
The Cq value is the PCR cycle number at which your sample’s reaction curve intersects the threshold line. This value tells how many cycles it took to detect a real signal from your samples. Real-Time PCR runs will have a reaction curve for each sample and therefore many C q values.
What is the C Q value in PCR?
The C q value is the PCR cycle number at which your sample’s reaction curve intersects the threshold line. This value tells how many cycles it took to detect a real signal from your samples. Real-Time PCR runs will have a reaction curve for each sample and therefore many C q values.
What is the CQ value or cycle quantification?
The Cq value or cycle quantification value is the PCR cycle number at which your sample’s reaction curve intersects the threshold line. This value tells how many cycles it took to detect a real signal from your samples.
What does CQ mean in qPCR?
The Cq value is the PCR cycle number at which your sample’s reaction curve intersects the threshold line. This value tells how many cycles it took to detect a real signal from your samples. How do you read qPCR results? What do qPCR results mean? What does qPCR measure?
What is CT value in PCR?
What is the Ct value? The cycle threshold (Ct) value of a reaction is defined as the cycle number when the fluorescence of a PCR product can be detected above the background signal. In order to calculate the Ct value, it is necessary to draw a horizontal line (threshold) on the amplification plot.

What is cq in real time PCR?
The cycle in which fluorescence can be detected is termed quantitation cycle (Cq for short) and is the basic result of qPCR: lower Cq values mean higher initial copy numbers of the target. This is the basic principle of the quantitative approach that real-time PCR provides.
What is CQ and Ct in qPCR?
Cq was introduced through the MIQE guidelines. Ct means cycle threshold, Cq quantification cycle.
How are CQ values calculated?
Apart from the threshold setting and PCR efficiency, Cq is mainly determined by the concentration, or number of copies of the target, at the start of the PCR. This copy number in the reaction is determined by pipetting the sample into the reaction well.
What is Delta CQ in qPCR?
What is the delta-delta Ct method? The delta-delta Ct method, also known as the 2–∆∆Ct method, is a simple formula used in order to calculate the relative fold gene expression of samples when performing real-time polymerase chain reaction (also known as qPCR).
What does the CQ value mean?
The Cq value is the PCR cycle number at which your sample's reaction curve intersects the threshold line. This value tells how many cycles it took to detect a real signal from your samples.
What is a good CT value qPCR?
"All patients with a CT value of equal to or less than 35 may be considered positive, while those with a CT value greater than 35 may be considered negative. All samples with a CT value equal to or less than 35, which is seen as a poor sigmoidal curve, should be essentially retested.
How do you analyze qPCR data?
There are two main ways to analyze qPCR data: double delta Ct analysis and the relative standard curve method (Pfaffl method). Both methods make assumptions and have their limitations, so the method you should use for your analysis will depend on your experimental design.
What is the ∆ ∆ CQ calculation comparing?
Overall, ∆∆Cq yields a normalized, relative gene expression value. This is accomplished by normalization of a gene target with experimental treatment to an endogenous reference gene(s) whose expression should remain unchanged by the treatment.
How do you analyze Taqman data?
0:503:51How to Analyze Real-time PCR Data -- Ask TaqMan® Ep. 16 by Life ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipMost people choose the untreated sample by the way at the end of the run. Simply go to either theMoreMost people choose the untreated sample by the way at the end of the run. Simply go to either the result or the analysis tab depending upon your version and to gene expression.
How do I analyze RT PCR data?
1:3310:07Real Time QPCR Data Analysis Tutorial - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe threshold cycle is determined mainly by the amount of template present at the start of theMoreThe threshold cycle is determined mainly by the amount of template present at the start of the amplification. Reaction. If a large amount of template is present at the start of the reaction.
How do you read qPCR results?
A RQ of 10 means that this gene is 10 times more expressed in sample x then in the calibrator sample. A RQ of 0,1 means that the gene is 10 times less expressed. We consider a RQ significant when there is a minimum of two-fold change: RQ of more than 2 or less then 0,5. This is within the variations of the technique.
How do you calculate Delta Ct for real time PCR?
2:016:59How To Perform The Delta-Delta Ct Method (In Excel) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo the next thing we need to do is calculate delta CT so delta CT is the average CT values of theMoreSo the next thing we need to do is calculate delta CT so delta CT is the average CT values of the gene of interest - the housekeeping gene to do this I'm just going to create another header in a car
Is Ct the same as CQ qPCR?
There is no difference between Cq and Ct. “Cq or Quantification cycle” is the correct naming according the MIQE guidelines as described in Bustin et al.; Clinical Chemistry 55:4; 2009.
