Explore
The causes of neuropathic pain
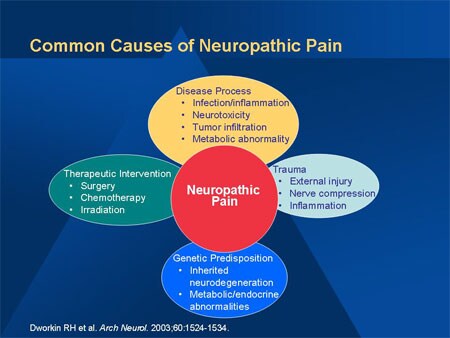
- Disease. Many diseases can cause neuropathic pain, but 30% of neuropathic pain cases are caused by diabetes.
- Injury. Even after a tissue, muscle, or joint injury heals, or back, hip, or leg problems improve, damage to the nervous system can remain.
- Infection. ...
- Limb loss. ...
What you should know about neuropathic pain?
To help you manage peripheral neuropathy:
- Take care of your feet, especially if you have diabetes. Check daily for blisters, cuts or calluses. ...
- Exercise. Regular exercise, such as walking three times a week, can reduce neuropathy pain, improve muscle strength and help control blood sugar levels. ...
- Quit smoking. ...
- Eat healthy meals. ...
- Avoid excessive alcohol. ...
- Monitor your blood glucose levels. ...
What is the best treatment for neuropathy?
What is the Best Nerve Pain Medication? Pregabalin & Gabapentin for Nerve Pain. The first group are anti-epilepsy medications, which work on the nerve itself. “Number Needed to Treat” (and why this is important). There’s an important number when you assess a medication: it’s... Nortriptyline and ...
What is the best nerve pain medication?
Top Twenty Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
- Severe strange pains in your feet, legs, hands and other parts of the body; including “crawling insects” under your skin;
- Balance is difficult when walking, getting dressed, getting out of bed or whenever you close your eyes;
- Numbness / heavy / cardboard / heavy cement feeling/ Novocain feeling in your feet and legs;
How do you describe neuropathy pain?

What are examples of neuropathic pain?
These symptoms include: Spontaneous pain (pain that comes without stimulation): Shooting, burning, stabbing, or electric shock-like pain; tingling, numbness, or a “pins and needles” feeling. Evoked pain: Pain brought on by normally non-painful stimuli such as cold, gentle brushing against the skin, pressure, etc.
What causes chronic neuropathic pain?
Common causes of neuropathic pain include nerve pressure or nerve damage after surgery or trauma, viral infections, cancer, vascular malformations, alcoholism, neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis and metabolic conditions such as diabetes. It may also be a side effect of certain medications.
How do you deal with chronic nerve pain?
5 Ways to manage the emotional stress of nerve painPractice self-care. Surround yourself with friends, family and people who give you support. ... Manage your stress. Pain is worse when you are stressed. ... Talk about how you are feeling. ... Control what you can. ... Seek physical relief from pain.
What does chronic neuropathic pain feel like?
One of the most common causes is diabetes. People with peripheral neuropathy generally describe the pain as stabbing, burning or tingling. In many cases, symptoms improve, especially if caused by a treatable condition. Medications can reduce the pain of peripheral neuropathy.
Can chronic neuropathic pain be cured?
There is no single treatment to cure or prevent neuropathic pain. Early treatment is important to treat the symptoms, however. Receiving care as soon as possible may help prevent or lessen problems that often accompany neuropathy, such as depression, sleeplessness, and diminished functioning.
What is the difference between chronic pain and neuropathic pain?
Neuropathic Pain These signals are oftentimes faulty due to a malfunction in the way nerves transmit pain signals to the brain. The body contains a network of nerves that make up the peripheral nerve system. Chronic pain occurs when these nerves are injured or diseased.
Is chronic neuropathic pain a disability?
Neuropathy is considered a disability by the SSA. The SSA refers to a medical guide called the Blue Book when evaluating eligibility for Social Security disability benefits. Section 11.14 of the Blue Book lists the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy that might make you eligible for financial assistance.
What is the number one medicine for neuropathy?
The main medicines recommended for neuropathic pain include: amitriptyline – also used for treatment of headaches and depression. duloxetine – also used for treatment of bladder problems and depression. pregabalin and gabapentin – also used to treat epilepsy, headaches or anxiety.
What vitamins are good for nerve damage?
