
The Cell Theory states:
- All living organisms are composed of cells. They may be unicellular or multicellular.
- The cell is the basic unit of life.
- Cells arise from pre-existing cells. (They are not derived from spontaneous generation .)
What is the cell theory and what does it state?
The cell theory states that all biological organisms are composed of cells; cells are the unit of life and all life come from preexisting life. The word cell was first used by Robert Hooke (1635–1703) when he looked at cork with a simple microscope and found what appeared to be blocks of material making up the cork.
What are the three concepts of cell theory?
They are the following:
- All living things or organisms are made of cells and their products.
- New cells are created by old cells dividing into two.
- Cells are the basic building units of life.
What does the cell theory tell us about cells?
In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory first formulated in the mid-nineteenth century, that living organisms are made up of cells, that they are the basic structural/organizational unit of all organisms, and that all cells come from pre-existing cells.
What are facts about cell theory?
Facts about Cell Theory. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and prokaryotic cells don’t have a nucleus. This makes eukaryotic cells 10 times larger than prokaryotic cells. Animal cells don’t have chloroplasts because animal cells don’t create chlorophyll. Every cell has a different type of job to do in an organism.
What is cell theory answer in short?
The cell theory was proposed by two scientists- Schleiden (1838)and Schwann (1839). It says that all the plants and animals are composed of cells and the cell is the basic unit of life. The cell theory was further expanded by Virchow (1855) by suggesting that all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
What is cell theory short answer 9?
Cell theory states that: → All living organisms are composed of cells. → Cell is the fundamental unit of life. → All new cells come from pre-existing cells. Types of Organisms on the Basis of Number of Cells.
What is the cell the theory?
The cell theory states that all biological organisms are composed of cells; cells are the unit of life and all life come from preexisting life. The cell theory is so established today that it forms one of the unifying principles of biology.
What is the cell theory Grade 7?
The cell theory is one of the fundamental principles of biology. The original version of the cell theory states: • Cells are the basic unit of life. All living organisms, both unicellular and multicellular, are composed of cells. Cells arise from pre-existing cells.
What is the cell theory class 8?
Cell theory states that all cells are similar in their basic structure and function but not identical.
Who explain cell theory?
Credit for developing cell theory is usually given to two scientists: Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden.
Why is the cell theory?
The cell theory definition states that cells are the building blocks of life. Cells both make up all living things and run the processes needed for life. Your hair, skin, organs, etc. are all made up of cells.
What is cell theory BSC 1st year?
Cell Theory states that cells are the basic units of all living organisms. But, the cell theory failed to explain how new cells arise. In 1855, Rudolf Virchow, a German physiologist stated in German 'Omnis cellula e cellula' which means that new cells come from already existing cells.
What is cell theory biology 11?
- Cell theory is understood as: - All living organisms are composed of cells and products of cells. - All cells originate from pre- existing cells. - Actions of an organism are the result of the sum total of activities and interactions of its component cells.
What is cell long answer?
“A cell is defined as the smallest, basic unit of life that is responsible for all of life's processes.” Cells are the structural, functional, and biological units of all living beings. A cell can replicate itself independently. Hence, they are known as the building blocks of life.
What is cell and cell theory class 9?
1) Cells are the basic unit of life and they are therefore considered to be the building blocks of living organisms. 2) All the living organisms are made up of cells; a cell is the basic structural and functional unit of each living organism. 3) All cells are produced by cells that already pre-exist.
What is cell theory and who gave it class 9?
Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann proposed the cell theory. According to this theory, all living beings are made up of one or more cells, and the cell is the most fundamental unit of life. Early cell theory comprised four statements, Cells are the building blocks of all living things.
What is cell class 9th Ncert?
A cell is able to live and perform all its functions because of these organelles. These organelles together constitute the basic unit called the cell. It is interesting that all cells are found to have the same organelles, no matter what their function is or what organism they are found in.
Who developed cell theory?