How do you calculate Ct in PCR?
0:553:35What are Ct values in real-time PCR?--Taq Talk Episode 3 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe ct value is inversely related to the starting amount of our target dna. For example if i haveMoreThe ct value is inversely related to the starting amount of our target dna. For example if i have one sample with 200 nanograms of cdna.
What is low CQ confidence?
CQCONF ( )—Calculated confidence in the C q value is low. This flag indicates that the calculated confidence for the C q (C t or C rt) value of the well is less than the minimum value defined in the analysis settings.
How is Ct threshold set?
0:542:50Real-Time PCR Thresholds and Where to Place Them -- Ask TaqManYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThat's generally somewhere toward the middle of the geometric phase or maybe slightly higher in anyMoreThat's generally somewhere toward the middle of the geometric phase or maybe slightly higher in any case with a really robust assay hitting a good spot is quite easy the default.
All Answers (3)
Cq is the quantitation cycle which is the first cycle whereby detection of the fluorophore released during amplification is detected. If you are running a lab experiment and the DNA that is specifically targeted by your probe was in the mix, it should have a Cq.
Similar questions and discussions
Why some wells in RT-PCR show Cq while others don't for the same sample?
What is the CQ value of a PCR sample?
The Cq value is the PCR cycle number at which your sample’s reaction curve intersects the threshold line. This value tells how many cycles it took to detect a real signal from your samples. Real-Time PCR runs will have a reaction curve for each sample and therefore many C q values. Your cycler’s software calculates and charts the Cq value for each of your samples.
What is the C q Value?
Real-time PCR (often called qPCR) is usually conducted to quantify the absolute amount of a target sequence or to compare relative amounts of a target sequence between samples. This technique monitors the amplification of the target in real-time via a target-specific fluorescent signal emitted during amplification.
What is the best PCR efficiency?
PCR reaction efficiency is dependent on the master mix performance, the specificity of the primers, the primer annealing temperature, and the sample quality. In general, PCR efficiency above 90% is acceptable. PCR efficiency of 100% indicates that the target sequence of interest doubles during each cycle. Perfect PCR efficiency coincides with a change of 3.3 cycles between 10-fold dilutions of your template.
How to determine PCR efficiency?
To determine the PCR efficiency for each primer pair, run serial dilutions of your template with five 10-fold dilution steps, and calculate the R 2, a statistical measure that describes how well one value can predict another. For PCR efficiency close to 100%, your R 2 value should be greater than 0.99.
How many cycles does a PCR instrument have?
Your PCR instrument will collect fluorescence data during each cycle. After about 15 cycles, you’ll have a good idea of your background fluorescence level – this will appear as a straight line starting from the zero cycle point. The threshold level will be just above this, but at the point where your samples start moving into the exponential phase of PCR amplification. Today, computer software calculates this exact point and all modern real-time cyclers have an automatic threshold line setting.
What is reaction value?
Reaction values are the ratio of the fluorescence of your FAM (reporter) dye to your ROX (passive reference) dye. Lower amounts of ROX produce higher reaction values, assuming FAM fluorescence doesn’t change.
What is a threshold line in PCR?
The threshold line is the level of detection or the point at which a reaction reaches a fluorescent intensity above background levels. Before conducting PCR, you (or the software in your cycler) set a threshold level. This is literally a line in your graph that represents a level above background fluorescence, that also intersects your reaction curve somewhere at the beginning of its exponential phase (Figure 1).
How accurate is qPCR?
The qPCR technique is a sensitive and sophisticated molecular genetic technique having 80 to 90% accuracy. Nonetheless, a few factors affect the specificity and sensitivity of the reaction. Those are;
What is qPCR used for?
PCR and associated modified techniques are used in many fields from research to diagnostic and from microbiology to environmental science. The qPCR and RT-PCR collectively used in the quantification of mRNA, gene expression studies, microbial studies, measuring infection and identification of template nucleic acid.
What is gene quantification?
Gene quantification gives researchers an idea regarding how many templates nucleic acid is present in a sample and that is the base to develop a quantitative method or qPCR that measures the template DNA or gene.
What is the Ct value?
“The Ct value is a value used to quantify the absolute amount of nucleic acid present in a sample. It is the number of cycles from where fluorescence increases significantly.”
When does Taq DNA polymerase start amplifying?
Now when the reaction starts entering into the exponential phase, templates start amplifying. Reaction utilizes reagents, Taq DNA polymerase starts amplifying the template, probes are hydrolyzed and fluorescence emitted.
