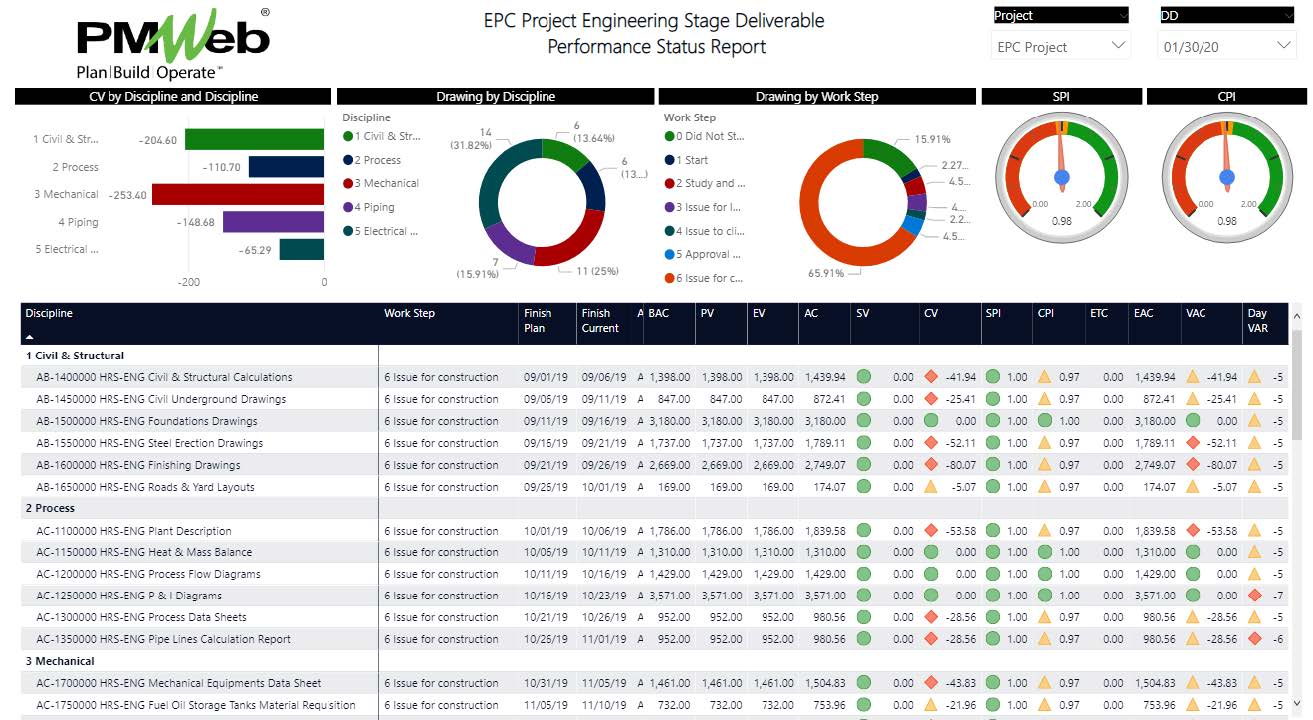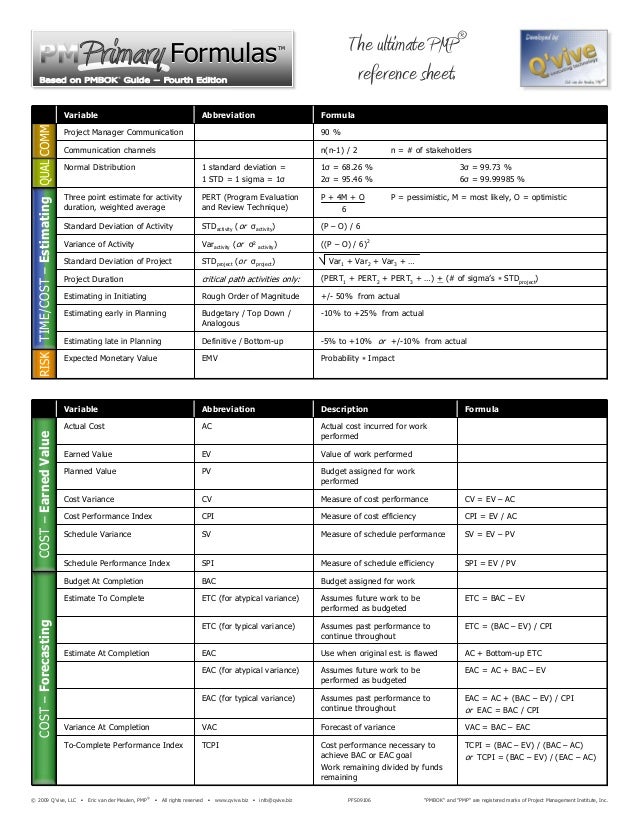
At any given point during the project:
- EAC is how much you expect the project to cost (total budget) when it's complete.