Schleiden and Schwann are generally credited as the developers of cell theory. 1855: Rudolf Virchow, another German scientist, describes the third part of cell theory, that all cells come from existing cells. Since then, microscopes have continued to become more and more refined, making it possible to study cells even more closely ...
What Is the Cell Theory? Why Is It Important?
The cell theory is one of the most important tenets of biology, and practically everything else you learn in science class relates back to it. But what is the cell theory? In this guide, we’ll give you a clear cell theory definition, explain key dates in the history of this theory, and explain why it’s so important to understand. After reading this guide, you’ll know everything you need to know about the cell theory!
How Is the Cell Theory Important for Biology?
However, that just goes to show how important the cell theory is. It’s one of the fundamental principles of bi ology, and it’s so important that it has become information many of us take for granted.
Why are cells important?
Cells even help us understand fundamental issues such as life and death: an organism whose cells are living is considered alive, while one whose cells are dead is considered dead. Before the cell theory existed, people had a very different view of biology.
What is a cell?
And what are cells? The literal definition is a cell is a group of organelles surrounded by a thin membrane. The cell theory definition states that cells are the building blocks of life. Cells both make up all living things and run the processes needed for life. Your hair, skin, organs, etc. are all made up of cells.
What is the newer part of the cell theory? What are some examples?
Examples of these processes include photosynthesis (where plant cells convert light energy into chemical energy) and cellular respiration (where both plant and animal cells convert glucose into energy). Part five refers to DNA and the fact it is passed from parent cell to child cell. Finally, part six of the cell theory tells us that all cells are made up of the same chemicals: water, inorganic ions, and organic molecules.
What are the parts of cell theory?
Some biology classes don’t require you to know these parts of the cell theory because they weren’t part of the original definition, but it’s still useful to be aware of them: 4. Energy flow occurs within cells. 5. Hereditary information is passed from cell to cell. 6.
Who is the cell theory?
Regina Bailey. Updated January 24, 2020. Cell Theory is one of the basic principles of biology. Credit for the formulation of this theory is given to German scientists Theodor Schwann (1810–1882), Matthias Schleiden (1804–1881), and Rudolph Virchow (1821–1902). The Cell Theory states:
What are the two types of cells?
Not all cells, however, are alike. There are two primary types of cells: eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Examples of eukaryotic cells include animal cells , plant cells , and fungal cells.
How do eukaryotic cells reproduce?
Cell Reproduction. Eukaryotic cells grow and reproduce through a complex sequence of events called the cell cycle. At the end of the cycle, cells will divide either through the processes of mitosis or meiosis. Somatic cells replicate through mitosis and sex cells reproduce via meiosis.
What type of cell reproduces through asexual reproduction?
Prokaryotic cells reproduce commonly through a type of asexual reproduction called binary fission. Higher organisms are also capable of asexual reproduction. Plants, algae, and fungi reproduce through the formation of reproductive cells called spores.
What are the processes that cells perform in the cell cycle?
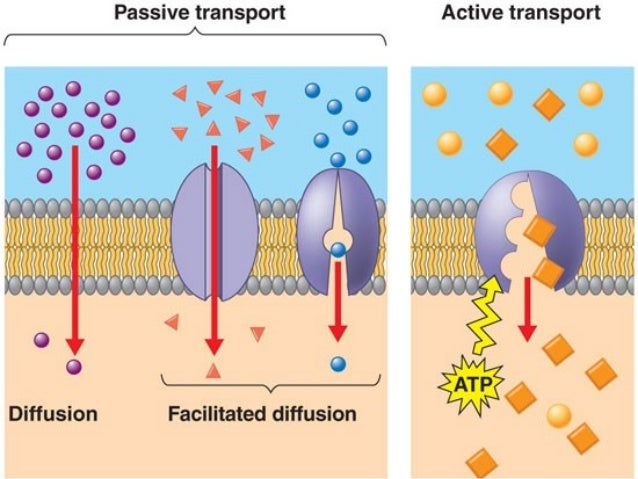
Cells also perform the active transport processes of endocytosis and exocytosis. Endocytosis is the process of internalizing and digesting substances, such as seen with macrophages and bacteria. The digested substances are expelled through exocytosis. These processes also allow for molecule transportation between cells.
