What is a buffer in chemistry?
In other words, a buffer is an aqueous solution of either a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. A buffer may also be called a pH buffer, hydrogen ion buffer, or buffer solution. Buffers are used to maintain a stable pH in a solution, as they can neutralize small quantities of additional acid of base.
What is an example of a buffer system?
A buffer system can be made of a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt. A classic example of a weak acid based buffer is acetic acid (CH3COOH) and sodium acetate (CH3COONa). A common weak base buffer is made of ammonia (NH3) and ammonium chloride (NH4Cl). Chemists can prepare buffer systems to be almost any pH they want.
What is the function of buffer system in human body?
1. Releasing hydrogen ions (acting as acids) when the pH increases, and. 2. Binding hydrogen ions (acting as bases) when the pH decreases. Three major chemical buffer systems in the body are the: Carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer system. Phosphate buffer system.
What is a protein buffer system?
Within cells, protein buffer systems are present to maintain a neutral pH. In this section, we will examine some of the specific buffer systems throughout the body. Amino acids that make up proteins can be positively or negatively charged with carboxyl groups.

What is a chemical buffer and how does it work?
A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base, thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable. This is important for processes and/or reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges.
What is an example of a chemical buffer?
For example, a buffer can be composed of dissolved acetic acid (HC 2H 3O 2, a weak acid) and sodium acetate (NaC 2H 3O 2, a salt derived from that acid). Another example of a buffer is a solution containing ammonia (NH 3, a weak base) and ammonium chloride (NH 4Cl, a salt derived from that base).
What makes a chemical buffer?
Buffers can be made from weak acids or base and their salts. For example, if 12.21 grams of solid sodium benzoate are dissolved in 1.00 L 0.100 M benzoic acid (C6H5COOH, pKa = 4.19) solution, a buffer with a pH of 4.19 will result: Buffers can be made from two salts that provide a conjugate acid-base pair.
What are the types of buffers?
Types of buffer solutions(a) Acidic Buffer: It is formed by the mixture of weak acid and its salt with a strong base. ... (b) Basic Buffer: It is formed by the mixture of a weak base and its salt with strong acid. ... (c) Simple Buffer: ... (a) Acidic Buffer: ... (b) Basic Buffer:
What are the 3 buffer systems in the body?
The body's chemical buffer system consists of three individual buffers: the carbonate/carbonic acid buffer, the phosphate buffer and the buffering of plasma proteins.
What is the importance of buffer?
The purpose of a buffer in a biological system is to maintain intracellular and extracellular pH within a very narrow range and resist changes in pH in the presence of internal and external influences.
What are common buffers in chemistry?
Buffer solutions commonly used include phosphoric, citric, or boric acids and their salts.
What is a good buffer system?
Good's buffers have the following characteristics: 1) High water-solubility 2) Low cell membrane permeability 3) Consistent acid-base dissociation constants 4) Low metal chelating capability 5) High chemical stability 6) Low absorption spectra in UV and visible regions.
Is HCl and NaOH a buffer system?
If you mix HCl and NaOH, for example, you will simply neutralize the acid with the base and obtain a neutral salt, not a buffer.
Is NaCl and NaNO3 a buffer system?
We cannot make a buffer solution using NaCl (sodium chloride), and NaNO3 NaN O 3 (sodium nitrate).
Which is a buffer solution?
Buffer Solution is a water solvent based solution which consists of a mixture containing a weak acid and the conjugate base of the weak acid, or a weak base and the conjugate acid of the weak base. They resist a change in pH upon dilution or upon the addition of small amounts of acid/alkali to them.
Is water a buffer?
Water is a buffer albeit a poor one. This is because H20 seelf ionises to form H30+ and OH-. To form an acidic buffer buffer you need a weak acid with the conjugate base. For alkali it is the vice versa.
Why do we need buffer solutions?
Many life forms thrive only in a relatively small pH range, so they utilize a buffer solution to maintain a constant pH.
What is the role of bicarbonate buffering?
The bicarbonate buffering system maintains optimal pH levels and regulates the carbon dioxide concentration that, in turn, shifts any acid–base imbalance.
What are some examples of buffers?
One example of a buffer solution found in nature is blood. The body’s acid–base balance is normally tightly regulated, keeping the arterial blood pH between 7.38 and 7.42. Several buffering agents that reversibly bind hydrogen ions and impede any change in pH exist. Extracellular buffers include bicarbonate and ammonia, ...
