
What is the main function of the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobes main functions are visual, olfactory, and auditory processing and memory creation. It also plays important roles in emotional responses and communication.
What can damage to the temporal lobe do?
The temporal lobe is one of four main brain regions involved in conscious perception. It processes sensory information regarding sound, sight, taste, and smell. Damage to or disease of the temporal lobe can cause problems with understanding words in conversation, remembering names, recognizing faces, and making new memories.
What happens if temporal lobe is damaged?
There are eight principal symptoms of temporal lobe damage:
- Disturbance of auditory sensation and perception.
- Disturbance of selective attention of auditory and visual input.
- Disorders of visual perception.
- Impaired organisation and categorisation of verbal material.
- Disturbance of language comprehension.
What does the temporal region of the brain control?
The temporal lobes are located at the sides of the brain, and can be considered the "middle" region of each brain hemisphere. As a whole, the temporal lobe is the part of your brain in charge of memory storage, the process of hearing sounds, visual recognition of faces and objects, and the use of language.
What are the 4 major roles of the temporal lobe?
The main functions of the temporal lobes include understanding language, memory acquisition, face recognition, object recognition, perception and processing auditory information.
What are three functions of the temporal lobe?
Located just beneath the lateral fissure and crossing both fissures of the brain is the temporal lobe. This vital structure helps process sensory input, including pain and auditory stimuli. It also helps you understand language, retain visual memories, and both process and remember emotions.
Does the temporal lobe control memory?
The temporal lobes are located at the sides of the brain, and can be considered the "middle" region of each brain hemisphere. As a whole, the temporal lobe is the part of your brain in charge of memory storage, the process of hearing sounds, visual recognition of faces and objects, and the use of language.
What do the frontal and temporal lobes control?
The temporal lobe processes memories, integrating them with sensations of taste, sound, sight and touch. Frontal lobe seizures are a common form of epilepsy, a neurological disorder in which clusters of brain cells send abnormal signals and cause seizures. These types of seizures stem from the front of the brain.
What part of the brain controls memory?
HippocampusHippocampus. A curved seahorse-shaped organ on the underside of each temporal lobe, the hippocampus is part of a larger structure called the hippocampal formation. It supports memory, learning, navigation and perception of space.
What happens when the temporal lobe is damaged?
The temporal lobe is responsible for interpreting and assigning meaning to various sounds. As a result, damage to the left temporal lobe often leads to problems understanding language, also known as receptive aphasia or Wernicke's aphasia.
Can you live without the temporal lobe?
Can You Live Without a Temporal Lobe? Theoretically speaking, you can live without your temporal lobe, but it will in most cases cause a disruption in your daily life. There is a type of surgery called a lobectomy, in which a part of a person's temporal lobe is removed.
What problems will be encountered when temporal lobes are affected?
A temporal lobe lesion may cause various symptoms which may not be noticed by other people. These symptoms may include forgetfulness, problems with speech and language (especially understanding what is being said by others) and problems with vision. Temporal lobe lesions may also cause fits (seizures).
What are the functions of the frontal lobe?
The frontal lobes are important for voluntary movement, expressive language and for managing higher level executive functions. Executive functions refer to a collection of cognitive skills including the capacity to plan, organise, initiate, self-monitor and control one's responses in order to achieve a goal.
How many temporal lobes are there?
one temporal lobeAs with the frontal, occipital, and parietal lobes, there is one temporal lobe located in each brain hemisphere.
What happens if temporal lobe is damaged?
The temporal lobe is responsible for interpreting and assigning meaning to various sounds. As a result, damage to the left temporal lobe often leads to problems understanding language, also known as receptive aphasia or Wernicke's aphasia.
What is the main function of the occipital lobe?
The occipital lobes sit at the back of the head and are responsible for visual perception, including colour, form and motion.
What is the main function of the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobes main functions are visual, olfactory, and auditory processing and memory creation. It also plays important roles in emotional re...
What is temporal lobe and its function?
The temporal lobes are a portion of the brain on each side of the cerebrum by the ears. They are responsible for memory, visual and olfactory proce...
What happens when the temporal lobe is damaged?
The effects of damage to the temporal lobe are dependent on where the damage is located. The different parts and structures of the temporal lobes h...
What are the temporal lobes?
Essentially, the temporal lobes interact with, and depend upon input, which can be from other brain regions, as well as from sensory input from the environment. The temporal lobes can convert sounds into visual images in the mind. We also would not be able to understand someone talking to us without the use of our temporal lobes helping us to make sense of language.
What is the test for temporal lobe function?
