
What allowed you to measure the amount of catalase activity?
what allowed you to measure the amount of catalase activity? the bubble height reaction the reaction rate would, ,if another substance competed with catalase for the active site.
What does catalase do in the body?
What Is the Role of Catalase?
- Cellular function. Oxygen is crucial to life; however, when we use oxygen our bodies constantly produce free radicals. ...
- Catalase test. Catalase test is extensively used by microbiologists in the laboratory to recognize and differentiate between bacterial species.
- Grey hair. ...
- Food industry. ...
- Cleaning agent. ...
What are the benefits of catalase?
The Health Benefits of Catalase
- Powerful Antioxidant Support. Catalases are perhaps the single most efficient enzymes found in the cells of the human body. ...
- Possible Anti-Aging and Anti-Degenerative Effects. Catalase is currently being studied for its applications on extending lifespan and vitality. ...
- Promotes Longevity
- Fat Reduction. ...
- Supports DNA Integrity. ...
What is the function of catalase in the human body?
What is the function of catalase in the human body? Catalase is one of the most important antioxidant enzymes. As it decomposes hydrogen peroxide to innocuous products such as water and oxygen, catalase is used against numerous oxidative stress-related diseases as a therapeutic agent.
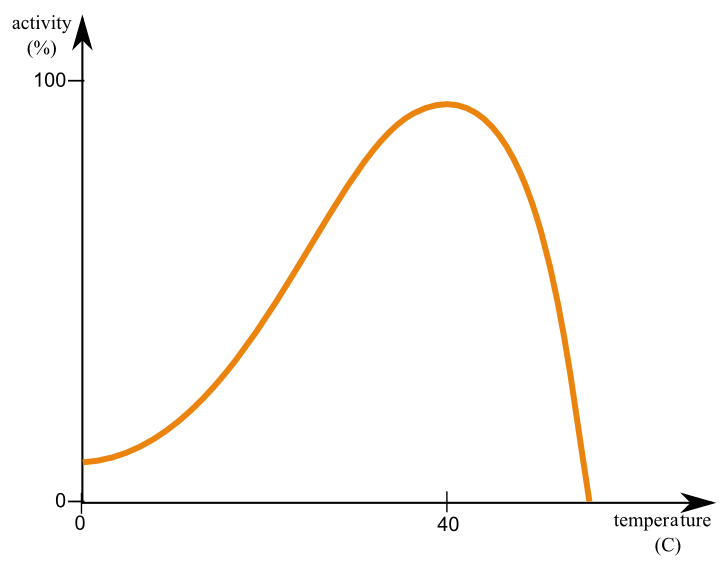
How is catalase activity determined?
The catalase activity in a sample is determined by measuring the decrease in H2O2 concentration observed following an incubation of the analyte sample with an H2O2 standard solution. In order to determine catalase activity using the Megazyme Catalase Assay Kit, two separate reactions must be completed.
What affects catalase activity?
The rate at which an enzyme works is influenced by several factors including the concentration of substrate (hydrogen peroxide in the case of catalase), temperature, pH, salt concentration and the presence of inhibitors or activators.
What is catalase in simple terms?
Catalase (CAT, 1.11. 1.6) is an antioxidant enzyme present in all aerobic organisms. It is known to catalyze H2O2 into water and oxygen in an energy-efficient manner in the cells exposed to environmental stress.
What is the importance of catalase?
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting the cell from oxidative damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS).
What is the purpose of catalase test?
The catalase test facilitates the detection of this enzyme in bacteria. It is essential for differentiating catalase-positive Micrococcaceae from catalase-negative Streptococcaceae. While it is primarily useful in differentiating between genera, it is also valuable in speciation of certain gram positives.
What happens if you have a catalase deficiency?
Mutations in the CAT gene greatly reduce the activity of catalase. A shortage of this enzyme can allow hydrogen peroxide to build up to toxic levels in certain cells. For example, hydrogen peroxide produced by bacteria in the mouth may accumulate in and damage soft tissues, leading to mouth ulcers and gangrene.