What buffers help keep blood pH in the narrow range that is compatible with life?
Chemical buffers, such as bicarbonate and ammonia, help keep the blood’s pH in the narrow range that is compatible with life.
What is the function of bicarbonate in the body?
bicarbonate: An alkaline, vital component of the pH buffering system of the human body that maintains acid–base homeostasis. buffer: A solution used to stabilize the pH (acidity) of a liquid. pH: In chemistry, a measure of the activity of the hydrogen ion concentration.
How does acid-base imbalances overcome the buffer system?
Acid–base imbalances that overcome the buffer system can be compensated in the short term by changing the rate of ventilation. This alters the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood and shifts the above reaction according to Le Chatelier’s principle, which in turn alters the pH.
What is acid base homeostasis?
Acid–base homeostasis concerns the proper balance between acids and bases; it is also called body pH. The body is very sensitive to its pH level, so strong mechanisms exist to maintain it. Outside an acceptable range of pH, proteins are denatured and digested, enzymes lose their ability to function, and death may occur.
What is a buffer system?
A buffer system has the property of resisting pH changes despite additions of acid or base. A buffer is a mixture of an acid that does not ionize completely in water and its corresponding base-for example, carbonic acid (H 2 CO 3) and sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO 3 ). If acid is added to this buffer, the added H + ions combine with bicarbonate ions ...
Why is buffer solution important?
Buffer solutions are very important in the treatment of domestic sewage, because the microorganisms which mineralize their organic matter thrive better in a neutral medium. A shift towards acidity or alkalinity inhibits the vital processes in the microbes, thus adversely affecting the working of sewage treatment plants.
What is the buffer of extracellular fluid?
The major buffer of extracellular fluid is the HCO 3 / H 2 CO 3) system.
How is pH determined in a buffer solution?
The pH of a buffer solution is determined not on the absolute concentrations of buffer constituents but on their ratio, i.e., on the ratio of the amount of salt to weak acid as stated in the Henderson Hasselbalch equation:
How does the respiratory system regulate pH?
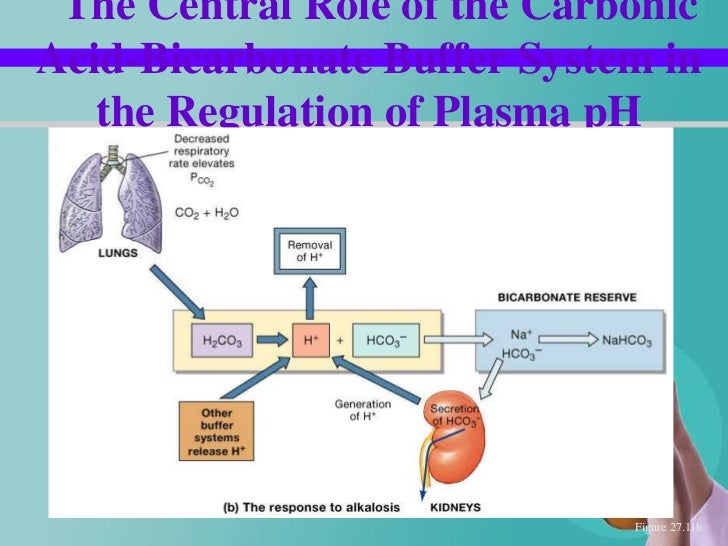
The latter are regulated by the nervous system at the respiratory centre which is sensitive to pH and pCO 2 of extracellular fluid. When the pH falls below the normal because of diminished [HCO 3– ], respiration is stimulated, lowering alveolar pCO 2 and hence extracellular [H 2 CO 3 ]. This tends to return the HOC 3− /H 2 CO 3 ratio to its normal value of 20:1 and thus to restore pH toward 7.4. With a high plasma pH, the respiratory rate falls, alveolar pCO 2 and hence plasma [H 2 CO 3] rise, and the pH moves toward 7.4.
How to get an adequate buffer system?
An adequate buffer system can be obtained from a weak acid mixed with the salt from that acid and a strong base. For example,
Why is buffering important in agriculture?
The buffering action of soils is very important in agriculture, because plants absorb artificial fertilizers from the soil to change the pH in solutions that they extract from the soil in an unfavourable direction. An imbalance in the buffering action of soil is detrimental to useful micro-organisms living in it.
