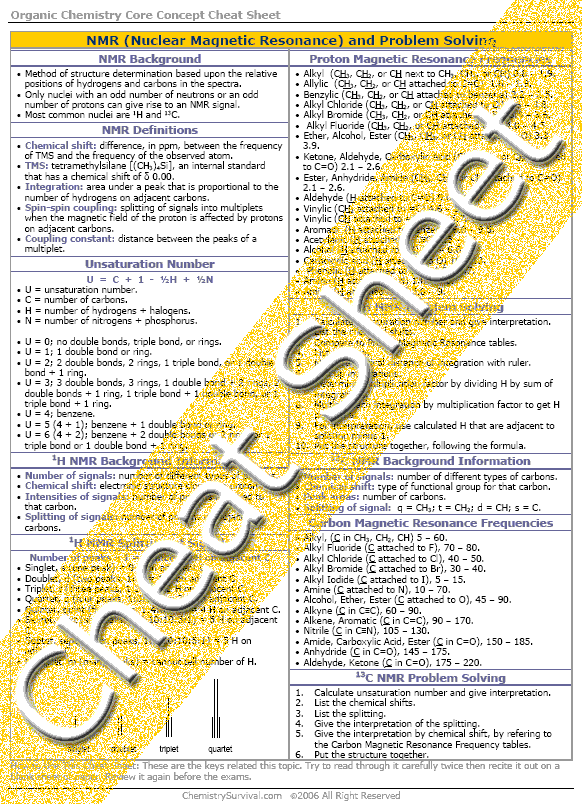
How bad is organic chemistry?
Aromatic compounds exhibit an abnormal stability compared to their open-chain (acyclic) versions. So, being aromatic is awesome. Molecules will typically do whatever it takes to become aromatic or maintain aromaticity. Aromatic conjugation also gives several unique chemical properties that we do not see in other types of molecules.
What makes an organic compound aromatic?
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a property of cyclic (ring-shaped), planar (flat) structures with a ring of resonance bonds that gives increased stability compared to other geometric or …
What makes something aromatic?
Aromatic compounds are organic molecules that contain rings with delocalised pi electrons, such as a benzene ring. They are also known as arenes. This article is an introduction to …
Which is the weirdest compound in organic chemistry?
Aromaticity is a property of conjugated cycloalkenes in which the stabilization of the molecule is enhanced due to the ability of the electrons in the [latex] \pi [/latex] orbitals to delocalize. This …
How is aromaticity defined?
What is aromatic compound with examples?
What aromatic means?
(Entry 1 of 2) 1 : of, relating to, or having aroma: a : having a noticeable and pleasant smell : fragrant aromatic herbs aromatic wines. b : having a strong smell The peat burns with a pungently aromatic smoke. c : having a distinctive quality.
Why is it called aromatic?
Why is pyrrole aromatic?
What are aromatic ketones?
What is the difference between aroma and aromatic?
What are aromatic ingredients?
What are the properties of aromatic compounds?
- Must be Cyclic.
- Must have (4n + 2) pi Electrons (n = 1,2,3,4,...)
- Resist Addition but Prefer Substitution.
- Must Possess Resonance Energy.
Why is benzene called aromatic?
What is the shape of aromatic?
...
Aromatic Rings.
| Benzene | 3D |
|---|---|
| Cinnamaldehyde | 3D |
| Download 3D |
What are aromatics used for?
What is aromaticity in chemistry?
Aromaticity is a property of conjugated cycloalkenes in which the stabilization of the molecule is enhanced due to the ability of the electrons in the π π orbitals to delocalize. This act as a framework to create a planar molecule.
Why do we care about aromatic compounds?
Why do we care if a compound is aromatic or not? Because we encounter aromatics every single day of our lives. Without aromatic compounds, we would not only be lacking many material necessities, our bodies would also not be able to function. Aromatic compounds are essential in industry; about 35 million tons of aromatic compounds are produced in the world every year to produce important chemicals and polymers, such as polyester and nylon. Aromatic compounds are also vital to the biochemistry of all living things. Three of the twenty amino acids used to form proteins (“the building blocks of life”) are aromatic compounds and all five of the nucleotides that make up DNA and RNA sequences are all aromatic compounds. Needless to say, aromatic compounds are vital to us in many aspects.
What is an aromatic ring?