There are also some common tests which are used to test for temporal lobe function. There is the Rey-Complex Figure which is a test for visual memory. The Wechsler Memory Scale- Revised is also a common test used to assess the verbal memory of an individual.
What is the outer surface of the temporal lobes called?
The outer surface of the temporal lobes is called the neocortex. There are many substructures within the temporal lobes which have specific functions. The most inner part of the temporal lobes, is the older part of the cortex, also known as the limbic system, which includes the hippocampus and the amygdala . The main functions of the temporal lobes ...
Why is temporal lobe damage common?
A common cause of temporal lobe damage is epilepsy, so a discussion of previous seizure activity can be discussed. A referral to a neuropsychologist may be necessary to enable an understanding of the precise nature of the problem and to help with managing the condition.
How to diagnose temporal lobe damage?
In order to diagnosis damage to the temporal lobes, a thorough history of the symptoms being experienced need to be investigated. This assessment can be accompanied by someone who knows the patient well and has witnessed the problems at hand.
Where is the auditory cortex located?
The auditory cortex, the main area responsible for processing auditory information, is located within the temporal lobe. The auditory cortex is a part of the superior temporal gyrus which essentially receives input from the ears and analyses it.
Which lobe is responsible for a person's memory?
The temporal lobes are also vital for declarative memory and long-term memory, as well as making us good at selective hearing.
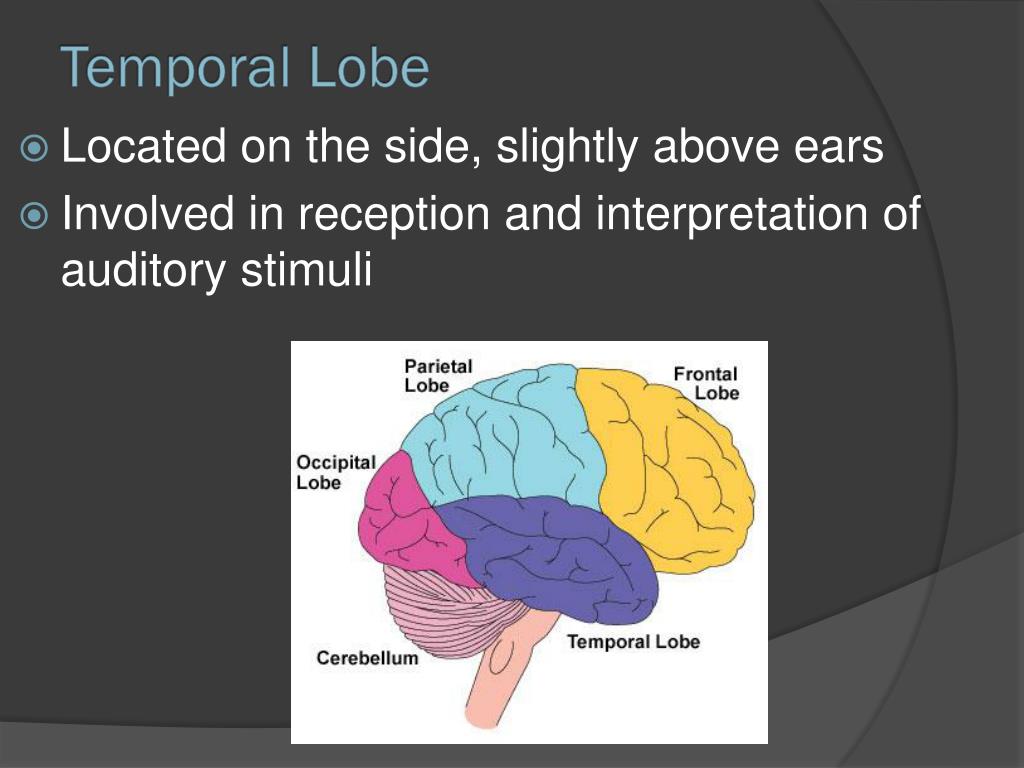
Where is the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobe sits at the bottom middle portion of the brain, just behind the temples within the skull, which is also where it gets its name. It also sits above the brain stem and cerebellum. The frontal and parietal lobes are above the temporal lobe. The occipital lobe sits just behind it.
What are the structures of the temporal lobe?
Key structures that are part of the temporal lobe include: 1 Wernicke’s area 2 Broca’s area 3 limbic system
What is the limbic system?
The limbic system is involved with motivation, emotion, learning, and memory. While the limbic system interacts with other areas of the brain, it works directly with the temporal lobe to influence the components of the limbic system. The limbic system itself contains important structures, including the amygdala and hippocampus.
