
Chronic Periodontitis
Periodontal Disease
A serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue and bone supporting the tooth.
What are the symptoms of periodontal disease?
Gum (periodontal) disease includes problems like gingivitis and periodontitis. Symptoms include swollen, bleeding gums; loose teeth and tooth sensitivity. Coronavirus
What are the signs of gum disease?
The most common symptoms to watch for include:
- Gums that bleed when you brush or floss
- Slightly swollen gumlines
- Red or irritated gums
- Mildly tender or itchy gums
Can periodontal disease be reversed?
Yes, periodontitis is reversible. Like any serious health condition, early treatment is key to successful treatment and periodontal disease is no exception. The first and most essential part is maintaining regular oral hygiene to fight off gingivitis.
How is periodontal disease treated?
Surgical treatments
- Flap surgery. Also known as pocket reduction surgery, flap surgery exposes the roots for more effective scaling and root planing.
- Soft tissue grafts. The loss of gum tissue causes the soft tissue of the gumline to recede. ...
- Bone grafting. Bone grafting is necessary when periodontal disease has destroyed bone surrounding tooth roots. ...
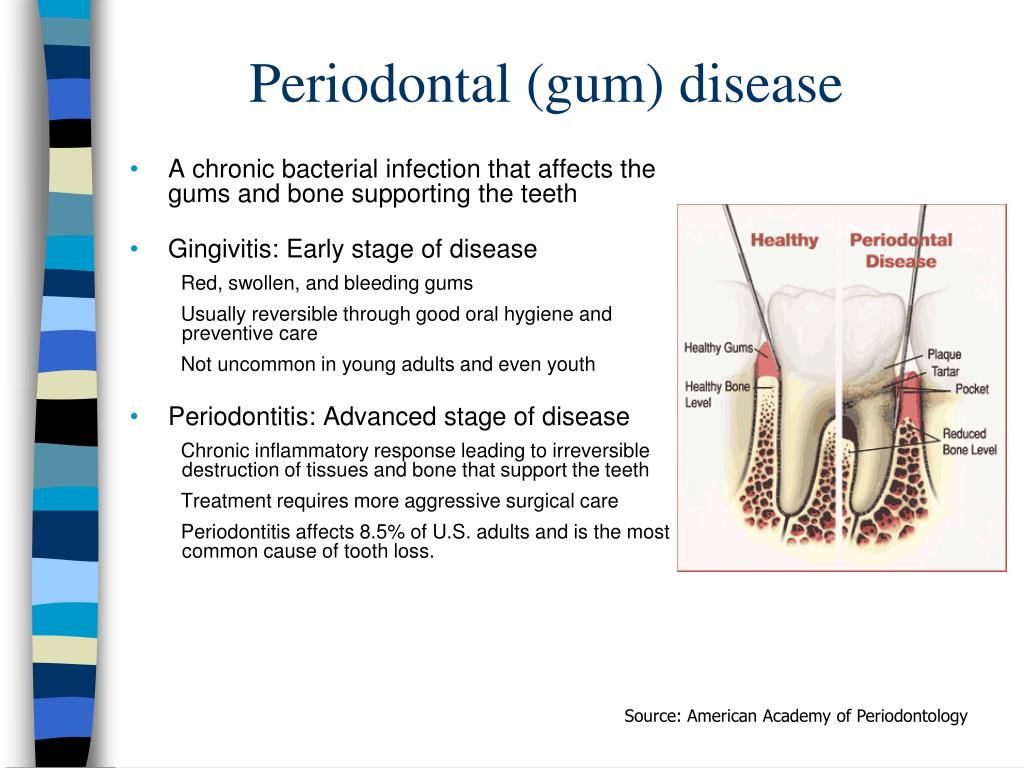
What is considered chronic periodontitis?
Chronic periodontitis is a disease of the oral cavity which consists of chronic inflammation of the periodontal tissues. The disease is caused by large amounts of dental plaque which accumulates over time.
What are signs of chronic periodontitis?
Signs and symptoms of periodontitis can include:Swollen or puffy gums.Bright red, dusky red or purplish gums.Gums that feel tender when touched.Gums that bleed easily.Pink-tinged toothbrush after brushing.Spitting out blood when brushing or flossing your teeth.Bad breath.Pus between your teeth and gums.More items...•
How do you fix chronic periodontal disease?
