
The Business Process Maturity Model (BPMM) rigorously follows the principles of Humphrey’s Process Maturity Framework and was developed by co-authors of the CMM for Software, CMMI, and the People CMM. The BPMM can be mapped to CMMI, but has been written to guide improvement of business processes which tend to be more transactional and are better
How to assess the process maturity of your business?
- Do we have a common language for how a given activity is performed? (a core, enabling or governing activity)
- Can we draw a common visual representation on how we collaborate on it? (check out our simple process mapping guide . )
- What proportion of our people work in this way?
- How do we keep it alive and present so we keep improving it?
How would you build a business process model?
- Get a clear picture of the entire organizational processes
- Identify the interactions in processes and bring about improved workflows using a graphical representation
- Make important business decisions after a thorough review of current processes
- Understand the need for automation and stop redundant tasks from eating into your workforce’s precious time
How to develop a business process model?
To create a business process model, you will take the following steps:
- Create a dossier structure
- Enter data
- Create a business process model and a few detailed sub process models, using the data
- Create links between the models
- Create views, using the models
- Create links between views
- Create a visualization, using the views
- Publish the visualization to the Viewer to have it commented by stakeholders
What is the value of Process Maturity Models?
process theory A maturity model is a tool that helps people assess the current effectiveness of a person or group and supports figuring out what capabilities they need to acquire next in order to improve their performance.
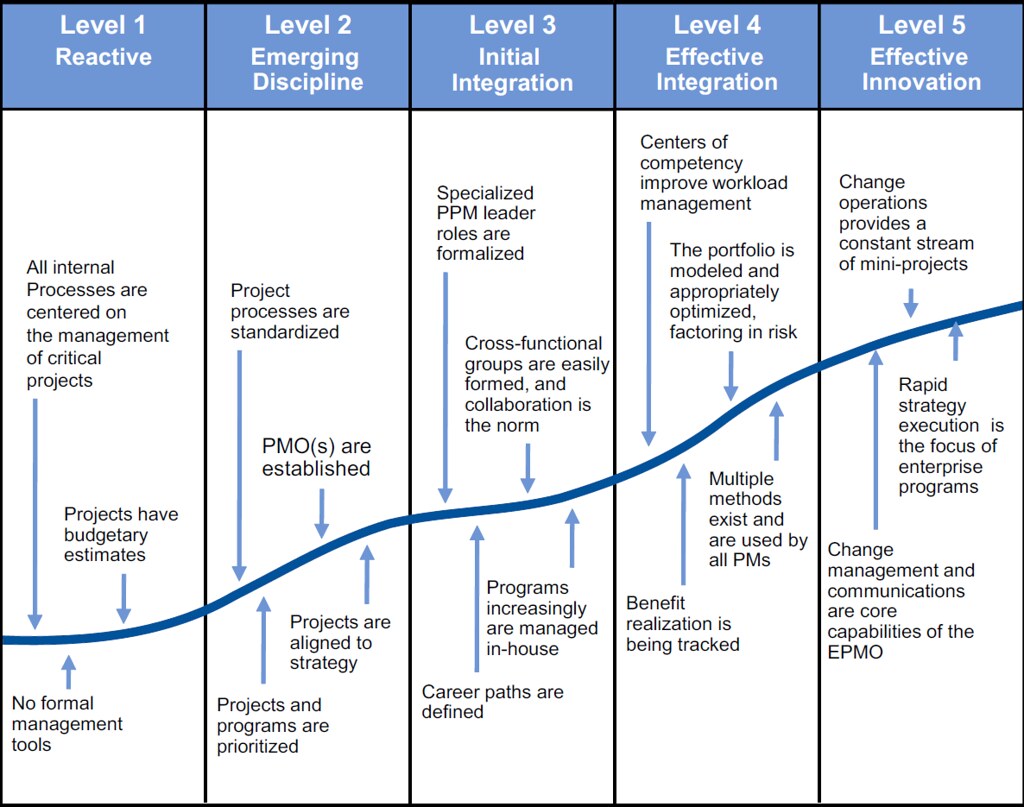
What is a business maturity model?