What is the term for a condition that affects the front and temporal lobe?
Pick’s disease. Pick’s disease, or frontotemporal dementia, is a less common form of dementia, that damage or atrophy in the front and temporal lobe causes. The condition may include changes to states such as mood, attention levels, or irritated or aggressive behaviors.
Where is schizophrenia found in the brain?
There is a link between schizophrenia and deficit or damage in the temporal lobe, within the primary auditory cortex in the left temporal lobe.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for interpreting information in the form of sounds from the ears?
The temporal lobe contains the primary auditory complex. This is the first area responsible for interpreting information in the form of sounds from the ears. The temporal lobe receives different frequencies, sounds, and pitches from the ears, and gives them meaning.
Which lobe is the limbic system?
Key structures that are part of the temporal lobe include: Wernicke’s area. Broca’s area. limbic system. These structures also span other lobes. For example, Wernicke’s area extends into the parietal lobe, and Broca’s area is part of the frontal lobe.
What are the functions of the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobes main functions are visual, olfactory, and auditory processing and memory creation. It also plays important roles in emotional responses and communication.
Where are the temporal lobes located?
The temporal lobes can be found on the sides of the head by the ears. There is one lobe in each hemisphere of the brain.
How many lobes does the cerebrum have?
The Cerebrum has four lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal.
Which lobe of the brain processes information in different ways?
The temporal lobes on each side of the brain process information in different ways and have slightly different jobs.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for the sense of smell?
The temporal lobes are where the sense of smell is refined and recognized.
Which lobes are most responsible for vision?
Vision is mostly processed in the occipital lobes, but some comprehension of that vision and any storage of memories from it happens in the temporal lobes.
Which part of the brain is responsible for voluntary muscle movements?
Cerebellum: this is a small part of the brain located at the back just above the brainstem; it has two hemispheres like the cerebrum and helps coordinate voluntary muscle movements like posture and balance.
What is the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain. The temporal lobe is involved in processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memory, ...
Which lobe of the temporal lobe is responsible for visual processing?
The areas associated with vision in the temporal lobe interpret the meaning of visual stimuli and establish object recognition. The ventral part of the temporal cortices appear to be involved in high-level visual processing of complex stimuli such as faces ( fusiform gyrus) and scenes ( parahippocampal gyrus ). Anterior parts of this ventral stream for visual processing are involved in object perception and recognition.
What lobe is affected by savant syndrome?
Damage specifically to the anterior portion of the left temporal lobe can cause savant syndrome.
What is temporal lobe epilepsy?
Temporal lobe epilepsy is a chronic neurological condition characterized by recurrent seizures; symptoms include a variety of sensory (visual, auditory, olfactory, and gustation) hallucinations, as well as an inability to process semantic and episodic memories.
What is the most common symptom of inferior temporal lobe damage?
The most common symptom of inferior temporal lobe damage is visual agnosia, which involves impairment in the identification of familiar objects. Another less common type of inferior temporal lobe damage is prosopagnosia which is an impairment in the recognition of faces and distinction of unique individual facial features.
What are the four lobes of the brain?
One of the four lobes of the mammalian brain. Temporal lobe . Frontal lobe. Temporal lobe. Parietal lobe. Occipital. lobe. Lobes of the human brain (temporal lobe is shown in green) Section of brain showing upper surface of temporal lobe.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for language comprehension?
The temporal lobe holds the primary auditory cortex, which is important for the processing of semantics in both language and vision in humans. Wernicke's area, which spans the region between temporal and parietal lobes, plays a key role (in tandem with Broca's area in the frontal lobe) in language comprehension, whether spoken language or signed language. FMRI imaging shows these portions of the brain are activated by signed or spoken languages. These areas of the brain are active in children's language acquisition whether accessed via hearing a spoken language, watching a signed language, or via hand-over-hand tactile versions of a signed language
What is the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobe subdivides further into the superior temporal lobe, the middle temporal lobe, and the inferior temporal lobe. It houses several critical brain structures including the hippocampus and the amygdala. The temporal lobe of the brain is often referred to as the neocortex. It forms the cerebral cortex in conjunction with ...
How to understand temporal lobe?
In order to fully comprehend the temporal lobe, it is best to analyze it also through its functional connectivity, not just its gross structure. The idea that certain parts of the brain perform certain functions is called localizationism. Localizationism does not always correspond to predictions of functions. Connections define functions. On the other hand, without understanding function, connections of structures are useless. Hence, in order to see the whole picture, structure, connections, and functions must be correlated. [1][2]
What are the three areas of the temporal gyrus?