Treatment may be performed by a periodontist, a dentist or a dental hygienist....If you have advanced periodontitis, treatment may require dental surgery, such as:Flap surgery (pocket reduction surgery). ... Soft tissue grafts. ... Bone grafting. ... Guided tissue regeneration. ... Tissue-stimulating proteins.
Is chronic periodontitis curable?
Periodontitis can only be treated but cannot be cured. Gingivitis, on the other hand, can be prevented by maintaining proper oral hygiene practices and visiting the dentist for checkups and exams.
Will I lose my teeth if I have periodontal disease?
Periodontitis is also known as gum disease, and is a gum infection that damages soft tissue. This disease can destroy the bone and eventually cause tooth loss if not treated promptly. Periodontitis slowly progresses, and can advance quickly before you may even notice you have an issue.
Can you live with periodontal disease?
Living with periodontal disease can cause aesthetic complications and bone loss of a serious nature. Unlike other injuries, periodontal disease does not cause any pain. It is a silent disease when the teeth gum becomes inflamed and bleeds.
Which mouthwash is best for periodontal disease?
Top 3 Best Mouthwash for Periodontal DiseaseTheraBreath Periodontist Recommended Healthy Gums Oral Rinse. ... Crest Pro-Health Gum and Breath Purify Mouthwash. ... Colgate Peroxyl Antiseptic Mouthwash and Mouth Sore Rinse, 1.5% Hydrogen Peroxide.
What is the best medicine for periodontitis?
Metronidazole (Flagyl): This antibiotic may be prescribed to those patients suffering from severe periodontitis. Metronidazole works best when used in a combination with amoxicillin or tetracycline.
When is it too late for gum grafting?
By treating it early, you can reduce the risk of adverse health effects. In any case, it's never too late to seek a diagnosis for gum grafting treatment with our Waldorf MD Periodontist.
Is periodontitis serious?
Periodontitis means “inflammation around the teeth.” As a severe form of periodontal disease (gum disease), it harms the pink tissue holding your teeth in place. Potential problems go beyond inflamed gums, too. If you don't get treatment, periodontitis can destroy the bones in your mouth and lead to loss of teeth.
How quickly does periodontitis progress?
The progression of periodontal disease is slow but steady. It only takes four days for plaque to reach its maximum extent, so you'll be able to physically see signs of gingivitis on day 5. Advanced stages of this disease can be seen in as little as a few weeks if you have not tried to reverse the gingivitis.
Can periodontitis be stopped?
Periodontitis can be stopped if caught and treated early enough. Treatment is typically very successful. If you have periodontitis, regular follow-ups with a dentist are essential to ensure that the disease doesn't continue.
What does advanced periodontitis look like?
Advanced Periodontitis. In the advanced stage of periodontitis, your gums will be visibly shrunken and large portions of your teeth will be exposed. Many teeth will be loose, even ones which look healthy, as the infection is now attacking your jawbone itself. Without treatment, tooth loss is now almost inevitable.
How quickly does periodontitis progress?
The progression of periodontal disease is slow but steady. It only takes four days for plaque to reach its maximum extent, so you'll be able to physically see signs of gingivitis on day 5. Advanced stages of this disease can be seen in as little as a few weeks if you have not tried to reverse the gingivitis.
How does chronic periodontitis progress?
The cumulative outcomes of chronic periodontitis become more apparent with increased age. These outcomes include alveolar bone loss, pocket formation in the gums, and detachment and loss of the teeth.
Can periodontal disease make you sick?
Fever, Chills, Bleeding Gums: Potential Periodontal Disease. As we mentioned when discussing dental abscesses, oral infections can present with flu-like symptoms. This holds true when you experience periodontal disease, also called gum disease.
What is periodontal disease?
Periodontal diseases are mainly the result of infections and inflammation of the gums and bone that surround and support the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums can become swollen and red, and they may bleed. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or even fall out. Periodontal disease is mostly seen in adults. Periodontal disease and tooth decay are the two biggest threats to dental health.
How many people have periodontal disease?
47.2% of adults aged 30 years and older have some form of periodontal disease . Periodontal disease increases with age, 70.1% of adults 65 years and older have periodontal disease. This condition is more common in men than women (56.4% vs 38.4%), those living below the federal poverty level (65.4%), those with less than a high school education ...