What is the Ct value of a reaction?
The number of cycles from which the reaction curve raises above the threshold line or intersects with it, is our Ct value. Simply, in a positive reaction amplification, a number of cycles required to cross the threshold line or exceeds the threshold in our Ct value from which machines start quantifying the nucleic acid.
How many cycles does a Ct value go up?
If the sample contains fewer templates, the Ct value goes high at it takes more cycles to progress the reaction. The average Ct value is near or around 29 to 30 cycles indicating a sufficient amount of template nucleic acid present in the sample.
What is the importance of qPCR?
A pivotal attraction of qPCR technology is its apparent lack of complication; an assay consisting of the simple procedure of combining oligonucleotides, PCR mastermix buffer and nucleic acid template to produce a qPCR reaction is perceived as undemanding. This practical simplicity is complemented by the absence of any requirement for post-assay handling, as well as the development of user-friendly data analysis software that makes data generation and visualisation in the shape of amplification plots remarkably simple. However, as we have set out in the first four articles of this series, the translation of an attractive amplification plot into accurate and meaningful data is far from trivial and requires a range of additional considerations.
What is data normalization?
Normalisation to total sample mass or volume is a legacy approach remaining from northern blotting techniques when gel loading and sample transfer to filter paper was validated by probing for rRNA or so-called housekeeping genes such as GAPDH, whose expression was assumed to be stable between individuals, experimental conditions or physiological states. While still used for RT-qPCR measurements, there are several disadvantage of measuring mRNA or miRNA levels relative to sample mass or volume. For example, in a comparison of samples of different origin e.g. tumour biopsies and normal tissue it is incorrect to assume that the same tissue mass contains similar cell numbers, or that the relative distribution of proliferating cells is equal. Normalisation against total RNA will underestimate the expression of target genes in the tumour biopsies. This approach may be more suitable when the samples are extracted using laser capture micro dissection and a precise number and similar cells are targeted; even then this approach is not ideal. A related technique, again reminiscent of northern blotting, is to normalise to DNA or RNA concentration. While measuring gene copy number relative to input DNA concentration is a perfectly valid approach, the situation is more complicated for transcript quantification. When RNA concentration is determined, the vast majority of the RNA component is ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Transcription of rRNA is independent of the transcription of messenger RNA (mRNA) since it is transcribed by different enzymes. Furthermore as rRNA makes up ~80 % of the RNA fraction, normalisation to rRNA would mask subtle changes in the mRNA component; which typically comprises 2-5%. In addition, this approach does not take into account variations in the template RNA quality, or changes in rRNA levels dependent on cellular differentiation/proliferation status. Nonetheless, while not ideal, there may be situations where there are no other alternatives but to measure relative to total RNA and some analysis packages such as GenEx software from MultiD6 allow the total RNA concentration to be evaluated as a normalisation technique alongside other approaches. One theoretical solution would be to purify mRNA and normalise against total mRNA. Unfortunately the purification process introduces inaccuracies and an extra processing step that is undesirable and in many cases the biopsy is too small to allow efficient purification of re mRNA. A very common approach to correct for sample differences is to express the target concentration relative to that of a single internal reference gene. In order for this approach to be valid the expression of the single reference gene must remain constant between all experimental samples. To find such a convenient target additional validation is necessary, yet even today the all too common and misguided approach is to select this gene at random without validation; GAPDH, b actin and 18S are particular favourites in the published literature, usually used without validation or justification. When the reference gene is not stably expressed between all samples, a ratio of the target gene of interest to the reference gene will reflect the expression changes of both targets. This is unhelpful when the expression behaviour of neither target has been defined and can lead to inaccuracies and false results7. An amendment to this approach is to validate the chosen reference gene8 or select a significant reference gene with defined biology where the transcriptional response is well characterised (an approach referred to as normalisation to a Specific Internal Reference, or SIR). In this way the biology of the target gene is expressed relative to the change in biology of the reference gene. The problem with using these single reference gene approaches is that their resolution (minimum confident measurement) is limited to the minimum error of the technique.
What is real time PCR?
Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qPCR, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence or gene that is present in a sample. Its very simplicity can sometimes lead to problems by overlooking some of the critical factors that make it work. This review will highlight these factors that must be considered when setting up and evaluating a real-time PCR reaction.
What are the factors used to determine the performance of a PCR reaction?
Efficiency, R 2 , precision, and sensitivity are used to determine performance of a PCR reaction when comparing different reaction conditions. For a rigorous evaluation, all factors listed in Table 1 must be evaluated together. In addition to these factors, proper experimental controls (such as no template control, no RT control) and template quality must be evaluated and validated.