Where is catalase used?
Catalase has various industrial applications. In the food industry, it is used in combination with other enzymes in the preservation of foodstuffs and in the manufacture of beverages and certain food items. Commercial catalases also are used to break down hydrogen peroxide in wastewater.
What type of enzyme is catalase?
Peroxidases, also known as catalases, are also an oxidoreductase class of enzymes, which catalyze oxidoreduction reactions. The peroxidase enzyme catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and molecular oxygen (see illustration). Catalase is a haem-containing enzyme.
What is another word for catalase?
In this page you can discover 14 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for catalase, like: peroxidase, trypsin, plasmin, rubisco, nitrogenase, esterase, catechol, hydrolytic, papain, polyamines and lyase.
Where is catalase produced in the human body?
In this case oxygen is generated when hydrogen peroxide breaks down into oxygen and water on contact with catalase, an enzyme found in liver. Enzymes are special protein molecules that speed up chemical reactions.
What is the source of catalase?
Cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli, cabbage, kale and collard and turnip greens, are rich in catalase. Eating plenty of these green leafy vegetables also stimulates your body's production of catalase.
What are the four types of catalase?
... on the physical and biochemical properties of catalases, these encompass four different types: mono-functional haem catalases (classical catalase), catalase- peroxidases (atypical catalase), non-haem catalases (pseudocatalases) and minor catalases ( Sooch et al., 2014b).
What are the 4 factors that affect enzyme activity?
Several factors affect the rate at which enzymatic reactions proceed - temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, substrate concentration, and the presence of any inhibitors or activators.
How does pH affect catalase activity?
Catalase is an enzyme, a large protein that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction. The optimum pH level of catalase is between pH 7 and pH 11. At a pH level lower or higher than this range, the catalase stops working.
Why does temperature affect catalase activity?
Temperature has an effect on both the structure of the catalase itself and the hydrogen bonds it is designed to cleave. As the temperature increases toward the optimum point, hydrogen bonds loosen, making it easier for catalase to act on hydrogen peroxide molecules.
How does cold temperature affect catalase activity?
Effect of Freezing on Enzyme Activity At very cold temperatures, the opposite effect dominates – molecules move more slowly, reducing the frequency of enzyme-substrate collisions and therefore decreasing enzyme activity.
What is catalase in plants?
Iti Sharma, Parvaiz Ahmad, in Oxidative Damage to Plants, 2014. Catalase (CAT, 1.11.1.6) is an antioxidant enzyme present in all aerobic organisms. It is known to catalyze H2 O 2 into water and oxygen in an energy-efficient manner in the cells exposed to environmental stress. Catalase is located in all major sites of H 2 O 2 production in ...
What is the role of catalase in the oxidation of acids?
Catalase also catalyzes peroxide-dependent oxidation of acids (e.g., hydrazoic, formic, and nitrous acids), lower aliphatic alcohols, and hydroxylamine. The enzyme is present in various living tissues and cells. It enters milk via somatic cells, in which it is associated with the membranes.
What is the enzyme that converts hydrogen peroxide to oxygen?
Catalase is another dismutase enzyme. It contains a heme moiety at the active site and converts two hydrogen peroxide molecules to oxygen and water (eqn [28] ). This reaction requires the presence of a small amount of hydrogen peroxide to bind at the active site in order to generate catalase compound I, which reacts with a second molecule of hydrogen peroxide. The Km of catalase for H 2 O 2 is in the m mol l −1 range, although its Vmax is extremely high. Because of the high Km, catalase is most effective at degrading high concentrations of hydrogen peroxide, such as might be found in peroxisomes, the subcellular organelle where most catalase is localized.
What is the enzyme that decomposes hydrogen peroxide?
Catalase (EC 1.11.1.6) is a tetrameric haem-containing enzyme, present in the cells of all aerobic organisms, which catalyses the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H2 O 2) to water and oxygen:
How many classes of catalases are there?