What is the most serious form of tooth decay?
In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or even fall out. Periodontal disease is mostly seen in adults. Periodontal disease and tooth decay are the two biggest threats to dental health.
What happens when bacteria in your mouth is on your teeth?
Bacteria in the mouth infect tissue surrounding the tooth, causing inflammation around the tooth leading to periodontal disease. When bacteria stay on the teeth long enough, they form a film called plaque, which eventually hardens to tartar, also called calculus.
How to treat gingivitis?
Gingivitis can be controlled and treated with good oral hygiene and regular professional cleaning. More severe forms of periodontal disease can also be treated successfully but may require more extensive treatment. Such treatment might include deep cleaning of the tooth root surfaces below the gums, medications prescribed to take by mouth or placed directly under the gums, and sometimes corrective surgery.
How to get rid of gum disease?
Brush and floss every day to remove the bacteria that cause gum disease.
Can tartar build up on gums be removed?
Tartar build-up can spread below the gum line, which makes the teeth harder to clean. Then, only a dental health professional can remove the tartar and stop the periodontal disease process.
What is the most common cause of periodontitis?
Chronic periodontitis, which is the most common and is caused by plaque buildup.
What are the different types of periodontitis?
There are three different types of periodontitis, including: 1 Chronic periodontitis, which is the most common and is caused by plaque buildup. 2 Aggressive periodontitis, which is hereditary and causes rapid loss of bone and teeth if untreated. 3 Necrotizing periodontal disease, which is the death of the gums, tooth ligaments, and bones due to lack of blood. It is typically linked to a suppressed immune system from cancer, HIV infections, or malnutrition.
Why do my gums turn red?
Chronic Periodontitis. Chronic periodontitis, the most common form of periodontitis, causes swelling and redness in the gums. Left untreated, it will lead to loss of soft tissue and bone. The gums will pull back from the teeth and eventually teeth will loosen and fall out. The primary cause of chronic periodontitis is poor oral hygiene.
What is the best treatment for periodontitis?
Treating periodontitis requires the support and guidance of your dentist. You’ll likely be prescribed an antiseptic mouthwash or spray you will use at home to combat the bacteria that has accumulated in the pockets of your gums. A deep cleaning, sometimes called scaling, is also a part of periodontitis treatment.
How to prevent periodontitis?
In most cases, you can eliminate the risk factor through diligent oral hygiene that includes brushing twice a day, flossing, and receiving routine dental checkups is enough to prevent periodontitis.
Can plaque buildup cause periodontitis?
It’s possible to reverse gingivitis with routine dental care. However, if it’s left untreated, it eventually leads to periodontitis. When this happens, pockets form between ...
Can periodontal surgeons save teeth?
Once teeth begin to move within your gums with light finger pressure, have become overly erupted, or have lost gum tissue allowing more than one-third of the tooth root to show, even the best periodontal specialist cannot save your teeth and return them to a state of health.
What is gum disease?
Periodontal (gum) disease is an infection of the tissues that hold your teeth in place. It's typically caused by poor brushing and flossing habits that allow plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to build up on the teeth and harden.
What is the goal of gum disease treatment?
The main goal of treatment is to control the infection. The number and types of treatment will vary, depending on the extent of the gum disease. Any type of treatment requires that the patient keep up good daily care at home. The dentist may also suggest changing certain behaviors, such as quitting smoking, as a way to improve your treatment results.
How to get rid of plaque on teeth?
These bacteria, along with mucus and other particles, constantly form a sticky, colorless “plaque” on teeth. Brushing and flossing help get rid of plaque. Plaque that is not removed can harden and form “tartar” that brushing doesn’t clean. Only a professional cleaning by a dentist or dental hygienist can remove tartar.
What is the most common cause of tooth loss?
Periodontal disease is the most common cause of tooth loss among adults. Overall, the prevalence of both moderate and severe periodontal disease in adults and Seniors has decreased from the early 1970s. In spite of this improvement, significant disparities remain in some population groups. Show All Data & Stats.
How to remove plaque from between teeth?
Flossing regularly to remove plaque from between teeth. Or, you can use a device such as a special brush, wooden or plastic pick, or a “water flosser” recommended by a dental professional.