How does PCR affect Ct?
The efficiency of a PCR reaction can also affect C t. A dilution series amplified under low efficiency conditions could yield a standard curve with a different slope from one amplified under high efficiency conditions. In Figure 5, two samples (X and Y) amplified under low and high efficiency conditions show different C t values for the same target concentration. In this example, although the high-efficiency condition (the blue curve in Figure 5) gives a later C t at high concentrations, it results in better sensitivity at low target concentrations. The PCR efficiency is dependent on the assay, the master mix performance, and sample quality. Generally, an efficiency between 90 and 110% is considered acceptable. the other, could be valuable in concluding that there is less template in the first sample, assuming all other factors such as instruments, reagents, and assays are equal. However, this is not true if different instruments, reagents, primers and probes, or reaction volumes are involved in producing the two C t s. Therefore, the absolute C t value comparison is only meaningful when comparing experiments using the same reaction conditions as defined above.
What is Rn in PCR?
Figure 1. Graphical representation of real-time PCR data. Rn is the fluorescence of the reporter dye divided by the fluorescence of a passive reference dye; i.e.,Rn is the reporter signal normalized to the fluorescence signal of Applied Biosystems™ ROX™ Dye. (A) In this view, Rn is plotted against PCR cycle number. (B) ΔRn is Rn minus the baseline; ΔRn is plotted against PCR cycle number. (C) An amplification plot shows the variation of log (ΔRn) with PCR cycle number.
What is the most common measure of precision?
The standard deviation (square root of the variance) is the most common measure of precision. If many data points are close to the mean, the standard deviation is small; if many data points are far from the mean, the standard deviation is large.
How to calculate Rn?
The Rn value is calculated as the ratio of the fluorescence of Applied Biosystems™ FAM™ Dye divided by the fluorescence of ROX dye. Therefore, a lower amount of ROX dye would produce a higher Rn value assuming fluorescence signal from FAM dye is unchanged. This would lead to an increase in baseline Rn and subsequently a smaller ΔRn as well as a different C t value. The new C t value obtained by lowering the level of ROX dye has no bearing on the true sensitivity of the reaction, but can have other unintended consequences. Low concentrations of ROX dye can result in increased standard deviation of the C t value, as shown in Figure 4. The greater the standard deviation, the lower the confidence in distinguishing between small differences in target concentration (see the precision section below).
What is CQ in PCR?
The term Cq was proposed in the Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-TIme PCR Experiments (MIQE) Guidelines. Therefore, most people actually prefer the term Cq, as opposed to Ct.
What is the difference between Ct and Cq values?
Basically, these terms all refer to the same value as the Ct value . Discrepancies in nomenclature have been historically inconsistent, with different qPCR manufacturers using different variations. The term Cq was proposed in the Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-TIme PCR Experiments (MIQE) Guidelines. Therefore, most people actually prefer the term Cq, as opposed to Ct.
How many cycles are there in qPCR?
This green line demonstrates the change in fluorescence over the number of cycles. Typically, in a qPCR experiment, there are 40 cycles. That is 40 rounds of amplification.
What happens when all reagents are used up in PCR?
Once all of the reagents, such as nucleotides, have been used up in the PCR reaction, the amplification will slow and ultimately plateau. This is the region where no more PCR products cannot be produced. This can be seen in cycles 30 and 40 in the above amplification plot.
What does the Ct value mean in PCR?
The Ct value is associated with the amount of PCR product in the reaction. The lower the Ct value, the more PCR product that is present. This is because it takes fewer PCR cycles for that product to be detected over the background signal.
When does PCR enter the exponential phase?
Once the amount of PCR product is amplified enough, it will enter the exponential phase. This is when the amount of PCR product doubles for every PCR cycle. This can be seen in cycles 15 and 25 in the above amplification plot.
What is the background signal in PCR?
At the start of the run, when the amount of PCR product is low, this produces very little fluorescence. This section of cycles (between cycles 0 and 15 in the above figure) is known as the background signal.
What does Cp mean in amplification?
Add: There is also the name "Cp" for "crossing point" (the point at which the amplification curve crosses the vertical threshold line / noiseband).
How are results of single case research designs evaluated?
Results of single-case research designs (i.e., n-of-1 trials) are often evaluated by visually inspecting the time-series graph and computing quantitative indices. A question our research team is...
Is Ct a CQ?
Ct becomes Cq nowadays but why not change Delta Ct to De lata Cq too. Formula is still in written Delta Ct or Delta Delta Ct but I haven't seen yet Delta Cq or Delta Delta Cq.