- ETC is how much more money you expect to spend to complete the remaining work on the project.
What is the difference between etc and EAC in project management?
In forecasting, the two primary metrics used are estimate to complete (ETC) and estimate at completion (EAC). ETC is the expected cost to finish the remaining work of the project, whereas EAC is the expected total cost of completing all work for the project.
What is the meaning of EAC in construction?
EAC = Estimate at Completion which means the project TOTAL estimated cost when the project will be complete.
What is the mathematical formula for etc and EAC?
ETC = Estimate to complete = remaining cost = the cost of the remaining work. EAC refers to the projected cost at the completion of the project, this situvation araises when BAC has been subjected to revision. Then the mathematical formula could be EAC = AC+ ETC.
What is the difference between BAC and EAC?
EAC is a “ forecast ” of the project cost, as the project progresses. Before the start of the project, EAC is the same as Budget At Complete (BAC). However, as the project progresses, EAC may differ from BAC depending upon the project performance. You are a project manager on a really large construction project.

Whats the difference between ETC and EAC?
The two forecasts utilized are the estimate at completion (EAC) – how much the project is forecasted to cost overall – and the estimate to complete (ETC) – how much funding is required to complete the remaining work.
What is the EAC used for?
Equivalent annual cost (EAC) is the annual cost of owning, operating, and maintaining an asset over its entire life. EAC is often used by firms for capital budgeting decisions, as it allows a company to compare the cost-effectiveness of various assets that have unequal lifespans.
What does ETC mean project management?
Estimate To CompleteThe Estimate To Complete (usually abbreviated ETC) is the project management measure that shows you the remaining cost you expect to pay in order to complete a project. Note that ETC isn't the final overall expected project budget - this is called Estimate at Completion (EAC).
What is ETC in EVMS?
In earned value analysis, the Estimate To Complete, usually abbreviated ETC, is the expected remaining cost to complete the project. It is not the final overall project cost (that's the EAC), rather it is the expenditure from now to the end of the project. It does not include what has already been spent.
What is EAC formula?
EAC = AC + (BAC - EV) This formula is used when the current deviation with the original estimation is thought to be different in the future. It is generally AC plus the remaining value of the work to perform.
How is EAC calculated example?
Example 1 – Calculated with an Estimate to Complete In this example, the Estimate to Completion (ETC) amounts to 130. Thus, the EAC is: EAC = AC + ETC = 120 + 130 = 250. The re-estimated EAC exceeds the planned budget at completion by 50.
How is etc calculated in project management?
How to Calculate the Estimate to Complete (ETC)Bottom-up Cost Estimation.ETC = Estimate at Completion – Actual Cost.
How is EAC and VAC calculated?
First, you need to calculate the EAC since the formula for VAC is BAC-EAC. The EAC formula for this question, since variances are atypical, is: EAC = AC + (BAC – EV). Plugging in the numbers from the question, you get 138 + (200-145) = EAC of 193. VAC = BAC – EAC, therefore 200 – 193 = 7.
What is the difference between estimate to completion and estimate at completion?
Estimate at completion (EAC) is used for forecasting the amount of money at the end of the project. Estimate to complete (ETC) is the amount of money needed to finish the project at any point.
How do you ask for estimated time of completion?
“Could you, please, estimate how long it takes you to finish this?” or “If I only had time!”
How is EVM calculated?
