Consumer’s Equilibrium in Indifference Curve Analysis is defined as a situation when the consumer maximizes his satisfaction, spending his given income across different goods with the given prices. Here, the indifference curve and budget line are used to determine the consumer equilibrium point.
How do you find consumers equilibrium using indifference curve?
CONSUMER EQUILIBRIUM USING INDIFFERENCE CURVE ANALYSIS. Consumer equilibrium using indifference curve analysis is an Ordinal Approach to Consumer Equilibrium. An indifference curve is a locus of all combinations of two goods which yield the same level of satisfaction (utility) to the consumers. Since any combination of the two goods on an indifference curve …
What is the highest indifference curve a consumer can reach?
What is Consumer equilibrium with the help of indifference curve? Consumer equilibrium refers to a situation, in which a consumer derives maximum satisfaction, with no intention to change it and subject to given prices and his given income. The point of maximum satisfaction is achieved by studying indifference map and budget line together.
How can we explain the equilibrium of consumer?
· (1) Budget Line Should be Tangent to the Indifference Curve: The consumer’s equilibrium is explained by combining the budget line and the indifference map. In the diagram …
What is the relationship between indifference curve and satisfaction curve?
When a consumer gets maximum satisfaction from his expenditure, he is said to be in equilibrium consumer’s equilibrium means maximum satisfaction level consumer can attain at given …

What is consumer equilibrium with the help of diagram?
In this article we will discuss about the concept of consumer's equilibrium, explained with the help of suitable diagrams and graphs. A consumer is said to be in equilibrium when he feels that he “cannot change his condition either by earning more or by spending more or by changing the quantities of thing he buys”.
What is consumer's equilibrium?
Consumer's equilibrium refers to the situation when a consumer is having maximum satisfaction with his limited income and has no tendency to change his way of existing expenditure. The consumer has to pay a price for each unit of the commodity. So he cannot buy or consume unlimited quantity.
What are indifference curves?
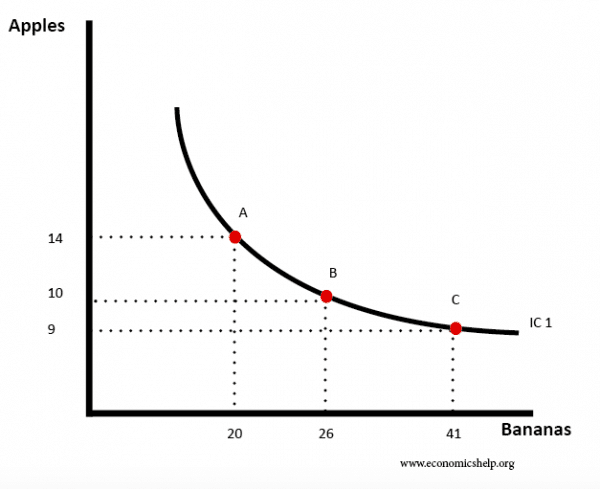
An indifference curve shows a combination of two goods that give a consumer equal satisfaction and utility thereby making the consumer indifferent. Along the curve, the consumer has an equal preference for the combinations of goods shown—i.e. is indifferent about any combination of goods on the curve.
What is indifference curve in economics?
indifference curve, in economics, graph showing various combinations of two things (usually consumer goods) that yield equal satisfaction or utility to an individual. Developed by the Irish-born British economist Francis Y.
When is a consumer in equilibrium?
A consumer is in equilibrium when he derives maximum satisfaction from the goods and is in no position to rearrange his purchases.
What is the second condition for consumer equilibrium?
The second condition for consumer’s equilibrium is that MRS must be diminishing at the point of equilibrium, i.e. the indifference curve must be convex to the origin at the point of equilibrium. Unless MRS continuously falls, the equilibrium cannot be established. Thus, both the conditions need to be fulfilled for a consumer to be in equilibrium.
What is equilibrium at tangency point?
At tangency point E, the absolute value of the slope of the indifference curve (MRS between X and Y) and that of the budget line (price ratio) are same. Equilibrium cannot be established at any other point as MRSXY > PX/PY at all points to the left of point E and MRSXY < PX/PY at all points to the right of point E. So, equilibrium is established at point E, when MRSXY = PX/PY.
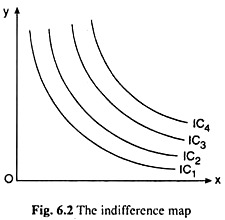
What is an Indifference Map?
Indifference Map – shows the consumer’s preference scale between various combinations of two goods
Is the price of the goods X and Y fixed?
The prices of the goods X and Y are fixed for the consumer.
What does the point E on the budget line mean?
All other points on the budget line to the left or right of point ‘E’ will lie on lower indifference curves and thus indicate a lower level of satisfaction. As budget line can be tangent to one and only one indifference curve, consumer maximizes his satisfaction at point E, when both the conditions of consumer’s equilibrium are satisfied:
Is the budget line tangential to the indifference curve?
Notice that at this point, the budget line PL is tangential to the indifference curve IC3. Also, in this position, the consumer buys OM quantity of X and ON quantity of Y.
When is a consumer in equilibrium?
The consumer is in equilibrium when he maximizes his utility, given his money income and commodity prices. In other words, a consumer is in equilibrium when he reaches the highest possible indifference curve, given his salary and commodity prices.