A maturity model shows how capable an organization or system is of achieving continuous improvement. Basically, maturity is being judged by how good your organization or system is at self-improvement.
What is the process maturity model and what is IT used for?
What is Capability Maturity Model (CMM)? The Capability Maturity Model (CMM) is a methodology used to develop and refine an organization's software development process. The model describes a five-level evolutionary path of increasingly organized and systematically more mature processes.
How is business process maturity measured?
Business Process Maturity TableLevel 1: No Processes Defined. ... Level 2: Reactive State. ... Level 3: Controlled State. ... Level 4: Improvement to Goal. ... Level 5: Best-In-Class. ... Challenge the Way You Think About Work.
What is meant by process maturity?
1. Is the extent to which processes are explicitly defined, managed, measured, controlled and effective. Process maturation implies that process capability is improved over time, (BPMM, 2007).
What are the 5 levels of CMM?
The five CMMI maturity levels are:Initial. Processes are seen as unpredictable, poorly controlled, and reactive. ... Managed. Processes are characterized by projects and are frequently reactive.Defined. Processes are well-characterized and well-understood. ... Quantitatively Managed. ... Optimizing.
What are the elements of a maturity model?
The Five Maturity Levels of the Capability Maturity ModelInitial Level. The initial level, as the name suggests, is the starting point for the utilization of an undocumented or new repeat process. ... Repeatable Level. ... Defined Level. ... Managed Level. ... Optimizing Level.
What are the benefits of using a BPM Maturity Model?
Benefits from conducting a BPM Maturity Assessmenta framework for better understanding of the BPM approach.detailed understanding of maturity at each of the 7Enablers of BPM.waypoints for the BPM development journey.facilitation of ongoing discussion of process matters.More items...
What are the 4 maturity levels?
The 4 Maturity Levels of Data Management for Stakeholder Engagement ActivitiesLevel 1 – Ground Level: No digital trail. ... Level 2 – Ad Hoc Level: Focus on data collection. ... Level 3 – Operational Level: Reporting with lagging indicators; operation and project-focused.More items...•
How do you use a maturity model?
There is a basic three step process.Step 1: Assess yourself. You need to first determine your current level of maturity. ... Step 2: Determine how far you want to go in maturity. This seems obvious, but once you know where you are today, you can make decisions about how far you want to go. ... Step 3: Identify gaps.
What is process maturity assessment?
A Process Maturity Assessment evaluates the attributes of a company's processes to determine the process' ability to consistently and continuously contribute to achieving organizational objectives. Processes with a high ability to contribute to these objectives, are considered mature.
What are the most commonly used maturity framework of IT business processes?
Two of the most widely used process maturity models—the SEI's CMMI and the Object Management Group's Business Process Maturity Model (BPMM)—both define five-level maturity models with corresponding process areas at each level, as listed in Table 5.3.
How is maturity model different from capability model?
Capability models are outcome based, maturity models are not By making this capability explicit, they tell organizations what they need to develop, and what that goal looks like in the very best teams.
What is BPMM in business?
It is for this reason the Business Process Maturity Model (BPMM) originated. BPMM helps achieve uniform standards, identify weaknesses in workflows, and create standardized tailored processes that simplify the requirements for enterprise applications. BPMM’s roots can be traced back to the Process Maturity Framework ...
What is BPMM conformance appraisal?
BPMM Conformance Appraisals help assure the implementation of practices at a level that achieve the intent and goals of the practices and their process areas. BPMM conformance appraisals are of 4 distinct types:
What is BPMM conformance?
Evaluating the BPMM conformance is about ensuring that the implemented system meets the needs of the client. Verification of conformance necessitates an effective appraisal technique to gather multiple forms of evidence to evaluate the performance of the practices contained in the BPMM.
What are the goals of a business process improvement program?