The Many Names of The Ct Value
What Is The CQ Value?
- Real-time PCR(often called qPCR) is usually conducted to quantify the absolute amount of a target sequence or to compare relative amounts of a target sequence between samples. This technique monitors the amplification of the target in real-time via a target-specific fluorescent signal emitted during amplification. Despite the fact that real-time PC...
Common Pitfalls
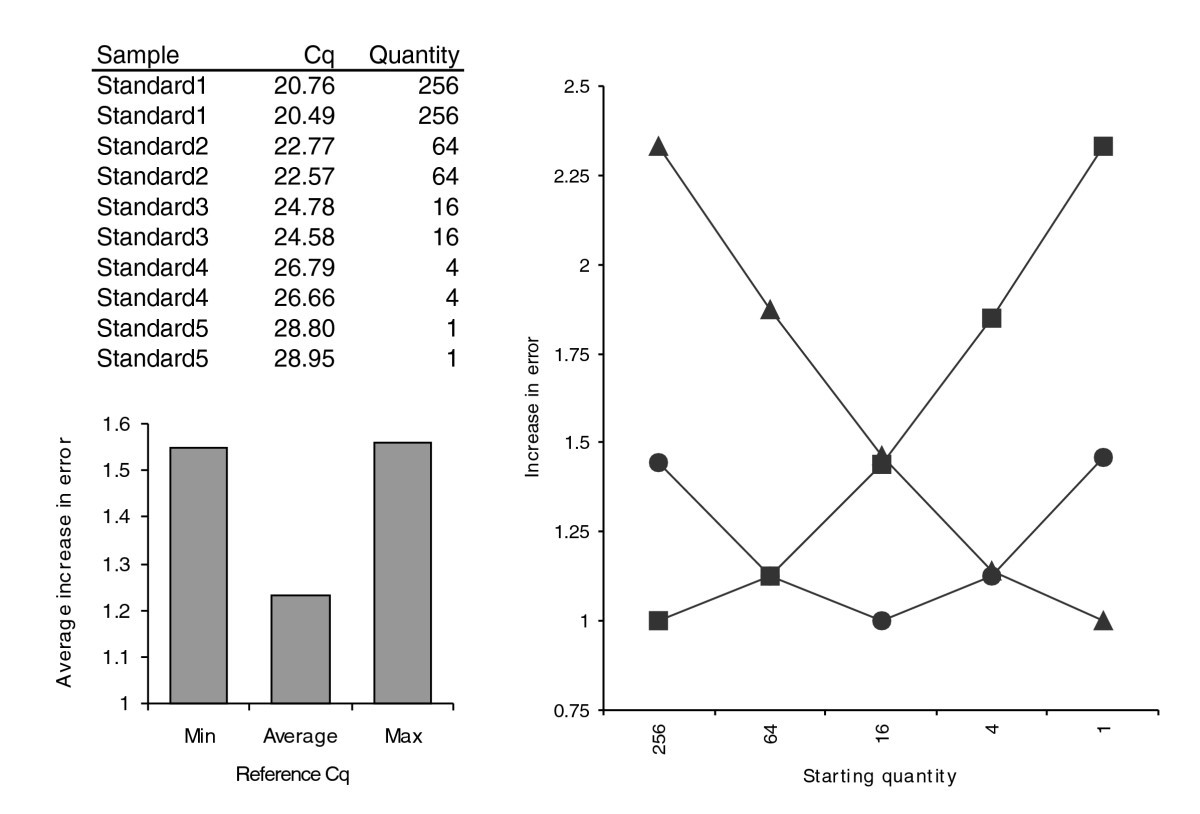
- Many factors can affect your Cq values. Some differences in Cq values between your samples will be due to biological events e.g. up/down-regulation of your target gene in response to a treatment. However, Cqvalues are just as easily influenced by the preparation of the PCR reaction and the PCR components themselves. The most common pitfall areas are:
Calling Delta-Delta CQ
- To be certain that the variations in Cq values are due to real biological changes and not technical issues, you will need to normalize your results. The most popular normalization method is known as “Delta-DeltaCt” or the Livak method. Here, you compare the Cq values of your sample to the Cq values of several reference (housekeeping) genes. It is imperative to choose reference genes…
References
- Bustin SA, et al. The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem. 2009. 55(4):611-22. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797.
- C. Schrader, et al.PCR inhibitors – occurrence, properties and removal. J Applied Microbiology. 113(5):1014-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05384.x