Is smoking bad for gums?
There are a number of risk factors for gum disease, but smoking is the most significant. Smoking also can make treatment for gum disease less successful. Other risk factors include diabetes; hormonal changes in girls and women; diabetes; medications that lessen the flow of saliva; certain illnesses, such as AIDS, and their medications; and genetic susceptibility.
What causes chronic periodontal disease and chronic gum disease?
Chronic periodontal disease, chronic gum disease and periodontitis are three names for the same disease. Dentists are taught that gum disease is an infection caused by germs. One of the more prestigious dental schools in the United States, Columbia University College of Dental Medicine supports this traditional view of gum disease, stating that “Periodontitis is caused by a bacterial infection.”
When does gum disease become chronic gum disease or chronic periodontal disease?
The gums can eventually separate from one or more of our teeth because the germs continue to produce enzymes that destroy the attachment of our gums to our teeth. The inflammatory enzymes our bodies make contribute to this process. This makes the normally small healthy space, called a sulcus, between our teeth and gums deeper. This space has now become an infected gum pocket usually filled with plaque, a kind of sticky substance made by the germs to insure their survival. The germs create and surround themselves by plaque, especially between the teeth where they are least likely to be disturbed.
What to do if you have gum disease?
If gum disease concerns you, and you are not eating a diet that supports healthy gums, now is the time to supplement your diet with specialized organic, whole food and all natural supplements that support your body’s ability to fight gum disease .
Can tarter cause gum disease?
Until this fairly recent scientific discovery of the connection of germs with gum disease, there were many different ideas among dental researchers about the possible cause or causes of gum disease. Hard dental plaque or tarter was the primary culprit for many years. For the most part, dental schools simply ignored the question of how tarter actually caused gum disease, and instead, focused on training dental students how to treat gum disease, mostly by scraping the tarter off teeth to make them clean, and cutting off diseased gum tissue.
Can you have bleeding gums if you have not been to the dentist?
If you are one of those people who see their dentist or dental hygienist regularly, you may have already been told that you have bleeding gums or gingivitis If you haven’t been to a dentist in a long time, and you do finally go, you may be surprised to hear that you have gum pockets, or chronic periodontal disease. In either case, it is very important that you follow the advice of your dentist or hygienist, because only these professionally trained people can thoroughly inspect your teeth and gums, and only a dentist can recommend appropriate treatment for your gums.
Can periodontal disease cause gum recession?
Wherever there are chronically infected gum pockets, some of the bone around the teeth is usually destroyed by the infection, and there may be some visible gum recession. At its worst, we can end up with the symptoms of a painful gum abscess, which destroys most of the jaw bone around a tooth, loosening it, and we ultimately lose the tooth. Not a desired outcome for most people.
Can gum disease spread to bone?
The problem is that the germs can spread deeper by penetrating into the bone around our teeth. It can take a long time for this to occur. When this happens, we call the gum infection, chronic gum disease or chronic periodontal disease.
Types of Periodontal Disease
When left untreated, gingivitis (mild gum inflammation) can spread to below the gum line. When the gums become irritated by the toxins contained in plaque, a chronic inflammatory response causes the body to break down and destroy its own bone and soft tissue.
Treatment for Periodontal Disease
There are many surgical and nonsurgical treatments the periodontist may choose to perform, depending upon the exact condition of the teeth, gums and jawbone. A complete periodontal exam of the mouth will be done before any treatment is performed or recommended.
What is the name of the infection that can cause tooth loss?
Open pop-up dialog box. Close. Periodontitis. Periodontitis. Periodontitis is a severe gum infection that can lead to tooth loss and other serious health complications. Periodontitis (per-e-o-don-TIE-tis), also called gum disease, is a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue and, without treatment, can destroy the bone ...
What is the sticky film that forms when you have periodontitis?
In most cases, the development of periodontitis starts with plaque — a sticky film composed mainly of bacteria. If left untreated, here's how plaque can eventually advance to periodontitis:
How do you know if you have periodontitis?
Signs and symptoms of periodontitis can include: Swollen or puffy gums. Bright red, dusky red or purplish gums. Gums that feel tender when touched. Gums that bleed easily. Pink-tinged toothbrush after brushing. Spitting out blood when brushing or flossing your teeth. Bad breath. Pus between your teeth and gums.