Vitamin B-12 is present in some foods and helps with proper nerve function and red blood cell production. People who don't get enough vitamin B-12 may have a higher risk of neuropathy and other nervous system (neurological) problems.
How long does chronic nerve pain last?
On average, a pinched nerve can last from as little as a few days to as long as 4 to 6 weeks — or, in some cases, even longer (in which case you should see your doctor).
How do you calm down neuropathy?
Regular exercise, such as walking three times a week, can reduce neuropathy pain, improve muscle strength and help control blood sugar levels. Gentle routines such as yoga and tai chi might also help. Quit smoking.
Does neuropathy pain hurt all the time?
People with this pain condition may experience shooting, burning pain. The pain may be constant, or may occur intermittently. A feeling of numbness or a loss of sensation is common, too. Neuropathic pain tends to get worse over time.
What are the three forms of neuropathic pain?
TypesPeripheral neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that affects the peripheral nervous system. ... Autonomic neuropathy. ... Focal neuropathy. ... Proximal neuropathy. ... Diabetic neuropathy. ... Compression mononeuropathy. ... Phantom limb syndrome. ... Trigeminal neuralgia.More items...•
What is the difference between neuropathic pain and nerve pain?
Neuropathic pain is also referred to as nerve pain and is usually chronic. Many different conditions and diseases cause neuropathic pain, including: diabetes. multiple sclerosis.
What is the best medicine for neuropathic pain?
Neuropathic Pain Treatment. Anticonvulsant and antidepressant drugs are often the first line of treatment. Some neuropathic pain studies suggest the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as Aleve or Motrin, may ease pain. Some people may require a stronger painkiller.
How painful is neuropathic pain?
Neuropathic pain is often described as a shooting or burning pain. It can go away on its own but is often chronic. Sometimes it is unrelenting and severe, and sometimes it comes and goes. It often is the result of nerve damage or a malfunctioning nervous system.
How do you stop neuropathy from progressing?
These changes can include:Losing weight.Exercising.Monitoring blood sugar levels.Not smoking.Limiting alcohol.Making sure injuries and infections don't go unnoticed or untreated (this is particularly true for people who have neuropathies of diabetes).Improving vitamin deficiencies.More items...•
Is neuropathic pain hard to treat?
Neuropathic pain results in persistent pain syndromes that have no biological function, but are difficult to treat and cause great distress to the individual. Neuropathic pain is also referred to as neurogenic pain, deafferentation pain, neuralgia, neuralgic pain and nerve pain.
Does neuropathy go away?
The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy may lessen or go away over time, but in some cases they never go away. These are some ways to learn to live with it: Use pain medicines as your doctor prescribes them. Most pain medicines work best if they are taken before the pain gets bad.
What are the three forms of neuropathic pain?
TypesPeripheral neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that affects the peripheral nervous system. ... Autonomic neuropathy. ... Focal neuropathy. ... Proximal neuropathy. ... Diabetic neuropathy. ... Compression mononeuropathy. ... Phantom limb syndrome. ... Trigeminal neuralgia.More items...•
What neurological disorders cause nerve pain?
Common causes of a neurological pain syndrome include:Diabetes.Alcoholism.Shingles.Scars.Amputation of a limb, resulting in phantom pain.Chemotherapy or radiation therapy.Spinal nerve injury due to compression or inflammation.Central nervous system disorders, including Parkinson's disease or multiple sclerosis.
What causes neuropathic pain?
Neuropathic Pain. About 30% of all nerve pain (neuropathic pain) happens because of diabetes, but other diseases like alcoholism and shingles can cause neuropathic pain. Treatment might include medicines, physical therapy, psychological counseling, and even surgery. Appointments & Access. Contact Us.
What is neuropathy in the nervous system?
Neuropathy is a disturbance of function or a change in one or several nerves. Diabetes is responsible for about 30% of neuropathy cases.
What is the nerve that causes pain in the body?
You can feel pain from any of the various levels of the nervous system—the peripheral nerves , the spinal cord and the brain. Together, the spinal cord and the brain are known as the central nervous system. Peripheral nerves are the ones that are spread throughout the rest of your body to places likes organs, arms, legs, fingers and toes.
What is evoked pain?
Evoked pain also may mean the increase of pain by normally painful stimuli such as pinpricks and heat. This type of pain is called hyperalgesia. An unpleasant, abnormal sensation whether spontaneous or evoked ( dysesthesia ). Trouble sleeping, and emotional problems due to disturbed sleep and pain.