According to the structure and sequence, catalases can be divided into three classes (Fig. 11.2 ): monofunctional catalase or typical catalase, catalase-peroxidase, and pseudocatalase or Mn-catalasee ( Zhang et al., 2010 ).
How much catalase is in milk?
Catalase has been purified (23 000-fold) and crystallized from bovine milk, yielding 0.1 mg kg -1 milk. Purification of catalase from milk, using buttermilk as starting material, involves extraction with n -butanol, (NH 4) 2 SO 4 fractionation (35–55% saturation), chloroform:methanol extraction, followed by chromatography of the extract on diethylaminoethyl (DEAE)-Sephacel and Sephacryl S-300.
Why is catalase in milk?
High catalase activity in raw milk may be an indicator of high microbial load and, hence, poor quality. It has been suggested that catalase plays a role in lipid oxidation because the enzyme contains a prosthetic ferric group; however, this role has not been demonstrated experimentally.
What is the role of catalase in the cell cycle?
By the end, catalase is frequently used by cells to catalyze rapidly the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into less-reactive gaseous oxygen and water molecules. Peroxisomes in plant cells are involved in the process of photorespiration in which oxygen is used in the production of carbon dioxide and symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Hydrogen peroxide is used as a potent antimicrobial agent when the cells in the organisms are infected with a pathogen. Catalase-positive pathogens, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Campylobacter jejuni, and Legionella pneumophila. These pathogens can make catalase deactivate the peroxide radicals, which allows them to survive unharmed within the host.
How to detect catalase in a microbial sample?
The presence of catalase in a microbial or tissue sample can be demonstrated by adding hydrogen peroxide and observing the reaction. The production of oxygen can be seen by the formation of bubbles. This easy test, which can be viewed with the naked eye, without the aid of instruments. It is possible only because catalase has a very high specific activity that helps to produce a detectable response, as well as the fact that one of the products is a gas.
Why is catalase used in contact lens cleaning?
Catalase is also used in the textile industry, in order to remove the hydrogen peroxide content from the fabrics to make sure the material is peroxide-free. A minor use is in the hygiene of contact lens, few of the lens-cleaning products can disinfect the lens using a hydrogen peroxide solution.
How many domains does catalase have?
Human catalase forms a tetramer that is composed of four subunits, each of which can be conceptually divided into four domains. The extensive core of each subunit is consists of an eight-stranded antiparallel b-barrel, where the nearest neighbor connectivity is by b-barrel loops on one side and a9 loops on the other side. A helical domain at one face of the b-barrel is composed of four helices of the C-terminal and four helices that are derived from residues between b4 and b5. Different protein variants are caused by the alternative splicing process.
What is the condition that is caused by the homozygous mutations in CAT?
Acatalasia: Acatalasia is a condition that is caused by the homozygous mutations in CAT, that results in a lack of catalase. Symptoms that are mild and include oral ulcers. A heterozygous CAT mutation is found lesser but still can have the presence of catalase.
What Is Catalase?
Catalase is an enzyme, a protein made by a living organism to help facilitate a chemical reaction. Specifically, catalase is an incredibly important and diverse antioxidant enzyme. Despite its importance, few people have heard of catalase.
How much catalase is in a serving?
Dosages for catalase supplements vary, but they typically contain 250-500 mg of the enzyme per serving.
What is acatalasemia caused by?
Acatalasemia is a rare genetic condition specifically caused by the lack of a functional catalase gene [ 46, 47 ].
What is the name of the enzyme that comes from oxygen?
Just about every living thing that comes in contact with oxygen, from bacteria to animals, produces some version of catalase [ 1 ].
Is catalase a natural enzyme?
Please note: the beneficial roles of catalase as a naturally occurring enzyme may not translate to the benefits of catalase supplementation.
Is catalase an antioxidant?