Temporal area 1 anterior (TE1a), middle (TE1m) and posterior (TE1p) are found in the MTG. All three areas have functional connectivity to different parcellations of the frontal, temporal and parietal lobes. TE1a has additional functional connectivity to some STS areas, temporal gyrus ventral (TGv), entorhinal cortex (EC), and hippocampus. All three areas have white matter connections (structural connectivity) to "u" fibers of the occipitotemporal system and arcuate/SLF. TE1a has an additional white matter connection to inferior longitudinal fasciculus (ILF). These areas are primarily responsible for processing visual information, including working memory for short term visual maintenance of information. [3][5]
Where is the superior temporal gyrus located?
Superior temporal gyrus region 'a' (STGa) is found on the superior temporal gyrus at its anterior superior surface. It is functionally connected to different parcellations of the insula opercular region and temporal lobe. It has white matter connections (structural connectivity) to inferior longitudinal fasciculus and local parcellations. STG areas are functionally involved in perceptual and conceptual acoustic sound processing. [6]
Which lobe has two social areas?
Social - two areas in the temporal lobe
Which lobe is inferior to the lateral fissure?
It is anterior to the occipital lobe and posterior to the frontal lobe. It is found inferior to the lateral fissure, also known as the Sylvian fissure or the lateral sulcus. The temporal lobe subdivides further into the superior temporal lobe, the middle temporal lobe, and the inferior temporal lobe.
Is TG dorsal or ventral?
It is composed of the TG dorsal (TGd) and TG ventral (TGv). They are both functionally connected to each other. TGd is also functionally connected to different parcellations of the frontal lobe, STS, STGa, PeEc, hippocampus and TE1a. Meanwhile, TGv is functionally connected to area 45.
What is the right temporal lobe?
The human brain has a right and left temporal lobe, wherein one mirrors the other. Mesial temporal lobe anatomy involves specific structures frequently implicated as a cause for seizures in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. The structures include the hippocampus, the parahippocampus, and the amygdala. Many or all of these will be removed during surgery to stop seizures arising in this area. The most common reason for which seizure surgery is performed in the temporal lobe is for scarring in the hippocampus, or hippocampal sclerosis. Removal of the hippocampus in this situation will lead to stopping seizures in the majority of the patients.
Why is temporal lobe removed?
The most common reason for which seizure surgery is performed in the temporal lobe is for scarring in the hippocampus, or hippocampal sclerosis.
What are the two main parts of the frontal lobe?
The general organization of the frontal lobe independent of side includes the formation of gyri (the gray and white matter convolutions of the brain) and sulci (the natural planes in the plane containing the blood vessels). The surfaces of the frontal lobe include the orbital (basal) surface, the lateral surface, and the mesial surface (see diagrams). Within the deep white matter of the frontal lobe is the anterior part of the lateral ventricle which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The posterior part of each frontal lobe known as the precentral gyrus contains the primary motor cortex. Here motor function is arranged according to the part of the body moved (somatotopic representation). The arrangement of cortex is known as the homunculus (see diagram).
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for language comprehension?
The dominant temporal lobe (left) often has a region specialized in language skills. This area of the brain is known classically as Wernicke's area and involves language comprehension.
Which cranial nerve innervates the sinoatrial node of the heart?
The vagus nerve is a mixed cranial nerve containing approximately 80% sensory fibers. Efferent fibers innervate the larynx and provide parasympathetic control to the heart, lungs, and abdominal viscera. The right vagus nerve innervates the sinoatrial node of the heart while the left innervates the atrioventricular node.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for coordination of smooth motor movements?
The frontal lobe is the largest in the brain extending from the anterior skull back to behind the ear. Within it's borders lies a region that moves the opposite side of the body (primary motor cortex), a part that allows for coordinated eye movements to the opposite side (frontal eye fields), a region concerned with initiation and coordination of smooth motor movements (supplementary motor area), and if on the dominant side a motor language area (Broca's area).
What is dominant side?
Dominant side refers simplistically to the side of the brain where language function is. Language is characterized by different areas within one side of the brain each serving a different function and connected by white matter tracts (see diagram).
What are the functions of the temporal lobes?
The temporal lobes of the human brain are in charge of a wide variety of functions: The lobes control memory, sound processing and facial recognition, and temporal lobe damage has been known to impact a person's personality in addition to impairing these functions. Left temporal lobe function in particular is critical for ...
What is the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobe of the human brain is in charge of a wide variety of important functions; the lobe controls language, facial recognition, memory and sound processing. Temporal lobe function is critical to an unhindered life, and damage to the lobe can lead to a variety of disorders. Sciencing_Icons_Science.