The goals are typically to continuously reduce costs, minimize errors, eliminate waste, improve productivity, and streamline activities. As we continue to deal with COVID-19 and its economic aftermath, most organizations will prioritize Business Process Improvement initiatives. This is true for a few reasons.
Why is process improvement important?
This is true for a few reasons. First, Process Improvement is one of the most common and effective ways of reducing costs. As the global economy slows down, Cost Management will jump to the forefront of most corporate agendas. Secondly, a downturn typically unveils ineffective and broken business processes.
What does it mean to have processes?
This means that work gets done in the best way every time, and also means that the teams who follow them will be able to point out obvious flaws and inefficiencies.
Is BPMM a good option?
The super specific BPMM that works great for a particular academic is not always the best option to deploy in your business. These super-specific BPMMs do not make it very clear that their use value is so limited. As such, not only are they not appropriate for many organizations, those organizations don’t know that.
What is process maturity?
The effectiveness and efficiency with which organizations implement and execute IT processes is often expressed in terms of process maturity, a relative measure of how well processes are fully defined, documented, implemented, and optimized for use in an organization. Appraisals of an organization’s process maturity examines the specific steps and activities the organization performs in a given business or technical domain and the extent to which the organization standardizes its processes to achieve more repeatable, predictable, and reliable results. The standards or normative references used to evaluate maturity specify process areas—categories of related practices and activities that collectively enable process improvement in a given domain—represent processes that organizations are expected to perform. To achieve specific maturity levels against these reference models, organizations must demonstrate that they have implemented and follow the processes included in each process area. Two of the most widely used process maturity models—the SEI’s CMMI and the Object Management Group’s Business Process Maturity Model (BPMM)—both define five-level maturity models with corresponding process areas at each level, as listed in Table 5.3. The number and type of processes specified in CMMI varies somewhat across the different versions of the model for acquisition, development, and services. All versions of the CMMI also include capability levels, where level zero means “incomplete” or not performed and levels one through three indicate “performed,” “managed,” and “defined” capabilities, respectively [25].
Who developed the maturity model?
Watts Humphrey laid the groundwork for maturity models. In the late 1980s, he developed the process maturity framework at Software Engineering Institute (SEI). This formed the basis for the Capability Maturity Model (CMM) for software in the mid-1990s and CMMI in early 2000.
What is maturity level?
A maturity level is not a universal solution that addresses all business processes of an enterprise. Maturity level 2, for example, includes requirements and configuration management, and maturity level 7 comprises further process areas.
What is system level audit?
System-level audits are commonly performed as part of internal auditing, often in support of IT governance, risk management, or information security programs. The opposite is true in commercial organizations in some industries and public sector organizations such as government agencies, which are subject to external system audits by government oversight agencies. For instance, external IT audit guidance from the FFIEC applies to banks and other financial institutions under the supervisory authority of regulators such as the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) or the Consumer Finance and Protection Bureau (CFPB). Many organizations in industries, not otherwise addressed by regulations on audits, may nonetheless face audits related to investigations by the U.S. Federal Trade Commission or European Commission. Government agencies are subject to laws and regulations that do not apply to nongovernment entities, including many that mandate IT management practices, information security provisions, and privacy protections. Maintaining compliance with these requirements drives substantial internal IT auditing activity in government agencies, in addition to external audits performed by authorized oversight bodies, such as the U.S. GAO. Public sector audits of information systems in the United States and many other countries follow specific procedures and methodologies such as those specified in the Federal Information System Controls Audit Manual (FISCAM) [33] and the Information System Security Review Methodology published by the International Organization of Supreme Audit Institutions [34].
What is business goals?
The business goals topic area entails concepts of business administration, marketing, and project management. Anyone who works in the business process environment should have basic knowledge of organizational forms of enterprises, market environment analyses, marketing, financial key figures, and business analysis methods.
What is technical certificate?
The technical certificates are intended for IT employees who implement business processes in systems, that is, architects, designers, and developers. Topics include, for example, detailed modeling aspects, information security, and architectures such as Service Oriented Architecture (SOA).
Can business processes be repeated?