What happens to the consumer equilibrium if the income of the consumer changes?
If at least one of these conditions changes, consumer equilibrium also will change. Change of both these factors affects the budget constraint. If the income of the consumer change, keeping prices of commodities constant, the position of the budget line will change, keeping its shape unchanged.
What is the commodity represented by the axis?
ICC angled towards one of the axes, the commodity represented by the axis is considered as a ‘luxury.’
What is it called when the demand increases at a lower rate than the increase in income?
The goods that the demand increases at a lower rate than the increase in income are called necessary or normal goods.
What happens to the budget line when prices change?
If prices of both commodities change by the same proportion in the same direction, the budget line will shift parallel to the original line. But, if they vary by different proportions, the slope of the budget line will also change.
What is the goal of the consumer?
The goal of the consumer is to maximize utility on the given income
What is the locus of all combinations of two (or more) commodities?
The locus of all combinations of two (or more) commodities, can be purchased with given money income and commodity prices.
What is the equilibrium of a consumer?
Consumer Equilibrium: Every consumer aims at a spending his income in a way that gives him maximum satisfaction. When a consumer gets maximum satisfaction from his expenditure, he is said to be in equilibrium consumer’s equilibrium means maximum satisfaction level consumer can attain at given income and prices.
What does it mean when an indifference curve is not convex?
It means that if indifference curve is not convex, but is of any other shape, the equilibrium cannot be achieved.
What is the point of interest in consumer satisfaction?
The point of interest here is the choice of that combination of two goods which give the consumer maximum satisfaction. To find out this we require the following information about the consumer.
Why can't a consumer move above the budget line?
Moreover, he will not stand below the budget line because there is an assumptions that the entire income is spent on two goods.
What is consumer equilibrium?
Consumer equilibrium refers to a situation, in which a consumer derives maximum satisfaction, with no intention to change it and subject to given prices and his given income. The point of maximum satisfaction is achieved by studying indifference map and budget line together. On an indifference map, higher indifference curve represents ...
What is the second condition for consumer equilibrium?
The second condition for consumer’s equilibrium is that MRS must be diminishing at the point of equilibrium, i.e. the indifference curve must be convex to the origin at the point of equilibrium. Unless MRS continuously falls, the equilibrium cannot be established. Thus, both the conditions need to be fulfilled for a consumer to be in equilibrium.
What is equilibrium at tangency point?
At tangency point E, the absolute value of the slope of the indifference curve (MRS between X and Y) and that of the budget line (price ratio) are same. Equilibrium cannot be established at any other point as MRS XY > P X /P Y at all points to the left of point E and MRS XY < P X /P Y at all points to the right of point E. So, equilibrium is established at point E, when MRS XY = P X /P Y.
What does higher indifference mean?
On an indifference map, higher indifference curve represents a higher level of satisfaction than any lower indifference curve. So, a consumer always tries to remain at the highest possible indifference curve, subject to his budget constraint.
What does the point E on the budget line mean?
All other points on the budget line to the left or right of point ‘E’ will lie on lower indifference curves and thus indicate a lower level of satisfaction. As budget line can be tangent to one and only one indifference curve, consumer maximizes his satisfaction at point E, when both the conditions of consumer’s equilibrium are satisfied:
What is the point of equilibrium where a consumer maximizes his satisfaction?
Therefore, E is a point of consumer's equilibrium where he maximizes his satisfaction. Point E is also called the"Optimum Consumption Point" where he consumes OX1 of X and OY1 of Y.
Is Indifference Curve IC3 affordable?
Bundles on the Indifference Curve IC3 are not affordable within budget.
Consumer Equilibrium
Derivation of The Consumer Equilibrium
- The consumer is in equilibrium when he maximizes his utility, given his money income and commodity prices. In other words, a consumer is in equilibrium when he reaches the highest possible indifference curve, given his salary and commodity prices. In analyzing consumer equilibrium, we assume that. For the equilibrium, Preference = Ability
Equilibrium Condition in Mathematical Form
- Utility function is U = f (x,y) Budget constrain is M = PxQx + PyQy Consumer equilibrium is a constrained maximization problem. It can write formally as,
Change of Consumer Equilibrium
- In analyzing the consumer equilibrium, we assumed that, 1. Gives income and prices of goods 2. Consumer preference remain unchanged If at least one of these conditions changes, consumer equilibrium also will change. Change of both these factors affects the budget constraint. If the income of the consumer change, keeping prices of commodities constant, the position of the bu…
Income Change and Consumer Equilibrium
- The analysis of the effect of change of all these factors on consumer equilibrium is very complicated. Thus, for simplicity, firstly, we will examine the impact of the change of consumer income on the equilibrium. In this case, prices of the commodities and consumer, preferences remain constant. When income change keeping other factors constant, the budget line will shift …
Questions
- 1. What are the conditions of consumer equilibrium in indifference curve analysis? 2. What is Consumer Equilibrium explain with diagram? 3. What do you mean by consumer equilibrium? 4. What is Consumer equilibrium with example? 5. What is the Engel curve in economics? 6. What is an Engel curve? How is the Engel curve derived from the income consumption curve? 7. Explain …
Conclusion
- All right then. In this article, we discussed What is consumer equilibrium, how to derive it, budget line, change of consumer equilibrium, engle curve, and engle’s law. Did I miss anything? Let me know by leaving a comment below and ask questions.