A ring that does have a loop of π π electrons is said to be aromatic. Thus, the rings in 2, 4, 5, and 7 are aromatic. A compound whose molecule contains one or more aromatic rings is called an aromatic compound. Thus, 2, 4, 5, and 7 are aromatic compounds. There are chemical and spectroscopic methods that can be used to experimentally determine whether a ring is aromatic or not. All aromatic rings share two structural features:
What is the Lewis diagram of a molecule?
The Lewis diagram of many a molecule, however, is not consistent with the observed properties of the molecule. The Lewis diagram of some molecules suggests a ring bearing a fully conjugated π π -electron system, or loop of π π electrons, provided each atom in the ring is sp 2 – or sp-hybridized.
What is an aromatic compound?
Aromatic compounds are substances that consist of one or more rings that contain alternating single and double bonds in its chemical structure. In real life, many aromatic compounds have an odor, however, there are some compounds that are chemically aromatic, but do not have a distinct smell. For example, benzene is an aromatic compound.
Is benzene an aromatic compound?
Benzene is aromatic; it follows Huckels Rule. While benzene and compounds that contain the benzene ring in its chemical structure are known to be aromatic compounds, there are other compounds that look slightly different but are aromatic nonetheless.
What is the chemical structure of benzene?
The chemical structure of benzene, as illustrated here, contains a hexagon ring with alternating double bonds. Here, you'll see there are two ways to draw benzene. Structure 1 shows all the carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms bonded together, and structure 2 shows a hexagon with alternating double bonds.
What are some examples of delocalized electrons?
Examples of the aromatic compounds toluene and naphthalene. Delocalized electrons are electrons that are not attached on a fixed atom. In the ring of an aromatic compound, electrons are delocalized, so they are spread out over the ring. Such electrons can also be described as 'floating' around the ring.
How to draw benzene?
Here, you'll see there are two ways to draw benzene. Structure 1 shows all the carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms bonded together, and structure 2 shows a hexagon with alternating double bonds. In structure 2, the edges of the hexagon are the carbon atoms, and the hydrogen atoms are not shown. Chemical structure of the aromatic compound benzene.
What is aromaticity in chemistry?
In chemistry, aromaticity is a property of cyclic ( ring-shaped ), planar (flat) structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to other geometric or connective arrangements with the same set of atoms . Aromatic rings are very stable and do not break apart easily.
What is an aromatic group?
An aromatic functional group or other substituent is called an aryl group. The earliest use of the term aromatic was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. Hofmann used the term for a class of benzene compounds, many of which have odors (aromas), unlike pure saturated hydrocarbons.
What are the characteristics of an aromatic ring?
An aromatic (or aryl) ring contains a set of covalently bound atoms with specific characteristics: 1 A delocalized conjugated π system, most commonly an arrangement of alternating single and double bonds 2 Coplanar structure, with all the contributing atoms in the same plane 3 Contributing atoms arranged in one or more rings 4 A number of π delocalized electrons that is even, but not a multiple of 4. That is, 4 n + 2 π-electrons, where n = 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. This is known as Hückel's rule.
What is Y-aromaticity?
Y-aromaticity is used to describe a Y-shaped, planar (flat) molecule with resonance bonds. The concept was developed to explain the extraordinary stability and high basicity of the guanidinium cation.
Is benzene an aromatic hydrocarbon?
Since the most common aromatic compounds are derivatives of benzene (an aromatic hydrocarbon common in petroleum and its distillates ), the word aromatic occasionally refers informally to benzene derivatives, and so it was first defined. Nevertheless, many non-benzene aromatic compounds exist.
What does the double arrow mean in resonance diagrams?
As it is a standard for resonance diagrams, the use of a double-headed arrow indicates that two structures are not distinct entities but merely hypothetical possibilities. Neither is an accurate representation of the actual compound, which is best represented by a hybrid (average) of these structures. A C=C bond is shorter than a C−C bond. Benzene is a regular hexagon —it is planar and all six carbon–carbon bonds have the same length, which is intermediate between that of a single and that of a double bond .
When was the term "aromatic" first used?