How to diagnose neuropathy?
Your healthcare provider will take a medical history and do a physical exam. If your provider knows or suspects you have nerve injury, they will recognize typical neuropathic pain symptoms. Your provider will then try to find the underlying cause of the neuropathy and trace the symptoms.
What is the spinal cord and the brain?
Together, the spinal cord and the brain are known as the central nervous system. Peripheral nerves are the ones that are spread throughout the rest of your body to places likes organs, arms, legs, fingers and toes. Damaged nerve fibers send the wrong signals to pain centers.
What causes phantom pain?
Other causes include: Chemotherapy drugs (cisplatin, paclitaxel, vincristine, etc.). Radiation therapy. Amputation, which can cause phantom pain. Spinal nerve compression or inflammation. Trauma or surgeries with resulting nerve damage. Nerve compression or infiltration by tumors.
What is neuropathic pain?
Neuropathic pain is now defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) as ‘pain caused by a lesion or disease of the somatosensory nervous system’.3This replaces the older definition of ‘pain initiated or caused by a primary lesion, dysfunction or transitory perturbation of the peripheral or central nervous system’.
What is the management of neuropathic pain?
The management of neuropathic pain can be challenging and , as with all pain, should be approached with a biopsychosocial framework. There are several options for drug treatment as part of an overall approach to improve patients’ quality of life and function.2
What percentage of people with diabetes have neuropathic pain?
Neuropathic pain is associated with impaired quality of life, and is often poorly managed. Around 7–8% of adults have pain with neuropathic characteristics. A quarter of people with diabetes and 35% of people with HIV have neuropathic pain.1
Which type of neuropathy is most commonly studied?
most studies were conducted in diabetic neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia
Is neuropathic pain a disease?
Additionally, neuropathic pain is not one disease entity but a number of diseases or lesions with a cluster of symptoms and signs, where understanding of pathophysiology is evolving.5
Does glycaemic control reduce neuropathy?
For instance, in patients with diabetic neuropathy, erratic glycaemic control worsens symptoms and improving glycaemic control may reduce progression of neuropathy. However, there is increased mortality with intensive insulin regimens in patients with established diabetic neuropathy compared to patients without neuropathy.7HIV-associated neuropathy presents an even more complex picture – starting antiretrovirals may initially improve symptoms although nerve damage may progress. Some antiretrovirals can cause neuropathy, and neurotoxicity may be a feature of concomitant medicines such as isoniazid for tuberculosis.8,9
Can cannabidiol be used for neuropathic pain?
The meta-analysis identified mostly negative data for a fixed-dose combination of cannabidiol and 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (nabiximols) in reducing pain in multiple sclerosis.4 A statement by the Faculty of Pain Medicine of the Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists on medicinal cannabis identifies no role for the use of cannabinoids in neuropathic pain, but notes pain and spasticity related to multiple sclerosis may be an exception.11
How to diagnose neuropathic pain?
To diagnose neuropathic pain, a doctor will conduct an interview and physical exam. They may ask questions about how you would describe your pain, when the pain occurs, or whether anything specific triggers the pain. The doctor will also ask about your risk factors for neuropathic pain and may also request both blood and nerve tests.
What are the best treatments for neuropathic pain?
Other kinds of treatments can also help with neuropathic pain. Some of these include: 1 Physical therapy 2 Working with a counselor 3 Relaxation therapy 4 Massage therapy 5 Acupuncture
What questions do neuropathic doctors ask?
The doctor will also ask about your risk factors for neuropathic pain and may also request both blood and nerve tests.
Can neuropathic pain get worse?
Acupuncture. Unfortunately, neuropathic pain often responds poorly to standard pain treatments and occasionally may get worse instead of better over time. For some people, it can lead to serious disability.
What is neuropathic pain?
Neuropathic pain is the result of an injury or malfunction in the peripheral or central nervous system. Tissue injury includes impairment of pain receptors, nerve fibers carrying pain from peripheral receptors to spinal nerves (neurons). Also chronic neuropathic pain is end result of malfunction of spinal nerves carrying pain impulses to brain.
What is the pathophysiology of chronic neuropathic pain?