What is the function of chemical buffers?
Chemical buffers resist pH changes and are the body's first line of defense. Ability of an acid-base mixture to resist sudden changes in pH is called its buffer action. Tissue cells and vital organs of the body are extremely sensitive to even the slightest change in the pH environment.
How do buffers work?
1. Releasing hydrogen ions (acting as acids) when the pH increases, and. 2. Binding hydrogen ions (acting as bases) when the pH decreases. Three major chemical buffer systems in the body are the: Carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer system. Phosphate buffer system.
What is the role of carbonic acid in blood?
The carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer system plays an extremely important role in maintaining pH homeostasis of the blood. Carbonic acid (H 2 CO 3) dissociates reversibly and releases bicarbonate ions (HCO 3–) and protons (H +) as follows: Response to an increase in pH - H+ proton donor. Response to a decrease in pH - H+ proton acceptor.
When the blood pH decreases, does the equilibrium move to the left?
In contrast, when the blood pH decreases (i.e., becomes more acidic from the addition of a strong acid), the equilibrium moves to the left.
What is the equilibrium between carbonic acid and bicarbonate?
Chemical equilibrium between carbonic acid (weak acid) and bicarbonate ion (weak base) works to resist sudden changes in blood pH. For example, when the blood pH increases (i.e., becomes more alkaline from the addition of a strong base), the equilibrium shifts to the right. A right shift forces more carbonic acid to dissociate, ...
What is the function of the body's buffering system?
To help regulate the pH in various biological fluids (such as blood and cerebrospinal fluid) and tissues, the body possesses various buffering systems that can generally accommodate changes in either direction.
What is the pH of buffer system?
Buffer Systems. For the body to function properly, it is essential that there is tight pH regulation, which maintains the body generally at a neutral pH of 7.4. If the pH is below this value, it is considered acidic. Above 7.4 is considered alkaline. To help regulate the pH in various biological fluids (such as blood and cerebrospinal fluid) ...
What are the buffers in blood?
These charged regions can bind hydrogen or hydroxyl ions, and thereby, proteins in the plasma and red blood cells themselves can act as buffers. Most of the buffering capacity of blood and cells within it comes from proteins. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin that acts as a carrier of oxygen to the tissues. Conversion of CO2 by the carbonic anhydrase enzymes results in bicarbonate and hydrogen ions. Hemoglobin can bind these free hydrogens ions, but this ability is reduced once oxygen becomes unbound to hemoglobin and enters the tissues. In the blood, phosphates are present in two forms: Na2H2PO4- (a weak acid) and Na2HPO4-2 (a weak base). The latter can bind hydrogen from HCL to form Na2H2PO4- and NaCl. In contrast, NaH2PO4- can react with NaOH to form Na2H2PO4- and H2O. Another buffer system present in the blood is the bicarbonate-carbonic acid buffer system that resembles how the phosphate buffer system works. The reaction of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) with HCL results in the formation of carbonic acid (H2CO3) and NaCl. In contrast, the reaction of carbonic acid with NaOH results in bicarbonate and water.
How does the respiratory system regulate acid-base levels?
The main goal of the respiratory system in regulating acid-base status is to regulate the levels of circulating carbonic acid. In the blood, CO2 and H2O can form carbonic acid until the point the levels of CO2 and carbonic acid reach a steady-state equilibrium. However, if there is a sudden increase in CO2 that can happen if one holds their breath to go underwater or for other reasons, the accumulated CO2 will bind to H2O to form carbonic acid, which will result in a lower blood pH or respiratory acidosis as the root cause is due to non-exhalation. However, after a period of holding one's breath or resurfacing from under the water, there will be an urge to increase the rate or depth of respiration. This will result in additional CO2 being exhaled and return to a normal blood pH. However, the opposite effect can occur with hyperventilation or rapid breathing, resulting in excess loss of CO2 with resulting reductions in carbonic acid. The net effect will be an increase in blood pH or respiratory alkalosis. Inhalation of CO2 from a paper bag that one has previously breathed into will correct this respiratory alkalosis.
Why does bicarbonate decrease blood pH?
When this occurs , it is considered a metabolic acidosis, as the loss of bicarbonate ion leads to decreased blood pH.
Which two buffering systems are in equilibrium?