How to get rid of plaque on gums?
Brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing once a day removes plaque, but plaque re-forms quickly. Plaque can harden under your gumline into tartar (calculus) if it stays on your teeth. Tartar is more difficult to remove and it's filled with bacteria.
What causes dry mouth and gums?
Genetics. Certain medications that cause dry mouth or gum changes. Conditions that cause decreased immunity, such as leukemia, HIV / AIDS and cancer treatment. Certain diseases, such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn's disease.
Can gingivitis be reversed?
Gingivitis can be reversed with professional treatment and good home oral care. Ongoing gum inflammation can cause periodontitis, eventually causing pockets to develop between your gums and teeth that fill with plaque, tartar and bacteria. In time, these pockets become deeper, filling with more bacteria.
Can you lose teeth from a deep infection?
In time, these pockets become deeper, filling with more bacteria. If not treated, these deep infections cause a loss of tissue and bone, and ultimately you may lose one or more teeth. Also, ongoing chronic inflammation can put a strain on your immune system.

What Is Periodontal Disease?
- Periodontal diseases are mainly the result of infections and inflammation of the gums and bone that surround and support the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums can become swollen and red, and they may bleed. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may...
Causes
- Bacteria in the mouth infect tissue surrounding the tooth, causing inflammation around the tooth leading to periodontal disease. When bacteria stay on the teeth long enough, they form a film called plaque, which eventually hardens to tartar, also called calculus. Tartar build-up can spread below the gum line, which makes the teeth harder to clean. Then, only a dental health profession…
Warning Signs
- The following are warning signs of periodontal disease: 1. Bad breath or bad taste that won’t go away 2. Red or swollen gums 3. Tender or bleeding gums 4. Painful chewing 5. Loose teeth 6. Sensitive teeth 7. Gums that have pulled away from your teeth 8. Any change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite 9. Any change in the fit of partial dentures
Risk Factors
- Certain factors increase the risk for periodontal disease: 1. Smoking 2. Diabetes 3. Poor oral hygiene 4. Stress 5. Heredity 6. Crooked teeth 7. Underlying immuno-deficiencies—e.g., AIDS 8. Fillings that have become defective 9. Taking medications that cause dry mouth 10. Bridges that no longer fit properly 11. Female hormonal changes, such as with pregnancy or the use of oral c…
Prevention and Treatment
- Gingivitis can be controlled and treated with good oral hygiene and regular professional cleaning. More severe forms of periodontal disease can also be treated successfully but may require more extensive treatment. Such treatment might include deep cleaning of the tooth root surfaces below the gums, medications prescribed to take by mouth or placed directly under the gums, and some…
What Is The CDC Doing About Periodontal Disease?
- The CDC is currently working with key partner organizations such as the American Academy of Periodontology and the American Dental Association to improve and sustain surveillance of periodontal disease in the adult U.S. population. The efforts of the CDC include (1) developing measures for use in surveillance of periodontal disease at the state and local levels, (2) improvin…
Podcasts About Periodontal Disease and Diabetes
- Listen to Summary: Periodontal Disease and Diabetes Podcast. Provides valuable information on the impact of periodontal disease and its link to diabetes (Length 1:36). View transcript. Listen to Periodontal Disease and Diabetes Podcast. Informative interview of two dental professionals about periodontal disease, diabetes complications, and the influence of poor oral health on bloo…
Additional Resources
- Periodontal (Gum) Diseases: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment. [PDF–1.26 M]external icon. National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research consumer brochure. Bethesda, MD. Reprinted January 2006. American Academy of Periodontologyexternal icon Journal articles on periodontal disease
Reference
- 1Eke PI, Dye B, Wei L, Thornton-Evans G, Genco R. Prevalence of Periodontitis in Adults in the United States: 2009 and 2010. J Dent Res. Published online 30 August 2012:1–7. View full textexternal icon. Top of Page
Prognosis
Prevention
- It is a common oral health problem but is almost entirely preventable. In most cases, you can eliminate the risk factor through diligent oral hygiene that includes brushing twice a day, flossing, and receiving routine dental checkups is enough to prevent periodontitis.