Business processes can be repeated at the local level; that is, specific departments or teams (work units) are able to execute defined flows repeatedly. Similar tasks in different teams can be processed with completely different approaches. 3 – Standardized. Standard processes derived from best practices are used.
Overview of Business Process Management Maturity Model (BPMM)
Such processes also reduce an organization’s ability to assess present and future risks. A Business Process Maturity Model (BPMM) serves as a platform for organizations to measure their BPM capabilities and achieve improvements through evaluation and comparison tools.
Why we need the Business Process Maturity Model in Businesses?
A BPMM is essentially an analysis tool for Business Process Management that an organization uses to evaluate and assess the maturity of its processes and the governance around them.
BPMM Implementation Approach
In the international BPM community, it is well recognized that there is only one maturity model that should be used. This is the model that was developed by the Object Management Group, and it is publicly available on their website ( www.omg.org ).
Applying Business Process Maturity Model (BPMM)
Let’s try to apply the BPMM model described above to your organization. Again, any maturity model should always focus on the “four pillars” of BPM. In case you’ve forgotten them, they are:
Other Considerations when Implementing the BPMM
The success of the maturity model is dependent on management’s ability to ignore the constant changes that face an organization. Because many times IT teams amended the processes due to new IT systems introduced.
Conclusion
There are many examples of enterprises wasting millions of dollars by attempting to fix their businesses, particularly through IT. The BPMM can play a vital role by developing a strong business foundation and standard practice in process management.
What is process maturity?
Process maturity is an indication of how close a developing process is to being complete and capable of continual improvement through qualitative measures and feedback. Thus, for a process to be mature, it has to be complete in its usefulness, automated, reliable in information and continuously improving.
What is a business process?
A business process can be described as a collection of related, structured activities or processes (a chain of events) that produce a specific service or product for a particular customer or customers (internal or external). A business process usually cuts across several functions for support (e.g., IT, finance, legal, etc.).
What is process in administrative?
Thus, a process is a predetermined course of action and a standing plan for people to follow in carrying out repetitive administrative tasks in a systematic way. They are a translation of general plans and policies into standard patterns of decisions and action.
Is it reasonable to prioritize business processes?
Thus, it is more reasonable for an organization to prioritize business processes and enhance the business maturity gradually. Business-critical processes are the ones that have a stronger impact on the overall Maturity of the organization. Business-critical processes can be arrived at by the following steps:
Does maturity of processes improve?
From the inception of an organization through its growth, the maturity of its processes usually improves. But this may not be the case for all its business processes. Some may still be at the lower levels. This shows that the organization has not had an all-round maturity of its processes.
What is a maturity model?
A maturity model is a tool that businesses and software development teams use to measure how well their business or project is doing and how capable they are of continuous improvement. Unlike other goal-driven measuring tools, maturity models can evaluate qualitative data to determine a company's long-term trajectory and performance.
Why are maturity models important?
Maturity models are important because they provide flexible performance monitoring that can reveal valuable information about a company's health and potential.
3 types of maturity models
There are several types of maturity models. The one you choose to use might depend on your industry or what you hope to evaluate. Here are three different model types to consider:
Benefits of using maturity models
There are a variety of benefits businesses can receive from using maturity models, including:

What Are Maturity Models?
Why Process Maturity Models?
- As you have read in this blog, measurement is the key to improvement. As a process maturity model measures how well an organisation applies process management, it thus helps to evolve to higher levels of process management capabilities. So that the organisation succeeds even better with optimal value creation and continuous improvement. It has been proven, indeed, that the qu…
History and Overview of The Main Maturity Models
- CMM
The origin of business process (management) maturity models can be found at the US Department of Defense in the nineties of previous century. This Department was looking for a way to assess the capabilityof its potential software development vendors to deliver on time and acc… - CMMI – Capability Maturity Model Integration
The limitation of CMM was its too high focus on software development, while there was a need to apply similar models in other parts of organisations. So, many specific variants popped up. E.g. the one for HRM, named the People CMM. This model aimed at assessing the maturity of an org…