The other two main buffering systems in the blood and circulating cells are phosphates and the bicarbonate-carbonic acid buffer system . In the respiratory system, CO2 and carbonic acid are normally in equilibrium.
Why is maintaining a neutral pH important?
Maintenance of proper pH in the body is essential to prevent the destruction of cells and tissues due to acidic or alkaline conditions. This lesson provides an overview of the various buffer systems that help the body maintain a neutral pH. Updated: 01/11/2021
What is buffer solution?
Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D. Updated May 04, 2019. A buffer is a solution containing either a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt, which is resistant to changes in pH. In other words, a buffer is an aqueous solution of either a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
How does a buffer work?
Most buffers work over a relative narrow pH range. An exception is citric acid because it has three pKa values. When a compound has multiple pKa values, a larger pH range becomes available for a buffer. It's also possible to combine buffers, providing their pKa values are close (differing by 2 or less), and adjusting the pH with strong base or acid to reach the required range. For example, McIvaine's buffer is prepared by combining mixtures of Na 2 PO 4 and citric acid. Depending on the ratio between the compounds, the buffer may be effective from pH 3.0 to 8.0. A mixture of citric acid, boric acid, monopotassium phosphate, and diethyl barbituic acid can cover the pH range from 2.6 to 12!
What is buffer capacity?
A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added before the pH of a buffer changes.
What is the pH range of a buffer?
Depending on the ratio between the compounds, the buffer may be effective from pH 3.0 to 8.0. A mixture of citric acid, boric acid, monopotassium phosphate, and diethyl barbituic acid can cover the pH range from 2.6 to 12!
Why do we need buffers?
Buffers are used to maintain a stable pH in a solution, as they can neutralize small quantities of additional acid of base. For a given buffer solution, there is a working pH range and a set amount of acid or base that can be neutralized before the pH will change.
What is the acid that is added to a buffer?
Typically a strong acid, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to lower the pH of acidic buffers. A strong base, such as sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH), is added to raise the pH of alkaline buffers.
Who wrote the book Reactions of Acids and Bases in Analytical Chemistry?
Hulanicki, A. (1987). Reactions of acids and bases in analytical chemistry. Translated by Masson, Mar y R. Horwood. ISBN 0-85312-330-6.
What Is a Buffer?
There are two key terms associated with buffers. A buffer is an aqueous solution that has a highly stable pH. A buffering agent is a weak acid or weak base that helps maintain the pH of an aqueous solution after adding another acid or base. If you add an acid or a base to a buffered solution, its pH will not change significantly. Similarly, adding water to a buffer or allowing water to evaporate will not change the pH of a buffer.
How Do Buffers Work?
When hydrogen ions are added to a buffer, they will be neutralized by the base in the buffer. Hydroxide ions will be neutralized by the acid. These neutralization reactions will not have much effect on the overall pH of the buffer solution .
How to make a buffer?
How Do You Make a Buffer? A buffer is made by mixing a large volume of a weak acid or weak base together with its conjugate. A weak acid and its conjugate base can remain in solution without neutralizing each other. The same is true for a weak base and its conjugate acid .
What is buffer in chemistry?
A buffer in chemistry prevents ‘wild’ swings in pH. For example:
What is buffer solution?
A buffer solution is a solution which resists the change in pH either by the addition of small amounts of acid or base or on dilution.
What is the major buffer system in the blood?
The major buffer system in the blood is the carbonic acid and bicarbonate buffer system. See below:
How to prepare buffers with different pH?
Buffers with different pH can be prepared by selection of a suitable weak acid / conjugate base combination .
What is the pH of a basic buffer?
A typical basic buffer is a combination of NH3 and NH4Cl. The optimum pH for this buffer combination is 9.25 , because that is the pKa of the ammonium ion.
What is the purpose of buffers?
A buffer is a weak acid and its salt (acetic acid and sodium acetate) or a weak base and its salt (ammonia and ammonium chloride). Its purpose is to stabilize pH . Physiological buffers serve the same purpose. Carbonate buffers in the blood control pH and I believe phosphate buffers are also common physiological buffers.
Why is sodium citrate used in shampoo?
These can be for example citric acid combined with sodium citrate. This is because the shampoo has surfactants in it to clean your hair. These surfactants can damage your hair. The sodium citrate/ citric acid buffer keeps the pH slightly acidic.