Why do cells need to be able to survive?
Cells undergo the complex process of cellular respiration in order to obtain energy stored in the nutrients consumed. Photosynthetic organisms including plants, algae, and cyanobacteria are capable of photosynthesis. In photosynthesis, light energy from the sun is converted to glucose. Glucose is the energy source used by photosynthetic organisms and other organisms that consume photosynthetic organisms.
What is the process of cell migration?
Cell migration is a process that is vital for the development of tissues and organs. Cell movement is also required for mitosis and cytokinesis to occur. Cell migration is made possible by interactions between motor enzymes and cytoskeleton microtubules.
What is cell theory?
Cell theory is a proposed and widely accepted view of how most life on Earth functions. According to the theory, all organisms are made of cells. Groups of cells create tissues, organs, and organisms. Further, cells can only arise from other cells. These are the main tenants of cell theory.
How to study cell theory?
Single-celled organisms are a great way to study cell theory. With modern microscopes, the processes behind cell theory can easily be viewed and studied. A great example of watching cell theory in action can be accomplished by putting a drop of pond water under a microscope.
How do organisms start?
Thus, all organisms start as single cells. These cells grow, divide through mitosis, and develop into multi-celled organisms. Mitosis is a form of cell division that produces identical cells. These cells can then differentiate when given different signals to produce different types of tissues and organs. This is how large and complex organisms are made. Single-celled organisms divide as well, but when they divide, the cells separate into two new individuals. This is known as asexual reproduction. For more, see our article on the Three Parts of Cell Theory.
What are the three major hypotheses of cell theory?
Cell theory has three major hypotheses: First, all organisms are made of cells. Second, cells are the fundamental building blocks used to create tissues, organs, and entire functioning organisms. The third, and probably most important part of the theory is that cells can only arise from other cells. Thus, all organisms start as single cells.
What is it called when cells separate into two new individuals?
Single-celled organisms divide as well, but when they divide, the cells separate into two new individuals. This is known as asexual reproduction. For more, see our article on the Three Parts of Cell Theory.
What is a scanning electron micrograph of red blood cells?
Below is a scanning electron micrograph of red blood cells. It distinctly shows how our red blood cells are separate, functional units of the human body. Blood cell. Like red blood cells, every part of the body is composed of different types of cells.
What is the science of testing cells?
None of the above. 3. A scientist in the lab is testing cells. The scientist has various chemicals that are applied to cells, and the reaction observed. The scientist puts some bleach on cells and watches the reaction. The bleach starts to destroy the cell membrane and eats its way to the DNA, which is also destroyed.
Overview
3 Parts of Cell Theory
- Cell theory has three major hypotheses: 1. First, all organisms are made of cells. 2. Second, cells are the fundamental building blocks used to create tissues, organs, and entire functioning organisms. 3. The third, and probably most important part of the theory is that cells can only arise from other cells. Thus, all organisms start as single cell...
Cell Theory Examples
- Single-Celled Organisms
Single-celled organisms are a great way to study cell theory. With modern microscopes, the processes behind cell theory can easily be viewed and studied.A great example of watching cell theory in action can be accomplished by putting a drop of pond water under a microscope. Belo… - In Plants
Cells were first discovered in plants. Plants, unlike the other examples in this article, have large structures called cell walls, which enable the plant to remain rigid. These cell walls are easily visible, even with the first microscope invented in 1665.Robert Hooke, the man who first identifie…
Contributions to Cell Theory
- Besides Robert Hooke and Theodor Schwann, a number of scientists have made significant contributions to cell theory. In fact, cell theory has been growing and changing since the first cells were observed, and many fantastic experiments have been devised to show various parts of cell theory.See our article on the Cell Theory Timelinefor more on these events.