The first known use of the word "aromatic" as a chemical term—namely, to apply to compounds that contain the phenyl group—occurs in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. If this is indeed the earliest introduction of the term, it is curious that Hofmann says nothing about why he introduced an adjective indicating olfactory character to apply to a group of chemical substances only some of which have notable aromas. Also, many of the most odoriferous organic substances known are terpenes, which are not aromatic in the chemical sense. But terpenes and benzenoid substances do have a chemical characteristic in common, namely higher unsaturation than many aliphatic compounds, and Hofmann may not have been making a distinction between the two categories. Many of the earliest-known examples of aromatic compounds, such as benzene and toluene, have distinctive pleasant smells. This property led to the term "aromatic" for this class of compounds, and hence the term "aromaticity" for the eventually discovered electronic property.
Naming benzene derivatives
Would a cyclohexatriene by any other name smell as sweet? In this tutorial, Sal and Jay explain how to name benzene derivatives, the sometimes sweet-smelling cyclic molecules that can be used in the synthesis of explosives and plastics.
Reactions of benzene
In this tutorial, Sal shows the mechanism of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution and the reactions of bromination and Friedel-Crafts Acylation.
Aromatic stability
In this tutorial, Sal and Jay explain the concept of aromatic stabilization and show how to determine if a compound or an ion exhibits aromaticity. Knowledge of MO theory is assumed.
Electrophilic aromatic substitution
In this tutorial, Jay shows several electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
Directing effects
In this tutorial, Jay shows you the directing effects of substituents on a benzene ring. Knowledge of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution reactions is assumed.
Other reactions and synthesis
In this tutorial, Jay covers a few more reactions of benzene derivatives and also shows how to approach the synthesis of substituted benzene rings.
Nucleophilic aromatic substitution
In this tutorial, Jay shows the addition-elimination mechanism and the elimination-addition mechanism.
What are aromatic hydrocarbons?
The aromatic hydrocarbons are “ unsaturated hydrocarbons which have one or more planar six-carbon rings called benzene rings, to which hydrogen atoms are attached” . Many aromatic hydrocarbons contain a benzene ring (also referred to as an aromatic ring). The benzene ring is stabilized by resonance and the pi electrons are delocalized in ...
What is the primary reactant in organic chemical reactions?
Many organic chemical reactions involve the use of aromatic hydrocarbons as the primary reactant. Some such reactions are listed in this subsection along with a brief description of each of these reactions.
What is the green pigment found in plants?
The green pigment found in plants, more commonly known as chlorophyll, consists of aromatic hydrocarbons and is very important in the process of food production in plants. The nucleic acids and amino acids in the human body also consist of these aromatic hydrocarbons.
How are carbon and carbon bonds formed?
Carbon-carbon bonds can be formed from the coupling reactions of arenes and products such as vinyl arenes, alkyl arenes, etc. are formed. The formation of carbon-oxygen bonds can occur in these reactions, forming aryloxy compounds. Carbon-nitrogen bonds can form in coupling reactions, giving products such as aniline.

What Are Aromatic compounds?
Aromatic Compounds Examples
- Aromatic hydrocarbon, are hydrocarbons containing sigma bonds and delocalized pi electrons between carbon atoms in a ring. For example, benzene. They are known as aromatic due to their pleasant smell. Aromatic compounds are broadly divided into two categories: benzenoids (one containing benzene ring) and non-benzenoids (those not containing a benzene ring) for example…
Huckel’s Rule of Aromaticity
- Huckel’s rule states that only planar, fully conjugated monocyclic polyenes having 4n + 2 π electrons, where n is an integer, that is, n = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, etc., should possess aromatic stability. An aromatic compound must be planar and contain a cyclic cloud of π electrons below and above the plane of the molecule. It contains SP2 hybridized carbon atoms and must obey the Huckel ru…
Properties of Aromatic Compounds
- Arenes are mostly nonpolar and non-miscible in water. These compounds are usually unreactive and are used as solvents for various other nonpolar compounds. Their carbon to hydrogen ratio is high therefore, they are characterized by sooty yellow flame.
Classification of Aromatic Compounds
- The classification of arenes is based on the position of the functional group. They are classified into two and we have discussed below:
IUPAC Nomenclature of Aromatic Compounds
- Earlier, most of the compounds with the same structural formula were known by different names depending on the regions where they were synthesized. This naming system was very trivial since it raised a lot of confusion. Finally, a common naming system enlisting standard rules was set up by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and Applied Chemistry) for the naming of compounds. Th…