Pathophysiology of Chronic Neuropathic Pain. Nerve fiber injury – leads to abnormal secretion of neuro transmitters in the spinal cord where signals are transmitted to pain centers in midbrain, thalamus a cortex. These nerves now misfire and cause pain. Pain also felt in adjacent normal tissues (hyperalgesia).
What is chronic regional pain syndrome?
Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome Type I (Causalgia): Pain is triggered by a Nerve Injury and may not be associated with actual surrounding soft tissue Damage.
How long does it take for opioids to help with neuropathic pain?
Regional pain therapy such as nerve block with corticosteroid may relieve the pain for short period of time. Pain relief could be 2 to 4 month with cortisone injections.
What age group is most likely to have low back pain?
70% of adult suffer with low back pain at least once or more and common age group is 35 to 55 years of age.
Is neuropathic pain a secondary disease?
Neuropathic pain is either secondary to cancer or non cancer etiology. Epidemiologic Studies : Epidemiological studies have revealed following Incidence and Prevalence of Chronic Pain. 70 Million Adults in United States suffer with chronic pain. 35% of population suffers with chronic back pain and spine pain.
Is neuropathic pain a cancer?
Neuropathic pain is observed in chronic non – cancer and also in cancer pain.
What is neuropathic pain?
Neuropathic pain is characterized by abnormal hypersensitivity to stimuli (hyperalgesia) and nociceptive responses to non-noxious stimuli (allodynia). The conditions and the pathophysiological states that determine the onset of neuropathic pain are heterogeneous, such as metabolic disorders, neuropathy caused by viral infections, and autoimmune diseases affecting the central nervous system (CNS). Neuropathic pain in the general population is estimated to have a prevalence ranging between 3% and 17%. Most of the available treatments for neuropathic pain have moderate efficacy and present side effects that limit their use; therefore, other therapeutic approaches are needed for patients. In this article, the current standard of care treatment, the emerging pharmacological approaches from the completed phase III clinical trials, and the preclinical studies on novel promising therapeutic options will be reviewed.
How common is neuropathic pain?
Moreover, neuropathic pain was more prevalent among women (60.5% of patients), reached a peak at 50–64 years of age, and was more frequently reported by manual workers, as well as among people from rural areas.4
Which opioids are most effective for neuropathic pain?
SNRIs inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine at the synaptic level. Duloxetine is the most effective in reducing neuropathic pain. Duloxetine and venlafaxine are associated with increased blood pressure and cardiac conduction abnormalities and therefore should be used cautiously in patients with cardiac disease. The opioids are widely used for pain management and inhibit nociceptive transmission through the presynaptic and post-synaptic μ-opioid receptors. Tramadol is a µ-opioid agonist, but also exerts effects that may contribute to its analgesic properties in neuropathic pain, including serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition. Tapentadol is the only opioid FDA approved for the management of neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy.7
What is chronic pain?
Chronic pain differs from another type of pain called acute pain. Acute pain happens when something hurts you. It doesn’t last long, and it goes away after your body heals from whatever caused the pain. In contrast, chronic pain continues long after you recover from an injury or illness.
How common is chronic pain?
Chronic pain is a very common condition, and one of the most common reasons why someone seeks medical care. Approximately 25% of adults in the United States experience chronic pain.
How long does chronic pain last?
Chronic pain is pain that lasts for a long time — months or years. It can happen anywhere in the body. The pain can be there all the time, or it may come and go. Chronic pain can interfere with your daily activities, such as working, having a social life and taking care of yourself or others. It can lead to depression, anxiety ...
How do healthcare providers treat chronic pain?
The approach depends on the type of pain, its cause (if known) and other factors that vary from person to person. The best treatment plans use a variety of strategies — medications, lifestyle changes and therapies.
What is the best treatment for chronic pain?
Counseling: Talk therapy can help you manage chronic pain, especially psychogenic pain. Occupational therapy: Activities teach you how to do everyday tasks differently to lessen pain or avoid injury. Physical therapy: Exercises stretch and strengthen your body.
What are some ways to relieve pain?
Certain lifestyle changes and types of alternative medicine have also been shown to relieve chronic pain over time: Acupuncture, which uses small needs placed in the body. Aromatherapy, which uses crushed plants.
What tests are done to check for pain?
Whether you’ve had any illnesses or surgeries. Your healthcare provider may examine your body and order tests to look for the cause of the pain: Blood tests. Electromyography to test muscle activity. Imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRI.