crisis is a life-threatening medical emergency that requires immediate treatment. Aldosterone also may be low, which leads to dehydration and low sodium and high potassium levels. The nonclassic form of CAH doesn't cause adrenal crisis.
When does CAH become evident?
Nonclassic CAH. This form is milder and more common, and may not become evident until childhood or early adulthood.
Can you prevent congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
There is no known way to prevent congenital adrenal hyperplasia. If you're thinking of starting a family and you're at risk of having a child with CAH, your doctor may recommend that you see a genetic counselor.
Can you have adrenal hyperplasia with a cure?
In people who have CAH, a genetic problem results in a lack of one of the enzymes needed to make these hormones. Although there is no cure, with proper treatment, most people who have congenital adrenal hyperplasia can lead normal lives . There are two major types of congenital adrenal hyperplasia: Classic CAH.
Is CAH a nonclassic condition?
Often there are no symptoms of nonclassic CAH when a baby is born. The condition is not identified on routine infant blood screening and usually becomes evident in late childhood or early adulthood. Cortisol may be the only hormone that's deficient.
What is endometrial hyperplasia?
A note from Cleveland Clinic. Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition that causes abnormal uterine bleeding. These symptoms can be uncomfortable and disruptive. Many women find relief through progestin hormone treatments. Women who have atypical endometrial hyperplasia have a higher risk of developing uterine cancer.
What are the risk factors for endometrial hyperplasia?
Other risk factors include: Certain breast cancer treatments ( tamoxifen ). Diabetes. Early age for menstruation or late onset of menopause.
What hormones are produced by endometrial hyperplasia?
Women who develop endometrial hyperplasia produce too much estrogen and not enough progesterone. These female hormones play essential roles in menstruation and pregnancy. During ovulation, estrogen thickens the endometrium, while progesterone prepares the uterus for pregnancy. If conception doesn’t occur, progesterone levels drop. The progesterone drop triggers the uterus to shed its lining as a menstrual period.
Does endometrial hyperplasia cause estrogen to rise?
Women who have endometrial hyperplasia make little, if any, progesterone. As a result, the uterus doesn’t shed the endometrial lining. Instead, the lining continues to grow and thicken. Additionally, obesity contributes to the elevation of estrogen levels.
Is endometrial hyperplasia cancerous?
Simple endometrial hyperplasia (without atypia): This type of endometrial hyperplasia has normal-looking cells that aren’t likely to become cancerous. This condition may improve without treatment. Hormone therapy helps in some cases.
Can endometrial hyperplasia cause uterine cancer?
Atypical endometrial hyperplasia raises the risk of endometrial cancer and uterine cancer. The condition tends to occur during or after menopause. Progestin therapy can ease symptoms. Women at risk for cancer may choose to get a hysterectomy.
Does obesity cause endometrial hyperplasia?
The adipose tissue (fat stores in the abdomen and body) can convert the fat producing hormones to estrogen. This is the how obesity contributes to elevated circulating levels of estrogen and increases the risk of endometrial hyperplasia. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
What is BPH in men?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) — also called prostate gland enlargement — is a common condition as men get older. An enlarged prostate gland can cause uncomfortable urinary symptoms, such as blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder. It can also cause bladder, urinary tract or kidney problems. There are several effective treatments ...
Does diabetes increase BPH?
Diabetes and heart disease. Studies show that diabetes, as well as heart disease and use of beta blockers, might increase the risk of BPH. Lifestyle. Obesity increases the risk of BPH, while exercise can lower your risk.
How does hyperplasia affect your risk for breast cancer?
Hyperplasia can affect your risk for breast cancer, but how much depends on what type it is:
What is the difference between lobular and ductal hyperplasia?
Ductal hyperplasia (also called duct epithelial hyperplasia) is an overgrowth of the cells that line the small tubes (ducts) inside the breast, while lobular hyperplasia is an overgrowth of cell lining the milk glands (lobules). Ductal and lobular hyperplasia occur at about the same rate, and have about the same effect on breast cancer risk.
What is the term for the overgrowth of the ducts in the breast?
Hyperplasia of the Breast (Ductal or Lobular) Hyperplasia is also known as epithelial hyperplasia or proliferative breast disease. It’s an overgrowth of the cells that line the ducts or the milk glands (lobules) inside the breast. Ductal hyperplasia (also called duct epithelial hyperplasia) is an overgrowth of the cells that line the small tubes ...
Is hyperplasia atypical or usual?
Hyperplasia is often described as either usual or atypical based on how the cells look under a microscope.
Is atypical hyperplasia a risk factor for breast cancer?
Atypical hyperplasia (ADH or ALH) is linked to a higher risk of breast cancer. Even though most women with atypical hyperplasia will not develop breast cancer, it's still important to talk with a health care provider about your risk and what, if any, options are best for you.
Can hyperplasia be felt?
Hyperplasia doesn’t usually cause a lump that can be felt, but it can cause changes that can be seen on a mammogram. It’s diagnosed by doing a biopsy. (A hollow needle may be used to remove a small piece of tissue that’s checked in the lab. Or, surgery may be done to take out the abnormal breast tissue.)
Do you need to treat atypical hyperplasia?
Most types of usual hyperplasia do not need to be treated. But if atypical hyperplasia (ADH or ALH) is found on a needle biopsy, more breast tissue around it might be removed with surgery to be sure that there is nothing more serious nearby, such as cancer. (This is more likely to be recommended for ADH than for ALH.)
Overview
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) refers to a group of genetic disorders that affect the adrenal glands, a pair of walnut-sized organs above the kidneys. The adrenal glands produce important hormones, including: 1. Cortisol, which regulates the body's response to illness or stress 2. Mineralocorticoids, such as aldosterone, which regulate sodium...
Symptoms
- Signs and symptoms of CAHvary, depending on which gene is affected and the level of enzyme deficiency. The imbalance of hormones the body needs to function may mean too little cortisol, too little aldosterone, excess androgens or a combination of these imbalances.
Causes
- The most common cause of CAH is the lack of the enzyme known as 21-hydroxylase. CAH may sometimes be called 21-hydroxylase deficiency. This enzyme is required by the body to make proper amounts of hormones. There are other much rarer enzyme deficiencies that also cause CAH. CAH is a genetic disorder, which means it's inherited from parents and is present at birth. …
Risk Factors
- Factors that increase the risk of having CAHinclude: 1. Parents who both have CAHor are both carriers of the genetic change for the disorder 2. Being of Ashkenazi Jewish, Latino, Mediterranean, Yugoslav or Yup'ik ancestry
Complications
- People who have classic CAHare at risk of adrenal crisis. This is a life-threatening medical emergency that requires immediate treatment. Adrenal crisis can occur within the first few days after birth. It can also be triggered at any age by infectious illness or physical stress such as surgery. Very low levels of cortisol in the blood can cause diarrhea, vomiting, dehydration, low bl…
Prevention
- There is no known way to prevent CAH. If you're thinking of starting a family and you're at risk of having a child with CAH, your health care provider may recommend that you see a genetic counselor.