What is the term for the damage of the temporal lobe?
Most often, you see this result in an inability to recall memories or information, but when certain regions of the dominant temporal lobe are damaged, such as Broca or Wernicke's areas, a certain type of brain damage known as an aphasia or an agnosia can develop.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for the formation of language?
Located at the front and middle of the left temporal lobe, respectively, Broca's area and Wenicke's area are the regions of the human brain that handle the formation and processing of language. Regardless of what language you're using, these two regions allow you to form sentences, understand the meaning of what others are saying and pick up on verbal patterns. These regions are the reason why a left temporal lobe hemorrhage can leave a person unable to understand what someone is saying, or lead them to babble incoherently.
Which lobe of the brain controls memory?
In most people, the left side of the brain is the dominant one, and in most people the left temporal lobe controls memories related to facts and information, along with the ability to recognize faces and objects. It also controls your ability to create and understand language, through the use of two specific regions of the left temporal lobe.
Which part of the brain is responsible for memory?
As a whole, the temporal lobe is the part of your brain in charge of memory storage, the process of hearing sounds, visual recognition of faces and objects, and the use of language. Though this seems like an incredible number of functions for one small part of the brain to command, the temporal lobes are actually more complex than they look;
Which lobe of the brain is the thumb shaped?
The temporal lobes of the brain may not seem like much at first glance: The thumb-shaped areas at the sides of your brain aren't as large as the frontal or parietal lobes, and they aren't referenced or discussed as often as the cerebellum positioned just below. However, these oft-overlooked lobes are one of the most important parts of your brain.
What is the function of the left temporal lobe?
The primary function of this lobe of the brain is to control sight and sound processing. It’s also responsible for language usage. The left temporal lobe is the reason we’re able to make sense of the words that we read and hear.
What Happens If You Damage Your Left Temporal Lobe?
Since the temporal lobe processes emotions and plays an important role in short-term memory, damage to this area of the brain can result in unique symptoms.
What Are The Symptoms Of Left Temporal Lobe Damage?
One of the most common symptoms of seizures is an aura . This unusual sensation often acts as the warning sign that a seizure is about to occur. However, not all people with seizures experience auras, and those who experience them don’t always remember them.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for organizing and assimilating all that we perceive?
The four lobes of the brain are responsible for organizing and assimilating all that we perceive. The four lobes of the brain include the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the occipital lobe, and the temporal lobe. The temporal lobe is further divided into the right and left temporal lobes.
What is the most important part of the brain?
Each part plays a role in the maintenance of our emotions, reactions, decisions, and actions. One of the most important parts of the brain is the left temporal lobe.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for long term memory?
It takes care of hearing and listening, visual input processing, and verbal material comprehension (including both speaking and reading). The temporal lobe is also where our long-term memories are stored.
How to protect the brain?
One of the best ways to protect the brain is by staying active. Regular exercise not only increases the feel-good neurotransmitters in the brain but can actually generate new brain cells. Just 30 minutes of exercise 3-5 times a week is more than sufficient.
What are the functions of the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobes play a role in many essential functions, including: Processing sensory information (mainly sound but also smell, vision, etc.) Memory. Language comprehension.
What is the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobe controls many functions including emotions, sensory processing, and memory. When the temporal lobe is impacted by a traumatic brain injury, it can impair these functions and significantly affect how individuals interact with their surroundings. To help you better understand temporal lobe damage, this article will address: ...
How to treat temporal lobe damage?
Treatment for temporal lobe damage will require a personalized plan that targets each individual’s unique secondary effects. Because damage to this region of the brain primarily affects cognitive functions like memory and communication, working on cognitive rehabilitation exercises can be effective.
What are the potential complications of temporal lobe damage?
Because many functions can be affected following temporal lobe damage, individuals may experience various complications that affect their ability to perceive and respond appropriately to their environment.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for forming emotional long term memories?
The hippocampus is a structure in the temporal lobe that is responsible for forming emotional, long-term memories. As a result, memory problems are a very common effect of temporal lobe damage.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for interpreting and assigning meaning to various sounds?
The temporal lobe is responsible for interpreting and assigning meaning to various sounds. As a result, damage to the left temporal lobe often leads to problems understanding language, also known as receptive aphasia or Wernicke’s aphasia.
How does occupational therapy help with cognition?
Occupational therapy will focus on helping individuals improve their functional cognition by practicing everyday activities. Because temporal lobe damage can affect memory and sensory processing, it’s essential to address how to perform daily activities such as preparing meals, grooming, and transportation.