Calculating earned value Earned value calculations require the following: Planned Value (PV) = the budgeted amount through the current reporting period. Actual Cost (AC) = actual costs to date. Earned Value (EV) = total project budget multiplied by the % of project completion.
What is bottom up etc?
A fresh ETC can by found by estimating the cost of remaining (unfinished) work in the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). It is called Bottom-up ETC. You can re-estimate the cost of remaining work components (work packages and activities) and then total them Upwards in the WBS to determine a Bottom-up ETC.
What does EAC certificate mean?
EAC certificate is a conformity document required for import and sales of products in the countries of the Eurasian Customs Union (EACU).
What is the EAC in Finding Nemo?
The East Australian CurrentEAC?" The East Australian Current is where Marlin and Dory meet Crush, Squirt, and other sea turtles on their way to find Nemo. Some of the animals that travel within the current include sea turtles, tunas, groupers, swordfish, lobsters, dolphins, and albatrosses (above the water).
What does EAC mean on electronics?
about the Eac certification mark Eurasian Conformity (EAC) certification demonstrates that your products meet the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU)'s regulations and standards for customs clearance and trading. An EAC mark is essential if you intend to sell consumer products and industrial equipment into the EAEU.
How EAC is calculated in a delivery metric?
Estimate at completion (EAC) is calculated as budget at completion divided by cost performance index. Formula 1 for EAC is as follows: Estimate at completion (EAC) = Budget at completion (BAC) / Cost performance index (CPI)
What is EAC in math?
EAC is always actuals spent till now plus estimates required to complete remaining work i.e. EAC = AC+ ETC
Is current variance a valid expense?
The current variance was one of the case, going forward the initial budgeted expenses looks valid, like whatever positive or negative variance we have let’s add that much in project budget. For more details, read our blog ‘How to calculate ETC when variance are typical’
Case Study
You are a project manager on a really large construction project. Your project requirement is to build a shopping mall on a square piece of land. However, due to economic crisis, the project is scaled down and reduced to building just the boundary walls!! The height of the wall needs to be a staggering 2m.
1. Original estimate is no longer valid
Either the original estimate was fundamentally flawed or is no longer valid due to change in circumstances (for example change in scope).
2. The current cost performance (CPI) will continue in the future
Let’s say after completing the first side, you spent $1200 instead of the original estimate of $1000/side. The increased cost was due to the fact that it required more raw material to build the wall than what you originally estimated. You think that you are likely to spend $1200 for each of the remaining 3 sides as well.
3. The current cost performance is atypical for future project work
In other words, future cost performance will be in line with the original estimate.
4. Project needs to meet a deadline
This following equation takes into consideration the schedule performance ( Schedule Performance Index) and cost performance ( Cost Performance Index) to date.
What is the difference between ETC and EAC?
ETC is the expected cost to finish the remaining work of the project, whereas EAC is the expected total cost of completing all work for the project. As EAC considers the total expected cost, it is the sum of actual cost incurred so far for the project (AC) and ETC. Putting it into an equation, you get:
What is ETC in math?
ETC is the cost needed to complete the remaining work. It’s driven by a performance factor or performance index. Putting it into an equation, you get:
What is the equation for EAC?
Again, our equation for EAC is: EAC = AC + ETC.
What is the formula for EAC?
EAC = AC + ETC. This is the main formula for EAC, which is derived from AC and EAC. However, you may come across sources that are confused about EAC. A number of books, articles and journals mention that EAC changes based on certain assumptions. In fact, EAC doesn’t change directly at all on various assumptions.
Does EAC change based on assumptions?
Don’t assume that EAC changes based on certain assumptions. ETC is what actually changes. You need to focus on ETC and how ETC is calculated based on various assumptions; The formula for EAC is “AC + ETC,” and therefore it is EAC which is changing based on ETC because EAC is derived from ETC.
Does ETC change based on EAC?
ETC doesn’t change based on EAC; and. By focusing on ETC and understanding ETC as the division of work remaining with a performance factor, and it is ETC that drives EAC, a PMP® aspirant can easily calculate various formulae related to EAC and ETC. Image resized and cropped.
Does EAC change with performance factor?
Now, let’s review assumptions based on which the performance factor changes. You’ll see that as the performance factor changes ETC, EAC will also change.