Symptoms
- Chronic periodontitis, the most common form of periodontitis, causes swelling and redness in the gums. Left untreated, it will lead to loss of soft tissue and bone. The gums will pull back from the teeth and eventually teeth will loosen and fall out. Symptoms of periodontitis include:
Causes
- The primary cause of chronic periodontitis is poor oral hygiene. Over time, plaque builds up and eventually leads to periodontitis. It begins when plaque is allowed to form on the teeth. Everyone is at risk of plaque build-up. Whenever you eat starchy or sugary foods, these things interact with the bacteria that naturally exists in your mouth. By brushing and flossing regularly, you prevent …
Clinical significance
- Plaque and tartar buildup cause gingivitis, a mild form of gum disease. It is characterized by inflammation and irritation of the gums around the base of the tooth. Its possible to reverse gingivitis with routine dental care. However, if its left untreated, it eventually leads to periodontitis.
Epidemiology
- Research has also shown that pregnant women with periodontitis tend to give birth prematurely more often and their babies are born with low birth weights. This could be due to the bacteria in the mothers mount transferring to the baby during the third trimester.
Treatment
- It is possible to treat periodontitis, even if its advanced. Choosing not to treat periodontitis can lead to: Treating periodontitis requires the support and guidance of your dentist. Youll likely be prescribed an antiseptic mouthwash or spray you will use at home to combat the bacteria that has accumulated in the pockets of your gums. Severe cases of periodontitis might require a pre…
Others
- A deep cleaning, sometimes called scaling, is also a part of periodontitis treatment. During a scaling, the dental hygienist will scrape away plaque and tartar with a special instrument, and then polish your teeth the same as a routine cleaning.
Benefits
- Treating chronic periodontitis is essential for restoring and maintaining good oral health. It improves the life of your teeth and reduces the risk youll need tooth extraction or that your teeth will fall out naturally as you age.
Preparation
- If you need information about oral health care or youre looking for a dentist, use our contact form or call us toll-free at the number provided for more information.
Causes
- Our mouths are full of bacteria. These bacteria, along with mucus and other particles, constantly form a sticky, colorless “plaque” on teeth. Brushing and flossing help get rid of plaque. Plaque that is not removed can harden and form “tartar” that brushing doesn’t clean. Only a professional cleaning by a dentist or dental hygienist can remove tartar. There are a number of risk factors fo…
Symptoms
- Symptoms of gum disease include: 1. Bad breath that won’t go away. 2. Red or swollen gums. 3. Tender or bleeding gums. 4. Painful chewing. 5. Loose teeth. 6. Sensitive teeth. 7. Receding gums or longer appearing teeth.
Diagnosis
- At a dental visit, a dentist or dental hygienist will: 1. Examine your gums and note any signs of inflammation. 2. Use a tiny ruler called a “probe” to check for and measure any pockets around the teeth. In a healthy mouth, the depth of these pockets is usually between 1 and 3 millimeters. This test for pocket depth is usually painless. 3. Ask about your medical history to identify condition…
Treatment
- The main goal of treatment is to control the infection. The number and types of treatment will vary, depending on the extent of the gum disease. Any type of treatment requires that the patient keep up good daily care at home. The dentist may also suggest changing certain behaviors, such as quitting smoking, as a way to improve your treatment results.
Helpful Tips
- You can keep your gums and teeth healthy by: 1. Brushing your teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste. 2. Flossing regularly to remove plaque from between teeth. Or, you can use a device such as a special brush, wooden or plastic pick, or a “water flosser” recommended by a dental professional. 3. Visiting the dentist routinely for a check-up and professional cleaning. 4. Quittin…
Additional Resources
- Periodontal DiseaseYou are leaving the NIH website. NIH does not endorse non-federal websites and cannot attest to their accuracy. You will be subject to the destination site’s privacy policy when...
- MedlinePlus: Gum Disease The NIH National Library of Medicine's collection of links to government, professional, and non-profit/voluntary organizations with information on periodo…
- Periodontal DiseaseYou are leaving the NIH website. NIH does not endorse non-federal websites and cannot attest to their accuracy. You will be subject to the destination site’s privacy policy when...
- MedlinePlus: Gum Disease The NIH National Library of Medicine's collection of links to government, professional, and non-profit/voluntary organizations with information on periodontal disease and g...