Since hydrogen peroxide is a powerful oxidizing agent, catalase is considered one of the more important antioxidant enzymes [ 2 ].
Does catalase help with cell damage?
Catalase helps regulate these systems and ensure that the toxic by-products don’t do too much damage to cells, but, as with many aspects of biology, this is a ‘Goldilocks’ scenario – ideally, catalase prevents damage without interfering with important signaling processes [ 1 ].
What are the functions of catalase enzyme?
Functions of Catalase Enzyme. By the process of oxidation, a living body continuously generates free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules which also tend to cause instability to other molecules in the body. This leads to cell damage and onset of other malfunctions.
How does catalase work?
To combat all of these, catalase plays a vital role by dealing with the free radicals generated in the body. In the first phase, catalase converts harmful free radicals into less harmful hydrogen peroxide and then catalyzes the conversion of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. 3.
How to tell if catalase is active?
The activity of catalase can be illustrated by taking a microbial sample and adding hydrogen peroxide to it. Bubble formation in the reaction indicates the release of oxygen. The activity of the enzyme is so rapid that it can be observed with naked eyes. This is because catalase has a higher rate of activity that generates a quick response. Besides, another by-product is gas which also releases in the reaction making the reaction easy to detect.
What enzyme prevents peroxide build up in the body?
Peroxide build-up and accumulation can turn toxic for cells and tissue in the body. So, enzyme catalase prevents the building up of peroxide in the organelles, cells, and tissues and safeguards them. Catalase is commonly found in mammalian liver.
Why is catalase so rapid?
This is because catalase has a higher rate of activity that generates a quick response. Besides, another by-product is gas which also releases in the reaction making the reaction easy to detect.
Why is catalase important?
The catalysis brought by catalase is energy efficient and helps the cells deal with environmental stress . The rate of catalysis is also very high for the catalase enzyme.
What is the pH of catalase?
Human catalase is stable at a pH level 7. For other catalases, the optimum pH range is between 4 to 11 depending upon the species. The temperature parameter for catalase to be the same is also similar. The Catalase enzyme is also present in some anaerobic microorganisms and some fungi.
What Is Catalase Enzyme?
As the name suggests, catalase is an enzyme bringing about the catalysis of a reaction through which hydrogen peroxide is decomposed into oxygen and water. Catalase is responsible for preventing the accumulation of cellular organelles and safeguards these organelles and tissues from any destruction by the peroxide as peroxide is continuously synthesized by a number of metabolic reactions. Catalase is mainly found in the liver of mammals.
What is the role of catalase in preventing oxidative damage?
Commonly found in almost all living entities enabled with oxygen exposure, catalase is pivotal in preventing cells from oxidative damage by the ROS (reactive oxygen species). This antioxidant enzyme is found in all aerobic entities and catalyzes in an energy-efficient manner in the cells uncovered to environmental stress.
What are the major sites of hydrogen peroxide production in plants?
In higher plants, they are situated in all the major sites of hydrogen peroxide production in the cellular components such as chloroplast, mitochondria, cytosol and peroxisomes. A factor which indicates its versatility in the plant system is the existence of catalase isozymes in multiple molecular forms. Structural genes Cat1, Cat2 and Cat3 encode ...
How to tell if catalase is present in a tissue?
When catalase is found in a tissue or microbial sample, it can be illustrated by the addition of hydrogen peroxide and then the reaction can be noted. Oxygen release is indicated through bubble formation. It is a simple and easy demonstration, visible to naked eyes as catalase is known to have a very high specific activity generating an evident ...
What is the pH of catalase?
The optimal pH level for human catalase is nearly 7. The optimal pH for other catalases fluctuates between 4-11 varying from species to species, same goes with the temperature parameter, it varies.
How many amino acids are in an enzyme?
The enzyme is a tetramer of four polypeptide chains wherein every chain possesses more than 500 amino acids. It contains 4 iron-containing heme groups which are key, enabling it to react with the hydrogen peroxide.
